Abstract
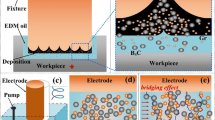
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) has been widely used in the machining of mechanical parts. However, the parts obtained by EDM have recast layers and micro-cracks on their surface, which seriously affect their mechanical properties. In order to remove the recast layers and micro-cracks resulted from EDM, this paper proposed to combine micro-EDM with negative polarity micro-EDM. First, the mechanical part was machined using conventional EDM, after which the surface of the part had a distinct recast layer and micro-cracks. As the conventional EDM was nearing completion, the power supply was replaced by a micro-EDM power supply and then the part was processed by micro-EDM to reduce the thickness of the recast layer. After micro-EDM, the part was processed by negative polarity micro-EDM, which can remove the recast layer and the micro-cracks on the surface of the part. Conventional EDM was performed on 304 stainless steel using a copper electrode with voltage of 250 V, pulse width of 7 ms, and pulse interval of 5 ms. The experimental results showed that the recast layer and micro-cracks on the surface of the part were obvious and the surface quality of the part was poor. After that, the same part was sequentially subjected to micro-EDM and negative polarity micro-EDM with voltage of 110 V, pulse width of 0.5 μs, and pulse interval of 15 μs. The experimental results showed that the recast layer and micro-cracks on the surface of the part were almost invisible and the surface quality of the part was greatly improved.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li C-J, Zhang B-W, Li Y, Tong H, Ding S-L, Wang Z-Q, Zhao L (2018) Self-adjusting EDM/ECM high speed drilling of film cooling holes. J Mater Process Technol 262:95–103
Li C-J, Xu X, Li Y, Tong H, Ding S-L, Kong Q-C, Zhao L, Ding J (2019) Effects of dielectric fluids on surface integrity for the recast layer in high speed EDM drilling of nickel alloy. J Alloys Compd 783:95–102
Wang C-C, Chow H-M, Yang L-D, Lu C-T (2009) Recast layer removal after electrical discharge machining via Taguchi analysis: a feasibility study. J Mater Process Technol 209:4134–4140
Xu Z-Y, Zhang C-X (2018) A tube electrode high-speed electrochemical discharge drilling method without recast layer. Procedia CIRP 68:778–782
Sun A-X, Chang Y-B, Liu H-J (2018) Metal micro-hole formation without recast layer by laser machining and electrochemical machining. Optik 171:694–705
Li X-Z, Zhou J-P, Wang K-D (2018) Research on removal characteristics of recast layer of laser-electrolytic machining on small holes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97:3903–3914
Wu X-Y, Li S-J, Jia Z, Xin B, Yin X-C (2019) Using WECM to remove the recast layer and reduce the surface roughness of WEDM surface. J Mater Process Technol 268:140–148
Zeng Z-Q, Wang Y-K, Wang Z-L, Shan D-B, He X-L (2012) A study of micro-EDM and micro-ECM combined milling for 3D metallic micro-structures. Precis Eng 36:500–509
Han Y-X, Liu Z-D, Cao Z-L, Kong L-L, Qiu M-B (2018) Mechanism study of the combined process of electrical discharge machining ablation and electrochemical machining in aerosol dielectric. J Mater Process Technol 254:221–228
Feng Y-R, Guo Y-F, Ling Z-B, Zhang X-Y (2019) Micro-holes EDM of superalloy Inconel 718 based on a magnetic suspension spindle system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 101:2015–2026
Murray J-W, Clare A-T (2012) Repair of EDM induced surface cracks by pulsed electron beam irradiation. J Mater ProcessTechnol 212:2642–2651
Feng W-J, Chu X-Y, Hong Y-Q, Wang K, Zhang L (2018) Studies on micro-EDM surface performance using a comprehensive method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96:1875–1889
Ji R-J, Liu Y-H, Zhang Y-Z, Cai B-P, Ma J-M, Li X-P (2012) Influence of dielectric and machining parameters on the process performance for electric discharge milling of SiC ceramic. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 59:127–136
Ji R-J, Liu Y-H, Zhang Y-Z, Cai B-P, Li H, Ma J-M (2010) Optimizing machining parameters of silicon carbide ceramics with ED milling and mechanical grinding combined process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51:195–204
Li H-C, Wang Z-L, Wang Y-K, Liu H-Z, Zhao Z-X (2018) Micro-EDM and micro-USM combined milling of ZrB2-SiC-graphite composite for 3D micro-cavities. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 99:2635–2645
Peng Z-L, Feng T-M, Wei Z-L, Zhang Y, Li Y-N (2019) Directly writing patterning of conductive material by high voltage induced weak electric arc machining (HV-mu EAM). Coatings 9:538
Tao X-T, Liu Z-D, Qiu M-B, Tian Z-J, Shen L-D (2018) Research on an EDM-based unitized drilling process of TC4 alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 97:867–875
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to their colleagues for their essential contribution to the work.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51605304, No. 51805333, No. 51575360), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2017A030313309, No. 2016A030310036), and the Science and Technology Innovation Commission Shenzhen (No. JCYJ20170817094310049, No. JSGG20170824111725200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, B., Chen, Sg., Liang, X. et al. Recast layer removal of 304 stainless steel by combining micro-EDM with negative polarity micro-EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107, 4713–4723 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05312-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05312-y