Abstract
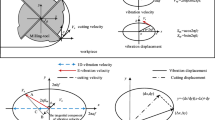
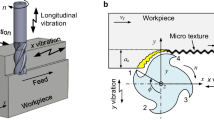
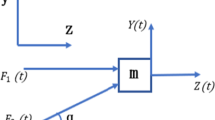
Elliptical ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling (EUVAM) adds high-frequency vibration to conventional milling (CM) to realize high-frequency intermittent milling. It has broad application prospects in the processing of difficult-to-cut materials such as titanium alloys, superalloys, and hard and brittle materials. To reveal the mechanism of the highly intermittent cutting nature in EUVAM, according to the motion relationship between the cutting edge and the workpiece and the Z-map representation of the workpiece, a method and its algorithm for calculating the undeformed cutting thickness and thus the cutting force in EUVAM are proposed. The simulation results show that EUVAM can improve the actual cutting speed when compared with CM, and the proportion of idle cutting time will directly determine the intermittent degree of the milling process. The experiment of EUVAM is performed to verify the correctness of the proposed cutting force model, and the impact of spindle speed on the cutting force in EUVAM is also analyzed. It is shown that UEVAM can reduce the cutting force by up to 50% under appropriate cutting conditions.














Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Jin X, Xie B (2015) Experimental study on surface generation in vibration-assisted micro-milling of glass. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 81(1–4):507–512
Shamoto E, Moriwaki T (1999) Ultraprecision diamond cutting of hardened steel by applying elliptical vibration cutting. CIRP Ann 48(1):441–444
Xu W, Zhang LC, Wu Y (2014) Elliptic vibration-assisted cutting of fiber-reinforced polymer composites: understanding the material removal mechanisms. Compos Sci Technol 92:103–111
Sui H, Zhang X, Zhang D, Jiang X, Wu R (2017) Feasibility study of high-speed ultrasonic vibration cutting titanium alloy. J Mater Process Technol 247(19):111–120
Jung H, Hayasaka T, Shamoto E, Xu L (2020) Suppression of forced vibration due to chip segmentation in ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting of titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. Precis Eng 64
Insperger T, Lehotzky D, Stepan G (2015) Regenerative delay parametric forcing and machine tool chatter: a review. IFAC-PapersOnLine 48(12):322–327
Altintas Y, Weck M (2004) Chatter stability of metal cutting and grinding. CIRP Ann 53(2):619–642
Xiao M, Karube S, Soutome T, Sato K (2002) Analysis of chatter suppression in vibration cutting. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42(15):1677–1685
Ma C, Ma J, Shamoto E, Moriwaki T (2011) Analysis of regenerative chatter suppression with adding the ultrasonic elliptical vibration on the cutting tool. Precis Eng 35(2):329–338
Wan S, Jin X, Maroju NK, Hong J (2019) Effect of vibration assistance on chatter stability in milling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 145:103432
Gao J, Altintas Y (2020) Chatter stability of synchronized elliptical vibration assisted milling. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 28:76–86
Muhammad R, Ahmed N, Deiral M, Roy A, Silberschmidt VV (2011) Computational study of ultrasonically-assisted turning of Ti alloys. Adv Mat Res 223:30–36
Tong J, Wei G (2019) Characteristics of cutting force during titanium alloy processed with UEVC. J Shock Vib 38(9):208–214
Liu J, Jiang X, Zhang G, Zhang M, Zhang D (2019) Investigation of the effect of vibration amplitude on the surface integrity in high-speed rotary ultrasonic elliptical machining for side milling of Ti-6Al-4V. J Mech Eng 55(11):215–223
Abootorabi Z, Razfar M, Abdullah A (2012) Investigation of the effect of cutting speed and vibration amplitude on cutting forces in ultrasonic-assisted milling. Proc Inst Mech Eng B J Eng Manuf 226(7):1185–1191
Han X, Zhang D (2020) Effects of separating characteristics in ultrasonic elliptical vibration-assisted milling on cutting force, chip, and surface morphologies. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 108:3075–3084
Lee SK, Ko SL (2002) Development of simulation system for machining process using enhanced Z map model. J Mater Process Technol 130(1):608–617
Li Z, Liu Q (2012) Z-map based surface machining accuracy in high-speed peripheral milling of flexible system. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Nat Sci 40:64–67
Li Z, Zhu L, Yang Z, Ma J, Cao W (2021) Investigation of tool-workpiece contact rate and milling force in elliptical ultrasonic vibration assisted milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 118:585–601
Gradisek J, Kalveram M, Weinert K (2004) Mechanistic identification of specific force coefficients for a general end mill. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 44(4):401–414
Funding
This research is financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2020JJ4270).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Xiao, J., Han, X. et al. Z-map based cutting force prediction for elliptical ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 120, 3237–3249 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08976-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08976-w