Abstract
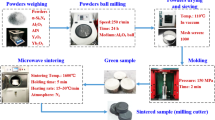
Two kinds of α/β-SiAlON ceramic tools with different ratio of α-SiAlON to β-SiAlON (10α:90β, 40α:60β) were prepared via spark plasma sintering (SPS). The orthogonal and single-factor experiments were conducted to optimize the milling parameters of the tool. Also, the tool life, failure modes, and wear mechanisms of α/β-SiAlON ceramic tools were studied. The optimal milling parameters for the high-speed face-milling of Inconel 718 by SPS-sintered SiAlON ceramic tools were vc = 800 m/min, fz = 0.12 mm/z, and ap = 1.5 mm. Life of the tool containing high α-SiAlON content (40α:60β) was twice that of the tool with lower content of α-SiAlON (10α:90β), and 2.7 times that of commercially available SiAlON ceramic tool. The SPS-sintered SiAlON ceramic tools displayed better wear resistance than that of a commercially available tool even under recommended cutting parameters of the commercial tool (vc = 1000 m/min, fz = 0.08 mm/z, and ap = 1.5 mm). The failure modes of SPS-sintered tools were dominated by the flaking of rake face, chipping of cutting edge, and flank wear. The primary wear mechanisms were adhesive, diffusive, and abrasive wear.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data and materials used in this manuscript are available.
References
Thakur A, Gangopadhyay S (2016) State-of-the-art in surface integrity in machining of nickel-based super alloys. Inter J Mach Tools and Manuf 100:25–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2015.10.001
Zhu D, Zhang XM, Ding H (2013) Tool wear characteristics in machining of nickel-based superalloys. Inter J Mach Tools and Manuf 64:60–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2012.08.001
Richards N, Aspinwall D (1989) Use of ceramic tools for machining nickel based alloys. Inter J Mach Tools and Manuf 29:575–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/0890-6955(89)90072-2
Balazinski M, Songmene V (1995) Improvement of tool life through variable feed milling of Inconel 600. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Techn 44:55–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)62274-4
Li HZ, Zeng H, Chen XQ (2006) An experimental study of tool wear and cutting force variation in the end milling of Inconel 718 with coated carbide tools. J Mater Process Tech 180:296–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.07.009
Thakur DG, Ramamoorthy B, Vijayaraghavan L (2012) Some investigations on high speed dry machining of aerospace material Inconel 718 using multicoated carbide tools. Mater Manuf Process 27:1066–1072. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2011.654158
Pervaiz S, Rashid A, Deiab I, Nicolescu M (2014) Influence of tool materials on machinability of titanium- and nickel-based alloys: a review. Mater Manuf Process 29:219–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2014.880460
Li L, He N, Wang M, Wang ZG (2002) High speed cutting of Inconel 718 with coated carbide and ceramic tools. J Mater Process Tech 129:127–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00590-3
Zheng GM, Zhao J, Song XY, Yan CQ, Li YE (2010) Ultra high speed turning of Inconel 718 with Sialon ceramic tools. Adv Mater Res 126–128:653–657. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.126-128.653
Hong DB, Yuan JT, Yin ZB, Peng HH, Zhu ZY (2020) Ultrasonic-assisted preparation of complex-shaped ceramic cutting tools by microwave sintering. Ceram Int 46:20183–20190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.097
Hong DB, Yin ZB, Yan SY, Xu WW (2019) Fine grained Al2O3/SiC composite ceramic tool material prepared by two-step microwave sintering. Ceram Int 45:11826–11832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.061
Choudhury IA, El-Baradie MA (1998) Machinability of nickel-base super alloys: a general review. J Mater Process Tech 77:278–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(97)00429-9
Zheng GM, Zhao J, Cheng X, Xu RF, Zhao GY (2016) Experimental investigation on Sialon ceramic tools for ultra-high-speed milling of Inconel 718. Mater Manuf Process 31:633–640. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1019090
Molaiekiya F, Stolf P, Paiva JM, Bose B, Goldsmith J, Gey C, Engin S et al (2019) Influence of process parameters on the cutting performance of SiAlON ceramic tools during high-speed dry face milling of hardened Inconel 718. Inter J Adv Manuf Technol 105:1083–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04210-2
Tian XH, Zhao J, Zhao JB, Gong ZC, Dong Y (2013) Effect of cutting speed on cutting forces and wear mechanisms in high-speed face milling of Inconel 718 with Sialon ceramic tools. Inter J Adv Manuf Technol 69:2669–2678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5206-4
Sun JF, Huang S, Ding HT, Chen WY (2020) Cutting performance and wear mechanism of Sialon ceramic tools in high speed face milling GH4099. Ceram Int 46:1621–1630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.134
Ming WW, Huang XH, Ji M, Xu JY, Zou F, Chen M (2021) Analysis of cutting responses of Sialon ceramic tools in high-speed milling of FGH96 superalloys. Ceram Int 47:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.118
Li YS, Zou B, Shi ZY, Huang CZ, Li L, Liu HL, Zhu HT et al (2020) Wear patterns and mechanisms of sialon ceramic end-milling tool during high speed machining of nickel-based superalloy. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.155
Huang XH, Zou F, Ming WW, Xu JY, Chen Y, Chen M (2020) Wear mechanisms and effects of monolithic Sialon ceramic tools in side milling of superalloy FGH96. Ceram Int 46:26813–26822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.07.157
Vagnorius Z, Sørby K (2011) Effect of high-pressure cooling on life of SiAlON tools in machining of Inconel 718. Inter J Adv Manuf Technol 54:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2944-4
