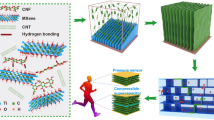
Abstract
Controlling the interaction of wetting surface with biomaterials is one of the key challenges in nanostructures to promote non-toxic and one-step fabrication technology. Here, a range spectrum of surface wettability characteristics and nanostructure modalities were demonstrated with a single treatment of glutaraldehyde (GA) on polyvinyl alcohol, poly (3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene)-poly (styrene sulfonate) (PVA/PEDOT:PSS) nanofiber mats. By modulating the density of coral-like dendritic nanostructure formation functionalized on PVA and PVA/PEDOT:PSS composite nanofibers and the degree of cross-linking between PVA/PEDOT:PSS and GA, the normally super hydrophilic behavior can be modified to show increasing hydrophobic characteristics correlating with an increased concentration of GA. The results of this study indicated the possibility and applicability of wettability effects available to a single application process alone, where the unique anti-dust wetting behavior can be predicted by estimating the adhesion force (~ maximum value of 24.20 μN) of water droplet. As a result of these nanostructure formations, the water droplet can exhibit hysteresis (CAr = 38 ± 0.5°, CAa = 106 ± 0.5°) and adhere to the nanofiber surface of glass substrate. This task may contribute to its potential optimization for use in a large range of future surface treatment for bio-coating and bio-sensing applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The development of nanofiber process that based on the one-step fabrication technology.
References
Zhang M, Feng S, Wang L, Zheng Y (2016) Lotus effect in wetting and self-cleaning. Biotribology 5:31–43
Wang L, Cai P, Luo J, Zhang F, Liu J, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Song Y, Yang B, Liu X, Chen X, Wang S (2018) Engineering subcellular-patterned biointerfaces to regulate the surface wetting of multicellular spheroids. Nano Res 11:5704–5715
Subramaniam DN, Egodawatta P, Mather P, Rajapakse JP (2015) Stabilization of stormwater biofilters: impacts of wetting and drying phases and the addition of organic matter to filter media. Environ Manage 56:630–642
Selway N, Chan V, Stokes JR (2017) Influence of fluid viscosity and wetting on multiscale viscoelastic lubrication in soft tribological contacts. Soft Matter 13:1702–1715
Breinlinger T, Polfer P, Hashibon A, Kraft T (2013) Surface tension and wetting effects with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J Comput Phys 243:14–27
Tavakolian M, Jafari SM, van de Ven TGM (2020) A review on surface-functionalized cellulosic nanostructures as biocompatible antibacterial materials. Nano-Micro Lett 12
Ina M, Cao Z, Vatankhah-Varnoosfaderani M, Everhart MH, Daniel WFM, Dobrynin AV, Sheiko SS (2017) From adhesion to wetting: contact mechanics at the surfaces of super-soft brush-like elastomers. ACS Macro Lett 6:854–858
Rasal M, Janorkar A, Hirt D (2010) Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog Polym Sci 35:338–356
Li G, Yu D, Song Z, Wang H, Liu W (2020) Facile fabrication of transparent paper with tunable wettability for use in biodegradables substrate. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 8:2176–2185
Xue P, Nan J, Wang T, Wang S, Ye S, Zhang J, Cui Z, Yang B (2017) Ordered micro/nanostructures with geometric gradient: from integrated wettability “library” to anisotropic wetting surface. Small 13:1601807
Bae J, H. kim, K. S. Kim, H, (2018) Choi, Effect of asymmetric wettability in nanofiber membrane by electrospinning technique on separation of oil/water emulsion. Chemosphere 204:235–242
Murillo DH, Girón AG, Romano JM, Cardoso JT, Cordovilla F, Walker M, Dimov SS, Ocaña JL (2019) Wettability modification of laser-fabricated hierarchical surface structures in Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Appl Surf Sci 463:838–846
