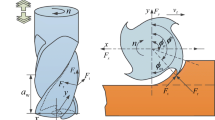
Abstract
Aluminum (Al)-based silicon carbide (SiC) material composites are considered as difficult-to-machine materials because of the presence of hard reinforced SiC particles, which results in a greater cutting force and poor surface integrity during the machining process. This paper established micro-anisotropic material mechanical models of SiCp/Al composites with a 10vol% SiC particles, and studied the difference in the machining mechanism between ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting (UEVC) and ordinary cutting (OC) about SiCp/Al. Moreover, this paper mainly focuses on the influence of UEVC on cutting force, von Mises stress distribution, surface integrity, and chip formation. The models are validated by comparing cutting force, chip shapes, and machined surface features in OC machining SiCp/Al experience from the literature. Simulation results indicate that the cutting mechanism of SiCp/Al on UEVC is different from that of OC and has several good properties. At the same cutting parameters, high-frequency vibration makes the cutting force of UEVC exhibit variable periodicity and reduces average cutting force. The instantaneous impact of tool and fast separation results in a more concentrated von Mises stress distribution, thereby resulting in the particles having a greater break degree than that obtained with OC. A comparison of the surface roughness values from the simulation result shows that UEVC obtains better surface integrity than OC does.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Su XF, Chena HR, Kennedy D (1999) Effects of interphase strength on the damage modes and mechanical behaviour of metal-matrix composites. Compos A 30(3):257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(98)00158-4
Gao HT, Liu XH, Qi JL, Chen JQ, Ai ZR (2019) Strengthening mechanism of surface-modified SiCp/Al composites processed by the powder-intube method. Ceram Int 45(17):22402–22408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.186
Ronald BA, Vijayaraghavan L, Krishnamurthy R (2012) Machining of metal matrix composites. Springer, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-85729-938-3_5
Pramanik A, Zhang LC, Arsecularatne JA (2008) Effect of ceramic particles on residual stress, surface roughness and chip formation. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 48:1613–1625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.07.008
Ozben T, Kilickap E, Çakir O (2008) Investigation of mechanical and machinability properties of SiC particle reinforced Al-MMC. J Mater Process Technol 198:220–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.06.082
Monaghan J, Brazil D (1998) Modelling the flow processes of a particle reinforced metal matrix composite during machining. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 29:87–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(97)00047-X
Zheng W, Wang YJ, Zhou M (2018) Material deformation and removal mechanism of SiCp/Al composites in ultrasonic vibration assisted scratch test. Ceram Int 44:15133–15144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.05.150
Dabade UA, Joshi SS, Balasubramaniam R (2007) Surface finish and integrity of machined surfaces on Al/SiCp composites. J Mater Process Technol 192:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.04.044
Cheung CF, Chan KC, To S (2002) Effect of reinforcement in ultra-precision machining of Al6061/SiC metal matrix composites. Scripta Mater 47(2):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(02)00097-0
Kannan S, Kishawy HA (2006) Surface characteristics of machined aluminium metal matrix composites. Int J Mach Tool Manu 46(15):2017–2025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2006.01.003
Dong GJ, Zhang HJ, Zhou M, Y.J. (2013) Zhang, Experimental investigation on ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning of SiCp/Al composites. Mater Manuf Process 28:999–1002. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2012.709338
Kadivar MA, Akbari J, Yousefi R, Rahi A, Nick MG (2014) Investigating the effects of vibration method on ultrasonic-assisted drilling of Al/SiCp metal matrix composites. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 30:344–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2013.10.001
Zhu Y, Kishawy HA (2005) Influence of alumina particles on the mechanics of machining metal matrix composites. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45(4–5):389–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.09.013
Duan C, Sun W, Cheng Fu, Zhang F (2018) Modeling and simulation of tool-chip interface friction in cutting SiCp/Al composites based on a three-phase friction model. Int J Mech Sci 142–143:384–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.05.014
Shijin LU, ZHANG J, Zengqiang LI, ZHANG J, Xiaohui WANG (2021) Cutting path-dependent machinability of SiCp/Al composite under multi-step ultra-precision diamond cutting. Chinese J Aeronaut 34:241–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2020.07.039
Wu Q, Si Y, Wang G-S, Wang L (2016) Machinability of a silicon carbide particle-reinforced metal matrix composite. RSC Adv 6:21765–21775. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA00340K
Wang T, Xie L, Wang X (2015) Simulation study on defect formation mechanism of the machined surface in milling of high volume fraction SiCp/Al composite. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79:1185–1194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6876-x