Şirin Ş, Sarıkaya M, Yıldırım ÇV, Kıvak T (2021) Machinability performance of nickel alloy X-750 with SiAlON ceramic cutting tool under dry, MQL and hBN mixed nanofluid-MQL. Tribol Int 153:106673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106673
Lima FF, Sales WF, Costa ES, Da Silva FJ, Machado ÁR (2017) Wear of ceramic tools when machining Inconel 751 using argon and oxygen as lubri-cooling atmospheres. Ceram Int 43:677–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.09.214
Zeilmann RP, Fontanive F, Soares RM (2017) Wear mechanisms during dry and wet turning of Inconel 718 with ceramic tools. Inter J Adv Manuf Technol 92:2705–2714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0329-7
Hao ZP, Fan YH, Lin JQ, Ji FF, Liu XY (2017) New observations on wear mechanism of self-reinforced SiAlON ceramic tool in milling of Inconel 718. Arch Civ Mech Eng 17:467–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2016.12.011
Zheng GM, Zhao J, Zhou YH, Li AH, Cui XB, Tian XH (2013) Performance of graded nano-composite ceramic tools in ultra-high-speed milling of Inconel 718. Inter J Adv Manuf Technol 67:2799–2810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4693-z
Zheng GM, Zhao J, Gao ZJ, Cao QY (2012) Cutting performance and wear mechanisms of Sialon–Si3N4 graded nano-composite ceramic cutting tools. Inter J Adv Manuf Technol 58:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-011-3379-2
Aucote J, Foster SR (1986) Performance of sialon cutting tools when machining nickel-base aerospace alloys. Mater Sci Technol 2:700–708. https://doi.org/10.1179/mst.1986.2.7.700
Zhou CR, Yu ZB, Krstic VD (2007) Pressureless sintered self-reinforced Y-α-SiAlON ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 27:437–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2006.04.185
Jones MI, Hirao K, Hyuga H, Yamauchi Y, Kanzaki S (2003) Wear properties of Y–α/β composite sialon ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 23:1743–1750. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-2219(02)00401-6
Joshi B, Lee HH, Wang H, Fu Z, Niihara K, Lee SW (2012) The effect of different rare earth oxides on mechanical and optical properties of hot pressed α/β-Sialon ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 32:3603–3610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2012.05.012
He W, Liu Q, Zhong H (2011) Composition controlled microstructure and mechanical properties of Yb/Lu co-doped SiAlON. Mater Sci Eng A 528:8359–8364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.08.032
Kurama S, Schulz I, Herrmann M (2011) Wear properties of α- and α/β-SiAlON ceramics obtained by gas pressure sintering and spark plasma sintering. J Eur Ceram Soc 31:921–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.11.010
Acikbas NC, Kara F (2017) The effect of z value on intergranular phase crystallization of αı/βı-SiAlON-TiN composites. J Eur Ceram Soc 37:923–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.10.006
Hu ZY, Zhang ZH, Cheng XW, Wang FC, Zhang YF, Li SL (2020) A review of multi-physical fields induced phenomena and effects in spark plasma sintering: fundamentals and applications. Mater Design 191:108662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108662
Ahmed BA, Hakeem AS, Laoui T (2019) Effect of nano-size oxy-nitride starting precursors on spark plasma sintering of calcium sialons along the alpha/(alpha + beta) phase boundary. Ceram Int 45:9638–9645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.11.005
Al Malki MM, Khan RMA, Hakeem AS, Hampshire S, Laoui T (2017) Effect of Al metal precursor on the phase formation and mechanical properties of fine-grained SiAlON ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. J Eur Ceram Soc 37:1975–1983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.12.025
Eser O, Kurama S, Gunkaya G (2010) The production of β-SiAlON ceramics with low amounts of additive, at low sintering temperature. J Eur Ceram Soc 30:2985–2990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.01.024
Hakeem AS, Khan M, Ahmed BA, Al Ghanim A, Patel F, Ehsan MA (2021) Synthesis and characterization of alkaline earth and rare earth doped sialon Ceramics by spark plasma sintering. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 97:105500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2021.105500
Evans AG, Charles EA (1976) Fracture toughness determinations by indentation. J Am Ceram Soc 59:371–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1976.tb10991.x
McMurdie HF, Hall FP (1949) Phase diagrams for ceramists, supplement no. 1. J Am Ceram Soc 32:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1949.tb19765.x
Guo FZ, Yuan JT, Hong DB, Yin ZB (2021) Influence of powder mixing processes on phase composition, microstructure, and mechanical properties of α/β-SiAlON ceramic tool materials. Ceram Int 47:30256–30265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.07.205
Shen ZJ, Ekstrom T, Nygren M (1997) Preparation and properties of stable dysprosium-doped α-sialon ceramics. J Mater Sci 32:1325–1332. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018512824740
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52075266, 51875291), Excellent Youth Fund of Jiangsu Province (BK20190070), and Jiangsu Provincial Six Talent Peaks Project (GDZB-016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
The authors declare that they are all co-authors of this manuscript.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that they all agree to publish this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, F., Yin, Z., Hong, D. et al. Cutting performance of a new spark plasma sintered SiAlON ceramic tool for high-speed milling of Inconel 718. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 119, 7327–7338 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08702-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08702-6