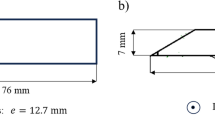
Abstract
Due to the features of Waspaloy, such as high-temperature resistance, easy to hardening, low thermal diffusivity, and low thermal conductivity, the milling cutter for internal threads suffers from serious wear. Particularly, the milling cutter for internal thread with a small diameter restricts the application of milling technology to Waspaloy threads. Based on the cutting flow stress control theory and the cutter wear control theory, a three-dimensional wear calculation model for milling cutter with small diameter internal thread was established. SEM was used to obtain the surface morphology and wear of the machined thread milling cutter, compared with the calculated results; the accuracy of the calculated results is verified. It employed the calculation model to study the variation law of tool wear under different milling parameters and front angle. The better milling parameters and front angles were obtained. In combination of the calculation results and the actual processing requirements, it is recommended: rotation speed, 600–900 r/min; revolution speed, 5–10 r/min; milling depth, 1/2–3/4 of the height of thread teeth; front angle, 5°–10°. And it is significant for the reduction of cutter wear and reasonable design and application of milling cutter for internal thread with a small diameter.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrazola PJ, Özel T, Umbrello D, Davies M, Jawahir IS (2013) Recent advances in modelling of metal machining processes. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 62(2):695–718
Zhu K, Yu X (2017) The monitoring of micro milling tool wear conditions by wear area estimation. Mech Syst Signal Process 93:80–91
Houdhury SK, Srinivas P (2004) Tool wear prediction in turning. J Mater Process Technol 153–154:276–280
Wada T (2016) Tool wear of aluminum/chromium/tungsten/silicon-based-coated solid carbide thread milling cutters in thread tapping of chromium-molybdenum steel. International Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,219–223
Jiang ZX, Sun J, Li GC, Jia XM, Li JF (2015) Investigation on the relationship among tool wear, cutting force and vibration in milling of tc4. Binggong Xuebao/Acta Armamentarii 36(1):144–150
Yao CF, Dou XT, Chen GC, Liang T (2017) Research of blade wear for TiAlN coated carbide in indexable tool high feed milling of titanium alloy. Mechanic Sci Technol Aerospace Engin 36(8):1212–1217 (In Chinese)
LIU D, WANG F, WANG JM (2018) Experimental study on tool life in milling TB6 titanium alloy. Aerospace Materials and Technology. (In Chinese)
Haque MS, Stewart CM (2016) Finite element analysis of Waspaloy using Sinh creep-damage constitutive model under triaxial stress state. J Press Vessel Technol 138(3)
Caruso S, Imbrogno S, Rinaldi S, Umbrello D (2016) Finite element modeling of microstructural changes in Waspaloy dry machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85(431):1–14
Prete AD, Filice L, Umbrello D (2013) Numerical simulation of machining nickel-based alloys. Procedia Cirp 8:540–545
Lotfi M, Amini S, Aghaei M (2018) 3D FEM simulation of tool wear in ultrasonic assisted rotary turning. Ultrasonics 88:106
Attanasio A, Umbrello D (2009) Abrasive and diffusive tool wear FEM simulation. Int J Mater Form 2(1):543–546
Zhang SF, Wang HH, Ma FJ, Huang WL, Sha ZH (2016) Cutting force finite element analysis and test verification of thread milling. Tool Engineering 50(8):23–27 (In Chinese)
Biermann D, Grünert S, Steiner M (2010) A macroscopic approach towards the finite element simulation of tapping and thread milling of continuously reinforced extrusions. Prod Eng 4(6):607–613
Caruso S, Imbrogno S, Rinaldi S, Umbrello D (2016) Finite element modeling of microstructural changes in Waspaloy dry machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85(431):1–14
Xiang J, Pang S, Xie L, Gao F, Hu X, Yi J, Hu F (2018) Mechanism-based FE simulation of tool wear in diamond drilling of SiCp/Al composites. Materials 11(2)
Wu HB, Zhang SJ (2014) 3D FEM simulation of milling process for titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71:1319–1326
Funding
This research was supported by Ministry of Education (Southwest Petroleum University), Scientific Research Starting Project of SWPU (No. 2017QHZ012), Sichuan science and technology program (2019YFG0305, 2018GZ0429, 2018CC0098), and National Science and Technology Major Project (2017ZX05023-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Wang, J., Zhu, X. et al. Study on the law of wear of milling cutter for Waspaloy internal threads with a small diameter. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107, 1327–1336 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05059-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05059-6