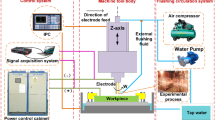
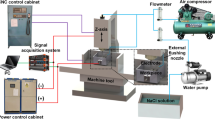
Abstract
The current application of short electrical arc discharge machining (SEAM) for cemented carbide removal is limited by its surface quality. In this study, tungsten-copper (W-Cu) alloy materials with different proportions as electrodes were studied by experimental methods. The mechanism of electrical parameters and composition content affecting the processing performance of SEAM was investigated, including surface roughness (Ra), material removal rate (MRR), micro-morphology, and the recast layer thickness (RLT). The results showed that the maximum MRR with W50-Cu electrode was 41 g/min, and the processing performance was the best with W90-Cu electrode in the U of 25 V, F of 2.3 KHz, and D of 55%. The W90-Cu electrode could provide good processing, and a thinner and more uniform recast layer was found on the workpiece surface. Therefore, W-Cu alloy tools are recommended when the hard surface materials machined by SEAM requires higher accuracy and surface finish.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li XZ, Zhou JP, Wang KD, Xu Y (2017) Temperature field simulation of the molten pool in SEAM. Int J Adv Manuf Techno 94(1–4):1–11
Perez R, Rojas H, Walder G, Flukiger R (2004) Theoretical modeling of energy balance in electroerosion. J Mater Proc Techno 149:198–203
Zhang M, Zhang QH, Wang HJ, Liu GW, Guo TD (2015) Research on a single pulse discharge to discriminate EDM and EAM based on the plasma tunnel and crater geometry. J Mater Proc Techno 219:248–256
Liang CH, Zhou JP, Zhu ZJ (2007) Study and application of short arc large current working technology. Mod Manuf Eng 12:92–93
Zhou JP, Liang CH, Teng WJ (2008) Study on rules in material removal rate and surface quality of short electric arc machining process. Adv Mater Res 33(5):1313–1318
Lu J, Liang CH, Zhou BS (2011) Base on the research of high efficiency characteristics of short arc machining technology. J electromachining & mould 2:57–60
Liu HS, Zhou JP, Yu Q (2014) Analysis of mechanical quality of nickel-base superalloy machined by short electric arc. Asian J Chemistry 26(17):5469–5472
Khan AR, Rahman MM, Kadirgama K (2015) An experimental investigation on surface finish in die-sinking EDM of Ti-5Al-2.5Sn. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 77:1727–1740
Jahan MP, Wong YS, Rahman M (2009) A study on the fine-finish die-sinking micro-EDM of tungsten carbide using different electrode materials. J Mater Proc Techno 209:3956–3967
Pellicer N, Ciurana J, Delgado J (2011) Tool electrode geometry and process parameters influence on different feature geometry and surface quality in electrical discharge machining of AISI H13 steel. J Intell Manuf 22(4):575–584
Ekmekci B (2007) Residual stresses and white layer in electric discharge machining (EDM). Appl Surf Sci 253(23):9234–9240
Dewangan S, Biswas CK, Gangopadhyay S (2014) Influence of different tool electrode materials on EDMed surface integrity of AISI P20 tool steel. Mater & Manuf Proc 29(11–12):1387–1394
Yong YW, Kang B (2012) Study on influence of electrode material on interelectrode discharge voltage and machining characteristics. Mach Des & Manuf 6:103–105
Rahman MM, Khan MAR, Kadirgama K, Noor MM, Bakar RA (2011) Optimization of machining parameters on tool wear rate of Ti-6Al-4V through EDM using copper tungsten electrode: a statistical approach. Adv Mater Res 152-153:1595–1602
Marafona J, Wykes C (2000) A new method of optimising material removal rate using EDM with copper-tungsten electrodes. Int J Mach Tools & Manuf 40(2):153–164
Yu JW, Duan W, He LH, Liu ZK, Yin SH (2015) Experimental investigation of CuW70 copper-tungsten electrode wear. Mech Sci & Tech Aero Eng 34(7):1016–1018
Kumar S, Singh R, Batish A, Singh TP, Singh R (2016) Investigating surface properties of cryogenically treated titanium alloys in powder mixed electric discharge machining. J Brazilian Soc Mech Sci & Eng 39(7):1–14
Wang WF (1997) Effect of tungsten particle size and copper content on working behaviour of W-Cu alloy electrodes during electro-discharge machining. Powder Metall 40(4):295–300
Bhaumik M, Maity K (2018) Effect of electrode materials on different EDM aspects of titanium alloy. Silicon 9-12:1–10
Shen Y, Liu YH, Zhang YZ, Dong H, Sun PF, Wang XL, Zheng C, Ji RJ (2016) Effects of an electrode material on a novel compound machining of Inconel718. Mater & Manuf Proc 31:845–851
TaoYQ WZP, Fang NX, Wu ZC (2002) Manufacture methods of tungsten-copper composites. Powder Metallurgy Tech 20(1):49–51
Xiong XJ, Liu YX (2007) Effect of tungsten particle size on structures and properties of infiltrated W-Cu compacts for electrodes. Mater Sci & Eng Power Metallurgy 12(2):101–105
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (51765063) and Autonomous University Scientific Research Program Natural Science Project (XJEDU2020Y011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhou, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Discharge characteristics of W-Cu electrode in short electrical arc discharge machining of Inconel 718. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 110, 2427–2437 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06041-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-06041-y