Pan YJ, Lin JH, Chiang KC (2016) Biomedical applications of antibacterial nanofiber mats made of electrospinning with wire electrodes. Appl Sci 6:46
Kweon OY, Lee SJ, Oh JH (2018) Wearable high-performance pressure sensors based on three-dimensional electrospun conductive nanofibers. Npg Asia Mater 10:540–551
Zhang L, Liu W, Wen X, Chen J, Zhao C, Castillo-Rodríguez M, Yang L, Zhang XQ, Wang R, Wang DY (2020) Electrospun submicron NiO fibers combined with nanosized carbon black as reinforcement for multi-functional poly(lactic acid) composites. Compos Part A 129:105662
de Gramont FB, Zhang S, Tomasello G, Kumar P, Sarkissian A, Cicoira F (2017) Highly stretchable electrospun conducting polymer nanofibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111:093701
Santos JPF, Arjmand M, Melo GHF, Chizari K, Bretas RES, Sundararaj U (2018) Electrical conductivity of electrospun nanofiber mats of polyamide 6/polyaniline coated with nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes. Mater Design 141:333–341
Jiang Q, Pang X, Geng S, Zhao Y, Wang X, Qin H, Liu B, Zhou J, Zhou T (2019) Simultaneous crosslinking and pore-forming electrospun carbon nanofibers towards high capacitive performance. Appl Surf Sci 479:128–136
Stachewicz U, Bailey RJ, Zhang H, Stone CA, Willis CR, Barber AH (2015) Wetting hierarchy in oleophobic 3D electrospun nanofiber networks. Appl Mater Interfaces 7:16645–16652
Dong Y, Kong J, Phua SL, Zhao C, Thomas NL, Lu X (2014) Tailoring surface hydrophilicity of porous electrospun nanofibers to enhance capillary and push- pull effects for moisture wicking. Appl Mater Interfaces 6:14087–14095
Kakunuri M, Wanasekara ND, Sharma CS, Khandelwal M, Eichhorn SJ (2017) Three-dimensional electrospun micropatterned cellulose acetate nanofiber surfaces with tunable wettability. J Appl Polym Sci 134:44709
Wang X, Zhang K, Yang Y, Wang L, Zhou Z, Zhu M, Hsiao BS, Chu B (2010) Development of hydrophilic barrier layer on nanofibrous substrate as composite membrane via a facile route. J Membrane Sci 356:110–116
Zuo F, Zhang S, Liu H, Fong H, Yin X, Yu J, Ding B (2017) Free-standing polyurethane nanofiber/nets air filters for effective PM capture. Small 13:1702139
Zubair NA, Rahman NA, Lim HN, Sulaiman Y (2017) Production of conductive PEDOT-coated PVA-GO composite nanofibers. Nanoscale Res Lett 12:113–125
Abidin SNJSZ, Mamat S, Rasyid SA, Zainal Z, Sulaiman Y (2018) Fabrication of poly(vinyl alcohol)-graphene quantum dots coated with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for supercapacitor. . J Polym. Sci Part A: Polym. Chem 56:50–58
Moreno-Cortez IE, Romero-García J, González-González V, García-Gutierrez DI, Garza-Navarro MA, Cruz-Silva R (2015) Encapsulation and immobilization of papain in electrospun nanofibrous membranes of PVA crosslinked with glutaraldehyde vapor. Mater Sci Eng C 52:306–314
Cho D, Hoepker N, Frey MW (2012) Fabrication and characterization of conducting polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers. Mater Lett 68:293–295
Yuan WL, Yang X, He L, Xue Y, Qin S, Tao GH (2018) Viscosity, conductivity, and electrochemical property of dicyanamide ionic liquids. Front Chem 6
Cho D, Netravali AN, Joo YL (2012) Mechanical properties and biodegradability of electrospun soy protein isolate/PVA hybrid nanofibers. Polym Degrad Stabil 97:747–754
Zubair NA, Rahman NA, Lim HN, Sulaiman Y (2017) Production of conductive PEDOT-coated PVA-GO composite nanofibers. Nanoscale Res Lett 12
Chen ZC, Chang TL, Liou DS, Fan JY, Wang CP (2021) Fabrication of a bio-inspired hydrophobic thin film by glutaraldehyde crosslinking electrospun composite self-cleaning nanofibers. Mater Lett 298:129975
