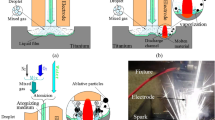
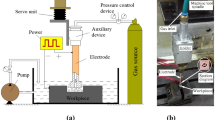
Abstract
Titanium alloy is widely used in aerospace and other industry fields because of its excellent physical and chemical properties. However, the fabrication process is still a challenge for the traditional machining processes due to the ultra hardness and chemical reactivity properties of titanium alloy. Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a significant processing approach to machine titanium alloy regardless of hardness, while accompanied by disadvantages such as electrode wear and low machining efficiency. This paper proposed a novel mixed-gas atomization discharge ablation process (MA-DAP) method for high-efficiency machining titanium alloy with low tool wear. An atomized dielectric formed by a mixed gas, which mainly composed of oxygen and supplemented by nitrogen, and water medium was used in the machining process. The exothermic oxidation between the oxygen component in the atomized dielectric and high-temperature molten material activated by spark discharges could multiply accelerate material removal of workpiece. The explosive effect generated by the vaporization expansion of the water component in the dielectric would improve the machining quality and the processing capability of large depth-to-diameter ratio holes. To investigate the machining characteristics of the new approach, comparative experiments were conducted in terms of material removal rate, electrode relative wear rate, machining accuracy, surface morphology, and recast layer. The experimental results showed that, compared with traditional EDM, the material removal rate of MA-DAP was dramatically increased by more than an order of magnitude, and other technological indexes are greatly improved simultaneously. A deep-shaped blind hole with a depth-to-diameter ratio greater than 12 was obtained by the MA-DAP.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials set supporting the results are included within the article.
References
Zi J, Chen XZ, Xu ZY, Zhu D, Fang ZD, Zhu D (2016) Experimental research on electrochemical machining of titanium alloy Ti60 for a blisk. Chin J Aeronaut 29(1):274–282
Shan CW, Xu ZB, Shen B, Zhang DH (2019) An improved analytical model of cutting temperature in orthogonal cutting of Ti6Al4V. Chin J Aeronaut 32(3):759–769
Ezugwu EO, Wang ZM (1997) Titanium alloys and their machinability––a review. J Mater Process Technol 68(3):262–274
Qu NS, Fang XL, Li W, Zeng YB, Zhu D (2013) Wire electrochemical machining with axial electrolyte flushing for titanium alloy. Chin J Aeronaut 26(1):224–229
Fonda P, Wang Z, Yamazaki K, Akutsu Y (2008) A fundamental study on Ti–6Al–4V’s thermal and electrical properties and their relation to EDM productivity. J Mater Process Technol 202:583–589
Wang XZ, Liu ZD, Qiu MB, Tian ZJ, Huang YH (2014) Research on the influence of gas pressure on the EDM Ablation of titanium Alloy. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica 35(12):3480–3488
Dhakar K, Chaudhary K, Dvivedi A, Bembalge O (2019) An environment-friendly and sustainable machining method: near-dry EDM. Mater Manuf Process 34(12):1307–1315
Manjaiah M, Narendranath S, Galpuji SB (2013) A review on machining of titanium based alloys using EDM and WEDM. Rev Adv Mater Sci 36(2):89–111
Tao J, Shih AJ, Jun N (2008) Near-dry EDM milling of mirror-like surface finish. J Manuf Sci Eng 13:29–33
Kao CC, Tao J, Shih A (2007) Near-dry electrical discharge machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47:2273–2281
Dhakar K, Dvivedi A, Dhiman A (2016) Experimental investigation on effects of dielectric mediums in near-dry electric discharge machining. J Mech Sci Technol 30(5):2179–2185
Fujiki M, Ni J, Shih AJ (2009) Investigation of the effects of electrode orientation and fluid flow rate in near-dry EDM milling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49(10):749–758
Gholipoor A, Baseri H, Shabgard MR (2015) Investigation of near dry EDM compared with wet and dry EDM processes. J Mech Sci Technol 29(5):2213–2218
Liu ZD, Yin CJ, Chen LH, Qiu MB, Tian ZJ (2014) Efficient combined machining of electrospark-induced controllable combustion and turning dressing for TC4. Mater Manuf Process 29(5):614–620
Xu AY, Liu ZD, Li WP, Tian ZJ, Qiu MB (2014) Study of high-efficiency electrical discharge machining-induced ablation machining of titanium alloy TC4 using a multi-function electrode. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 72(1-4):377–385
Kong LL, Liu ZD, Han YX, Qiu MB (2017) Research on the efficient and stable sinking electrical discharge machining ablation process of Ti-6Al-4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 80:704–711
Kong LL, Liu ZD, Qiu MB, Han YX (2019) Processing factors of controllable die-sinking ablation processing on Ti-6Al-4V. J Manuf Process 39:338–345
Marashi H, Jafarlou DM, Sarhan AAD, Hamdi M (2016) Review article: State of the art in powder mixed dielectric for EDM applications. Precis Eng 46:11–33
Kong LL, Liu ZD, Bai SK, Qiu MB, Han YX (2019) Investigation of the controllable characteristics of electrical discharge ablation of Ti6Al4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105:1645–1654
Funding
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51675272, 51975290). The authors extend their sincere thanks to those who contributed in the preparation of the instructions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have been personally and actively involved in substantive work leading to the report.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, L., Liu, Z., Wang, X. et al. Study on the machining characteristics of high-efficiency mixed gas atomized discharge ablation process of titanium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 113, 2715–2724 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06767-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06767-3