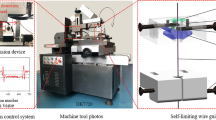
Abstract
Surface machined by high-speed wire electrical discharge machining (HS-WEDM) at super-high thickness (more than 1000 mm) cutting suffers from uneven surface, a major problem that has been investigated in this paper. According to the analysis, as wire frame span increases, the rigidity of the wire electrode decreases, and under the action of discharge explosive force, wire electrode vibration intensifies. As a result, the machining stability inevitably decreases. However, the core problem is whether there is enough working fluid in the slit to dampen and absorb the vibration of the wire electrode so as to ensure the positional stability of the wire electrode. To verify the above point of view: first, the wire guide and gravity take-up with bidirectional tension in the wire feeding system were installed to improve the positional accuracy of the wire electrode; second, to improve the flow of the working fluid into the slit, the slit width was increased by improving the working fluid and a medium carrier with a higher melting point and vaporization point can reduce the vaporization of the working fluid in the slit as much as possible. The experiment showed that the outlet flow of the improved working fluid is 56.72% higher than that of the original working fluid when cutting a 750-mm thick workpiece, which increases the damping and vibration absorption effect of the working fluid on the wire electrode in the long and narrow gap. After the above measures were implemented, super-high thickness cutting can be carried out continuously and steadily, the surface evenness was significantly improved, and the workpiece with a thickness of 2000 mm was cut successfully.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials set supporting the results are included within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
China Society of mechanical engineering non-traditional machining branch (2016) Nontraditional manufacturing technology roadmaps. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing
Liu ZD (2013) Current situation and development of HS-WEDM. Mach Build Autom 2:1–6
Li MH, Bu FL (1996) Theoretical research on super-high thickness of WEDM. Electromach Mould 30(9):122–126
Wan ZY (2008) Research on super-large thickness machining technology of HS-WEDM. Guangdong University Technol 2008:2–5
Li CR, Liu ZD, Fang LJ, Pan HW, Qiu MB (2017) Super-high-thickness high-speed wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 2017:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1246-5
Liu ZD (2006) Research on cooling liquid used in super-high thickness workpiece cutting of HS-WEDM. Electromach Mould 1:25–27
Zhang YQ, Liu ZD, Pan HW (2017) Dielectric fluid lifespan detection based on pulse discharge probability in wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:1481–1491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0211-7
Li LL, Liu ZD, Li XF, Li MM (2014) Non-even wire tension in high-speed wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 78(1–4):503–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6661-2
Liu ZD (2005) Research on the general feature of emulations & dielectrics and its tendency in WEDM-HS. Aviat Precis Manuf Technol 41:38–42
Liu ZD, Wang ZX (2011) Research on high speed wire-cut electrical discharge machine based on analysis of inter-electrode flow. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ 45(001):61–65
Pan HW, Liu ZD, Li CR (2017) Enhanced debris expelling in highspeed wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93:2913–2292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0716-0
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their sincere thanks to those who contributed in the preparation of the instructions.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.51975290).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have been personally and actively involved in substantive work leading to the report.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, C., Liu, Z., Zhang, M. et al. Study on surface evenness of super-high-thickness cutting in high-speed wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 117, 3705–3715 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07919-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-07919-1