Mengistie DA, Wang PC, Chu CW (2013) Effect of molecular weight of additives on the conductivity of PEDOT:PSS and efficiency for ITO-free organic solar cells. J Mater Chem A 1:9907–9915
Wang F, Jin Z, Zheng S, Li H, Cho S, Kim HJ, Kim SJ, Choi E, Park JO, Park S (2017) High-fidelity bioelectronic muscular actuator based on porous carboxylate bacterial cellulose membrane. Sens Actuators B Chem 250:402–411
Mahato S (2017) Composition analysis of two different PEDOT:PSS commercial products used as an interface layer in Au/n-Si Schottky diode. RSC Adv 7:47125–47131
Xu Z, Zhou H, Tan S, Jiang X, Wu W, Shi J, Chen P (2018) Ultralight super-hydrophobic carbon aerogels based on cellulose nanofibers/poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide (CNFs/PVA/GO) for highly effective oil-water separation. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:508–519
Extrand CW, Kumagai Y (1995) Liquid drops on an inclined plane: the relation between contact angle, drop shape, and retentive force. J Colloid Interface Sci 170:515–521
ElSherbini AI, Jacobi AM (2006) Retention forces and contact angles for critical liquid drops on non-horizontal surfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 299:841–849
Destaye AG, Lin CK, Lee CK (2013) Glutaraldehyde vapor crosslinked nanofibrous PVA mat with in situ formed silver nanoparticles. Appl Mater Interfaces 5:4745–4752
Cortez IEM, García JR, González VG, Gutierrez DIG, Navarro MAG, Silva RC (2015) Encapsulation and immobilization of papain in electrospun nanofibrous membranes of PVA crosslinked with glutaraldehyde vapor. Mater Sci Eng C 52:306–314
Liao S, Chan CK, Ramakrishna S (2010) Electrospun nanofibers: work for medicine? Front Mater Sci China 4:29–33
Samuel B, Zhao H, Law KY (2011) Study of wetting and adhesion interactions between water and various polymer and superhydrophobic surfaces. J Phys Chem C 115:14852–14861
Ramanathan R, Weibel DE (2012) Novel liquid-solid adhesion superhydrophobic surface fabricated using titanium dioxide and trimethoxypropyl silane. Appl Surf Sci 258:7950–7955
Li Z, Kong Q, Ma X, Zang D, Guan X, Ren X (2017) Dynamic effects and adhesion of water droplet impact on hydrophobic surfaces: bouncing or sticking. Nanoscale 9:8249–8255
Heckenthaler T, Sadhujan S, Morgenstern Y, Natarajan P, Bashouti M, Kaufman Y (2019) Self-cleaning mechanism: why nanotexture and hydrophobicity matter. Langmuir 35:15526–15534
Lee KY, Hong J, Chung SK (2017) Smart self-cleaning lens cover for miniature cameras of automobiles. Sens Actuators B Chem 239:754–758
Funding
The support of the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan, Republic of China (Grant Nos.: MOST109-2628-E-003–001-MY3, and MOST 109–2622-E-003–005-CC3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.C. Chen: methodology, investigation, validation, writing—original draft. T.L. Chang: methodology, conceptualization, validation, writing—review and editing, funding acquisition, supervision. H.S. Lee: validation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. J.Y. Fan: validation, software, visualization, measurement. C.P. Wang: validation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent to participate
All of the authors have read and agree to publish the submit manuscript.
Consent for publication
All of the authors have read and agree to publish the submit manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, ZC., Chang, TL., Lee, HS. et al. Investigation into anti-dust wetting surface with coral-like nanostructures reinforced by electrospun composite nanofibers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 118, 2601–2612 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08070-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-08070-7