Abstract
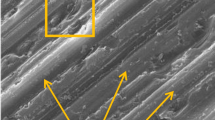
At present, the fixed abrasive wire sawing (FAWS) technology is gradually used in the photovoltaic industry to cut polycrystalline silicon slices. However, there are obvious directional wire marks, parallel grooves, and amorphous silicon layer on the surface of the slices formed by the FAWS, which leads to a high optic reflectivity of the textured surface obtained after the mature acid etching texturization technology. So the slices cannot meet the requirements of the photovoltaic cell. In the paper, a novel fixed-free abrasive combined wire sawing (FFACWS) technology for cutting PV polycrystalline silicon is presented to solve this problem, by adding loose SiC abrasives to cooling lubricant during the fixed abrasive wire sawing. A single-factor and orthogonal experimental study on sawing characteristics was carried out. The effect of size and mass fraction of SiC abrasives in the slurry, workpiece feed speed and wire speed on the surface morphology, roughness, and kerf loss were studied. The results show that within the range of the processing parameters in the paper studied, the obvious wire marks, parallel grooves, and ductile layers on the surface of the slices can be removed by the FFACWS. The surface roughness of the slices along the wire movement direction and the workpiece feed direction increases with the increase of the mass fraction of SiC abrasives in the slurry and workpiece feed speed and it decreases with the increase of wire speed. But the effect of the size of SiC abrasives is related to the matching of the protruding height of the fixed abrasives on the wire surface along the workpiece feed direction. In the wire movement direction, it increases with the size of SiC abrasives. The kerf loss increases with the increase of size and mass fraction of SiC abrasives in the slurry and the wire speed but has little effect with the change of workpiece feed speed.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demirbas A (2006) Global renewable energy resources. Energy Sources 28(8):779–792
Lucio CA, Bozzola A, Kowalczewski P, Liscidini M, Redorici L (2019) Silicon solar cells: toward the efficiency limits. Adv Phys-X 4:01–24
Santhakumari M, Netramani S (2019) A review of the environmental factors degrading the performance of silicon wafer-based photovoltaic modules: failure detection methods and essential mitigation techniques. Renew Sust Energ Rev 110:83–100
Deng R, Chang NL, Ouyang Z, Chong CM (2019) A techno-economic review of silicon photovoltaic module recycling. Renew Sust Energ Rev 109:532–550
Bhagavat M, Prasad V, Kao I (2000) Elasto-hydrodynamic interaction in the free abrasive wafer slicing using a wiresaw: modeling and finite element analysis. ASME J Tribol 122:394–404
Li HS, Gao YF, Ge PQ, Bi WB, Zhang L (2020) Study on process parameters of fabrication fine diameter electroplated diamond wire for slicing crystalline silicon solar cell. Int J Adv Manuf Tech DOI 106:3153–3175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04860-2
Gao YF, Ge PQ, Zhang L, Bi WB (2019) Material removal and surface generation mechanisms in diamond wire sawing of silicon crystal. Mat Sci Semicon Proc 103:104642
Yang F, Kao I (2001) Free abrasive machining in slicing brittle materials with wiresaw. J Electron Packaging 123(3):123–128
Chen WH, Liu XM, Li M, Yin CQ, Zhou L (2014) On the nature and removal of saw marks on diamond wire sawn multicrystalline silicon wafers. Mat Sci Semicon Proc 27:220–227
Wu H, Yang C, Melkote S (2016) Modeling and analysis of the grit level interaction in diamond wire sawing of silicon. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 84:907–913
Huang H, Zhang Y, Xu X (2015) Experimental investigation on the machining characteristics of single-crystal SiC sawing with the fixed diamond wire. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 81:955–965
Gupta A, Chen CC, Hsu HW (2019) Study on diamond wire wear, surface quality, and subsurface damage during multi-wire slicing of c-plane sapphire wafer. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 100:1801–1814
Liu XM (2014) Studies of surface properties and texturization methods of diamond wire sawn multi-crystalline silicon wafers. Doctoral dissertation, Nanchang university, China
Zhou ZZ, Wu Z, Feng KP (2015) A review on surface texturing technology for multicrystalline silicon. Int Mater Rev 29(09):55–61+67
Meinel B, Koschwitz T, Acker J (2012) Textural development of SiC and diamond wire sawed Sc-silicon wafer. Energy Procedia 27:330–336
Bidiville A, Wasmer, Kraft R, Ballif C (2009) Diamond wire-sawn silicon wafers-from the lab to the cell production. In: 24th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference 1400–1405
Liu XM, Li M, Chen WH, Zhou L (2014) The surface characteristics of diamond wire sawn multicrystalline silicon wafers and their acidic texturization. Acta photon sin 43(08):144–149
Gopala Krishna Murthy HS (2015) Evolution and present status of silicon carbide slurry recovery in silicon wire sawing. Resour Conserv Recy 104:194–205
Meißner D, Schoenfelder S, Hurka B, Zeh J, Sunder K, Koepge R, Wagner T, Grün A, Hagel HJ, Moeller HJ, Schwabe H, Anspach (2014) Loss of wire tension in the wire web during the slurry based multi wire sawing process. Sol Energ Mat Sol C 120:346–355
Li XY, Gao YF, Ge PQ, Zhang L, Bi WB (2019) The effect of cut depth and distribution for abrasives on wafer surface morphology in diamond wire sawing of PV polycrystalline silicon. Mat Sci Semicon Proc 91:316–326
Han CA (2014) Black multicrystalline silicon solar cells prepared by all-liquid two-step metal-catalyzed chemical etching. Master’s dissertation, Soochow university, China
Yang C, Wu H, Melkote S, Danyluk S (2013) Comparative analysis of fracture strength of slurry and diamond wire sawn multicrystalline silicon solar wafers. Adv Eng Mater 15(5):358–365
Li XY, Gao YF, Yin YK, Wang LY, Pu TZ (2020) Experiment and theoretical prediction for surface roughness of PV polycrystalline silicon wafer in electroplated diamond wire sawing. J Manuf Process 49:82–93
Li SY, Wang Z, Wu YL (2008) Relationship between subsurface damage and surface roughness of optical materials in grinding and lapping processes. J Mater Process Tech 205:34–41
Funding
The work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51875322); Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (No.ZR2019MEE012); and Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province, China (No.2017GGX30139).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, T., Gao, Y., Wang, L. et al. Experimental investigation on the machining characteristics of fixed-free abrasive combined wire sawing PV polycrystalline silicon solar cell. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107, 843–858 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05099-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05099-y