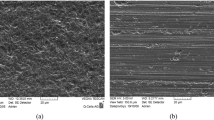
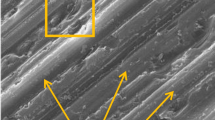
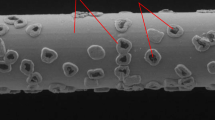
Abstract
In the slicing process of KDP crystal, due to the characteristics of long sawing kerf length, low hardness, and easy cracking, etc., there is a high requirement for the lubrication and chip discharge performance of the sawing area during slicing. So there are higher requirements on the structure and cutting performance of the saw wire to improve the sawn surface accuracy and the stress distribution in the processing area to avoid crystal cracking. In this paper, based on the technical idea of orderly arrangement of abrasives on the surface of superhard abrasive tool, the fabrication process, surface structure parameters, and sawing performance of a new type of abrasives-helix-distribution electroplated saw wire for slicing KDP crystal are carried out. The manufacturing process of the abrasives-helix-distribution saw wire was established, and the electroplating process parameters were determined. The relationship between the surface structure parameters of the new type wire was analyzed, and the influences of different structural parameters on the cutting performance of the new type wire were studied; then, the reasonable combination of the surface structure parameters of the new type wire was determined. The results are helpful to further understand the influences of surface structure parameters on the sawing performance of the new type wire, and provide experimental basis and reference for the development of the abrasives-helix-distribution saw wire for slicing KDP crystal.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen M, Pang Q, Wang J, Cheng K (2008) Analysis of 3D microtopography in machined KDP crystal surfaces based on fractal and wavelet methods. Int J Mach Tool Manu 7-8:905–913
Li Z, Ge P, Bi W, Liu T, Wang P, Gao Y (2018) Coupling stress caused by thermal and slicing force in KDP crystal slicing with fixed abrasive wire saw. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96:4333–4343
Ge M, Bi W, Ge P, Bi Y (2016) Experimental research on KDP crystal slicing with resin bonded diamond abrasive wire saw. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87:1671–1676
Chen N, Chen M, Guo Y, Wang X (2015) Effect of cutting parameters on surface quality in ductile cutting of KDP crystal using self-developed micro PCD ball end mill. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 78(1–4):221–229
Ge M, Gao Y, Ge P, Jiao Y, Bi W (2017) A finite element analysis of sawing stress in fixed-abrasive wire saw slicing KDP crystal. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91:2049–2057
Zhang N, Zhang Q, Wang S, Sun Y (2011) Research on cutting effects of the large-size KDP crystal by numerical simulation method. J Synth Cryst 40(2):323–328
Jiao Y, Ge P, Gao Y (2014) Analysis of temperature and thermal stress distribution on KDP crystal wire saw slicing. Adv Mater Res 1027:28–31
Deng L, Duan J, Zeng X (2013) A study on dual laser beam separation technology of KDP crystal. Int J Mach Tool Manu 72:1–10
Martínez Krahmer D, Polvorosa R, López de Lacalle LN, Alonso-Pinillos U, Abate G, Riu F (2016) Alternatives for specimen manufacturing in tensile testing of steel plates. Exp Tech 40(6):1555–1565
Gao Y, Ge P, Zhang L, Bi W (2019) Material removal and surface generation mechanisms in diamond wire sawing of silicon crystal. Mater Sci Semicond Process 103:104642
Yin Y, Gao Y, Li X, Pu T, Wang L (2020) Experimental study on slicing photovoltaic polycrystalline silicon with diamond wire saw. Mater Sci Semicond Process 106:104779
He Z, Huang H, Yin F, Xu X (2017) Development of a brazed diamond wire for slicing single-crystal SiC ingots. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91:189–199
Wang K, Jiang F, Yan L, Xu X, Wang N, Zha X, Lu X, Wen Q (2019) Study on mechanism of crack propagation of sapphire single crystals of four different orientations under impact load and static load. Ceram Int 45:7359–7375
Li H, Gao Y, Ge P, Bi W, Zhang L (2020) Study on process parameters of fabrication fine diameter electroplated diamond wire for slicing crystalline silicon solar cell. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106:3153–3175
Gao Y, Ge PQ, Bi W, Bi Y (2013) Study on surface defects of KDP crystal sawed by diamond wire saw. J Synth Cryst 42:1278–1282
Li H, Wang J, Zheng L, Wang J, Shang P, Chen W, Liu F (2013) Study on cutting performance of electroplated three-core twisted diamond wire saw. Diam Abrasives Eng 33:67–70
Park C, Kweon H, Peng B, Jung B (2016) A study on new twist-diamond wire characteristics for improving processing performance. J Korean Soc Manuf Process Eng 15(1):26–33
Tian H (2019) Development of twisted pair resin bonded diamond wire saw. Dissertation, Shandong University
Ortega N, Martynenko V, Perez D, Martínez Krahmer D, López de Lacalle LN, Ukar E (2020) Abrasive disc performance in dry-cutting of medium-carbon steel. Metals 10(4):538
González H, Calleja A, Pereira O, Ortega N, López de Lacalle LN, Barton M (2018) Super abrasive machining of integral rotary components using grinding flank tools. Metals 8(1):24
Jiang J, Sun S, Wang D, Yang Y (2020) Surface texture formation mechanism based on the ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding process. Int J Mach Tool Manu 156:103595
Meng J, Xiao B, Wang B, Yuan W (2014) Study on orderly arranged brazing diamond millstone disc. Diam Abrasives Eng 34:22–25
Guo G, Zhang F, Zhou Y (2013) Effect of the form for orderly arraying of cBN grits in monolayer brazed CBN grinding wheels on the surface roughness of workpieces. Superhard Mater Eng 25:1–5
Xiao L, Lin F, Chen C, Su Y, Cheng Y, Zhang L (2014) Influences of orderly arrangement on grinding performance of diamond grinding discs. Superhard Mater Eng 10:1–4
Liu T, Ge P, Bi W, Gao Y (2020) A new method of determining the slicing parameters for fixed diamond wire saw. Mater Sci Semicond Process 120:105252
Teomete E (2011) Roughness damage evolution due to wire saw process. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 12(6):941–947
Funding
The work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51875322), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (No. ZR2019MEE012), and Project for Scientific Research Innovation Team of Young Scholar in Colleges and Universities of Shandong Province (2020KJB001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Gao, Y., Wang, L. et al. Fabrication and cutting performance of a new type of abrasives-helix-distribution saw wire for slicing KDP crystal. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 112, 2187–2199 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06429-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06429-w