Wang Y, Liao W, Yang K (2019) Investigation on cutting mechanism of SiCp/Al composites in precision turning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100:963–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2650-1
Eiji S, Toshimichi M (1994) Study on elliptical vibration cutting. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 43:35–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)62158-1
Zhang J, Wang D (2019) Investigations of tangential ultrasonic vibration turning of Ti6Al4V using finite element method. Int J Mater Form 12:527–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12289-018-1402-y
Gao J, Jin X (2019) Effects of ultrasonic vibration assistance on chip formation mechanism in cutting of Ti-6Al-4V. J Manuf Sci Eng 141(12):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4045129
Patil S, Joshi S, Tewari A, Joshi SS (2014) Modelling and simulation of effect of ultrasonic vibrations on machining of Ti6Al4V. Ultrasonics 54(2):694–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2013.09.010
Mitrofanov AV, Ahmed N, Babitsky VI, Silberschmidt VV (2005) Effect of lubrication and cutting parameters on ultrasonically assisted turning of Inconel 718. J Mater Process Technol 162–163:649–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.02.170
Mitrofanov AV, Babitsky VI, Silberschmidt VV (2004) Finite element analysis of ultrasonically assisted turning of Inconel 718. J Mater Process Technol 153:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.04.299
Bai W, Sun R, Leopold J, Silberschmidt VV (2017) Microstructural evolution of Ti6Al4V in ultrasonically assisted cutting: Numerical modelling and experimental analysis. Ultrasonics 78:70–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2017.03.005
Zheng W, Wang Y, Zhou M (2018) Material deformation and removal mechanism of SiCp/Al composites in ultrasonic vibration assisted scratch test. Ceram Int 44(13):15133–15144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.05.150
Zhenlong PENG, Deyuan ZHANG, Xiangyu ZHANG (2020) Chatter stability and precision during high-speed ultrasonic vibration cutting of a thin-walled titanium cylinder. Chin J Aeronaut 33(12):3535–3549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2020.02.011
Tan R, Zhao X, Sun T, Zou X, Hu Z (2019) Experimental investigation on micro-groove manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V alloy by using ultrasonic elliptical vibration assisted cutting. Materials (Basel) 12(19):3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193086
Zhang J, Han La, Zhang J, Liu H, Yan Y, Sun T (2019) Brittle-to-ductile transition in elliptical vibration-assisted diamond cutting of reaction-bonded silicon carbide. J Manuf Process 45:670–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.08.005
Huang W, Deping Yu, Zhang X, Zhang M, Chen D (2018) Ductile-regime machining model for ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting of brittle materials. J Manuf Process 36:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.09.029
Zhang XQ, Arif M, Liu K, Kumar AS, Rahman M (2013) A model to predict the critical undeformed chip thickness in vibration-assisted machining of brittle materials. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 69:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2013.03.006
Nath C, Rahman M (2008) Effect of machining parameters in ultrasonic vibration cutting. Int J Mach Tool Manuf 48:965–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2008.01.013
Kim GD, Loh BG (2008) Characteristics of elliptical vibration cutting in micro-V grooving with variations in the elliptical cutting locus and excitation frequency. J Micromech Microeng 18:025002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/18/2/025002
Teng X, Chen W, Huo D, Shyha I, Lin C (2018) Comparison of cutting mechanism when machining micro and nanoparticles reinforced SiCp/Al metal matrix composites. Compos Struct 203:636–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.07.076
Dandekar CR, Shin YC (2013) Multi-scale modeling to predict sub-surface damage applied to laser-assisted machining of a particulate reinforced metal matrix composite. Int J Mater Process Technol 213:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.09.010
Umer U, Ashfaq M, Qudeiri JA (2015) Modeling machining of particle-reinforced aluminum-based metal matrix composites using cohesive zone elements. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 78:1171–1179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6715-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wenxiang Chen: investigation; methodology; validation; writing—original draft; Xu Zhang: supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The content studied in this article belongs to the field of metal processing, and does not involve humans and animals. This article strictly follows the accepted principles of ethical and professional conduct.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Zhang, X. Investigation on the cutting mechanism of SiCp/Al composites in ultrasonic elliptical vibration machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 120, 4707–4722 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08926-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08926-6