Abstract
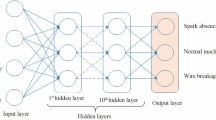
The study aims to develop a neural network classification model to predict machining failures during wire electric discharge machining. Also, a process control algorithm retunes the process parameters based on the remaining useful time before failure. In the proposed methodology, an artificial neural network (ANN) classifier receives four in-process discharge characteristics as input. These extracted features are discharge energy, spark frequency, open spark ratio, and short circuit ratio. Output classes are labeled normal machining, wire breakage, and spark absence. One hundred eight experiments were conducted according to a full factorial design to train the classifier model, with 90% classification accuracy.Parallelly, another trained ANN model predicts the remaining useful time before failure, based on which process parameters are retuned to restore the machining stability. The algorithm was successful in ensuring continuous failure-free machining.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data is available in the manuscript.
References
Ho KH, Newman ST, Rahimifard S, Allen RD (2004) State of the art in wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM). Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44:1247–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.04.017
Mandal A, Dixit AR (2014) State of art in wire electrical discharge machining process and performance. Int J Mach Mach Mater 16:1. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMMM.2014.063918
Rajurkar KP, Wang WM (1991) On-line monitor and control for wire breakage in WEDM. Ann CIRP 40:219–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.059
Kwon S, Yang MY (2006) The benefits of using instantaneous energy to monitor the transient state of the wire EDM process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 27:930–938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-004-2252-y
Yan MT, Liao YS (1996) A self-learning Fuzzy controller for wire rupture prevention in WEDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 11:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01351284
Liao YS, Woo JC (2000) Design of a fuzzy controller for the adaptive control of WEDM process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 40:2293–2307. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(00)00036-5
Bufardi A, Akten O, Arif M, Xirouchakis P, Perez R (2017) Towards zero defect manufacturing with a combined online-offline fuzzy-nets approach in wire electrical discharge machining. WSEAS Transactions on Environment and Development 13:401–409.
Abhilash PM, Chakradhar D (2020) ANFIS modelling of mean gap voltage variation to predict wire breakages during wire EDM of Inconel 718. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 31:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2020.10.007
Abhilash PM, Chakradhar D (2021) Sustainability improvement of WEDM process by analysing and classifying wire rupture using kernel - based naive Bayes classifier. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng:43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-021-02805-z
Janardhan V, Samuel GL (2010) Pulse train data analysis to investigate the effect of machining parameters on the performance of wire electro discharge turning (WEDT) process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50:775–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.05.008
Yan MT, Hsieh PH (2015) An on-line monitoring system for wire electrical discharge turning process. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 229:1945–1954. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954405414543488
Oßwald K, Lochmahr I, Schulze H-P, Kröning O (2018) Automated analysis of pulse types in high speed wire EDM. Procedia CIRP 68:796–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.157
Conde A, Sanchez JA, Plaza S, Ostolaza M, de la Puerta I, Li Z (2018) Experimental measurement of wire-lag effect and its relation with signal classification on wire EDM. Procedia CIRP 68:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.035
Cabanes I, Portillo E, Marcos M, Sánchez JA (2008) An industrial application for on-line detection of instability and wire breakage in wire EDM. J Mater Process Technol 195:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.04.125
Klocke F, Welling D, Klink A, Perez R (2014) Quality assessment through in-process monitoring of wire-EDM for fir tree slot production. New Prod Technol Aerosp Ind - 5th Mach Innov Conf (MIC 2014)-Procedia CIRP 24:97–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.07.136
Caggiano A, Perez R, Segreto T, Teti R, Xirouchakis P (2016) Advanced sensor signal feature extraction and pattern recognition for wire EDM process monitoring. Procedia CIRP 42:34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.181
Caggiano A, Teti R, Perez R, Xirouchakis P (2015) Wire EDM monitoring for zero-defect manufacturing based on advanced sensor signal processing. Procedia CIRP 33:315–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2015.06.065
Bergs T, Tombul U, Herrig T, Olivier M, Klink A, Klocke F (2018) Analysis of characteristic process parameters to identify unstable process conditions during wire EDM. Procedia Manuf 18:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2018.11.018
Rajeswari R, Shunmugam MS (2019) Investigations into process mechanics of rough and finish die sinking EDM using pulse train analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100:1945–1964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2701-7
Marrocco V, Modica F, Fassi I (2019) Analysis of discharge pulses in micro-EDM milling of Si3N4-TiN composite workpiece by means of power spectral density (PSD). J Manuf Process 43:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.05.017
Marrocco V, Modica F, Bellantone V, Medri V, Fassi I (2020) Pulse-type influence on the micro-edm milling machinability of si3 n4 –tin workpieces. Micromachines 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100932
Mwangi JW, Bui VD, Thüsing K, Hahn S, Wagner MFX, Schubert A (2020) Characterization of the arcing phenomenon in micro-EDM and its effect on key mechanical properties of medical-grade Nitinol. J Mater Process Technol 275:116334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116334
Mendes LA, Amorim FL, Weingaertner WL (2014) Automated system for the measurement of spark current and electric voltage in wire EDM performance. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci Eng 37:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-014-0171-x
Zhidong L, Haoran C, Huijun P, Mingbo Q, Zongjun T (2014) Automatic control of WEDM servo for silicon processing using current pulse probability detection. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 76:367–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6252-2
Thakur DG, Ramamoorthy B, Vijayaraghavan L (2009) Study on the machinability characteristics of superalloy Inconel 718 during high speed turning. Mater Des 30:1718–1725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2008.07.011
Reed RC (2006) The superalloys fundamentals and applications. Cambridge University Press
Sargent DJ (2001) Comparison of artificial neural networks with other statistical approaches: Results from medical data sets. Cancer 91:1636–1642. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(20010415)91:8+<1636::aid-cncr1176>3.0.co;2-d
P. M., Abhilash D., Chakradhar (2020) Prediction and analysis of process failures by ANN classification during wire-EDM of Inconel 718. Advances in Manufacturing 8(4) 519-536 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-020-00327-w
Abhilash PM, Chakradhar D (2021) Failure detection and control for wire EDM process using multiple sensors. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 33:315–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2021.04.009
Arunachalam C, Aulia M, Bozkurt B, Eubank PT (2001) Wire vibration, bowing, and breakage in wire electrical discharge machining. J Appl Phys 89:4255–4262. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1355281
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Central Instrumentation Facility (CIF), Indian Institute of Technology Palakkad for providing the test facilities.
Code availability
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abhilash, P., Chakradhar, D. Wire EDM failure prediction and process control based on sensor fusion and pulse train analysis. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 118, 1453–1467 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07974-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07974-8