Abstract
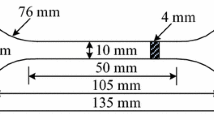
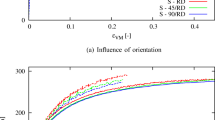
This paper presents a numerical and experimental study of the compression uniaxial properties of PLA material manufactured with FDM based on product specifications. A first experimental test in accordance with the requirements and conditions established in the ISO 604 standard characterizes the mechanical and elastic properties of PLA manufactured with FDM technology and product requirements in a uniaxial compression stress field by testing six specimens. A second experimental test allows analyzing the structural behavior of the industrial case, evaluating the compression stiffness, the compression yield stress, the field of displacements, and stress along its elastic area until reaching the compression yield stress and the ultimate yield stress data. To improve the structural analysis of the case study, a numerical validation was carried out using two analytical models. The first analytical model applies an interpolation procedure to the experimental results of the tested specimens in order to characterize the uniaxial tension-compression curve versus the nominal deformations by means of an 8-degree polynomial function. The second model defines the plastic material as elastic and isotropic with Young’s compression modulus constant and according to the guidelines established in ISO standard 604. The comparison between experimental tests and numerical simulation results for the study case verify that the new model that uses the proposed polynomial function is closer to the experimental solution with only an 0.36% error, in comparison with the model with Young’s compression modulus constant that reaches an error of 4.27%. The results of the structural analysis of the mechanical element indicate that the elastic region of the plastic material PLA manufactured with FDM can be modeled numerically as an isotropic material, using the elastic properties from the experimental results of the specimens tested according to ISO standard 604. In this way, it is possible to characterize the PLA FDM material as isotropic, obtaining as an advantage its easy definition in the numerical simulation software as it does not require the modification of the constitutive equations in the material database. SEM micrographs have indicated that the fracture of the failed test specimens is of the brittle type, mainly caused by the separation between the central plastic filament layers of the specimens. The results presented suggest that the use of FDM technology with PLA material is promising for the manufacture of low volume industrial components that are subject to compression efforts or for the manufacture of components by the user.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Primo T, Calabrese M, Del Prete A, Anglani A (2017) Additive manufacturing integration with topology optimization methodology for innovative product design. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(1–4):467–479
Leary M, Merli L, Torti F, Mazur M, Brandt M (2014) Optimal topology for additive manufacture: a method for enabling additive manufacture of support-free optimal structures. Mater Des 63:678–690
Mercado-Colmenero JM, Paramio MR, Perez-Garcia JM, Martin-Doñate C (2016) A new hybrid method for demoldability analysis of discrete geometries. Comput Aided Des 80:43–60
Mercado-Colmenero JM, Muriana JAM, Rubio-Paramio MA, Martín-Doñate C (2017) An automated manufacturing analysis of plastic parts using faceted surfaces. In: Advances on Mechanics, Design Engineering and Manufacturing. Springer, Cham, pp 119–128
Doñate CM, Paramio MR (2013) New methodology for demoldability analysis based on volume discretization algorithms. Comput Aided Des 45(2):229–240
Thompson MK, Moroni G, Vaneker T, Fadel G, Campbell RI, Gibson I, Martina F (2016) Design for Additive Manufacturing: Trends, opportunities, considerations, and constraints. CIRP Ann 65(2):737–760
Mercado-Colmenero JM, Rubio-Paramio MA, Guerrero-Villar F, Martin-Doñate C (2018) A numerical and experimental study of a new Savonius wind rotor adaptation based on product design requirements. Energy Convers Manag 158:210–234
Zhai Y, Lados DA, LaGoy JL (2014) Additive manufacturing: making imagination the major limitation. JOM 66(5):808–816
Wohlers T (2012) Wohlers report 2012. Wohlers Associates, Inc
Puigoriol-Forcada JM, Alsina A, Salazar-Martín AG, Gomez-Gras G, Pérez MA (2018) Flexural fatigue properties of polycarbonate fused-deposition modelling specimens. Mater Des
Stephens B, Azimi P, El Orch Z, Ramos T (2013) Ultrafine particle emissions from desktop 3D printers. Atmos Environ 79:334–339
Pearce JM (2015) Applications of open source 3-D printing on small farms. Organic Farming
Caulfield B, McHugh PE, Lohfeld S (2007) Dependence of mechanical properties of polyamide components on build parameters in the SLS process. J Mater Process Technol 182(1–3):477–488
Tymrak BM, Kreiger M, Pearce JM (2014) Mechanical properties of components fabricated with open-source 3-D printers under realistic environmental conditions. Mater Des 58:242–246
Popescu D, Zapciu A, Amza C, Baciu F, Marinescu R (2018) FDM process parameters influence over the mechanical properties of polymer specimens: a review. Polym Test 69:157–166
Matsuzaki R, Ueda M, Namiki M, Jeong TK, Asahara H, Horiguchi K, Hirano Y (2016) Three-dimensional printing of continuous-fiber composites by in-nozzle impregnation. Sci Rep 6:23058
Sood AK, Ohdar RK, Mahapatra SS (2010) Parametric appraisal of mechanical property of fused deposition modelling processed parts. Mater Des 31(1):287–295
Lanzotti A, Grasso M, Staiano G, Martorelli M (2015) The impact of process parameters on mechanical properties of parts fabricated in PLA with an open-source 3-D printer. Rapid Prototyp J 21(5):604–617
Rodrı́guez JF, Thomas JP, Renaud JE (2003) Design of fused-deposition ABS components for stiffness and strength. J Mech Des 125(3):545–551
Ahn SH, Montero M, Odell D, Roundy S, Wright PK (2002) Anisotropic material properties of fused deposition modeling ABS. Rapid Prototyp J 8(4):248–257
Anitha R, Arunachalam S, Radhakrishnan P (2001) Critical parameters influencing the quality of prototypes in fused deposition modelling. J Mater Process Technol 118(1–3):385–388
Lee BH, Abdullah J, Khan ZA (2005) Optimization of rapid prototyping parameters for production of flexible ABS object. J Mater Process Technol 169(1):54–61
Croccolo D, De Agostinis M, Olmi G (2013) Experimental characterization and analytical modelling of the mechanical behaviour of fused deposition processed parts made of ABS-M30. Comput Mater Sci 79:506–518
Domingo-Espin M, Puigoriol-Forcada JM, Garcia-Granada AA, Lluma J, Borros S, Reyes G (2015) Mechanical property characterization and simulation of fused deposition modeling Polycarbonate parts. Mater Des 83:670–677
Casavola C, Cazzato A, Moramarco V, Pappalettere C (2016) Orthotropic mechanical properties of fused deposition modelling parts described by classical laminate theory. Mater Des 90:453–458
Casavola C, Cazzato A, Moramarco V, Pappalettera G (2017) Residual stress measurement in fused deposition modelling parts. Polym Test 58:249–255
Li H, Wang T, Li Q, Yu Z, Wang N (2018) A quantitative investigation of distortion of polylactic acid/PLA) part in FDM from the point of interface residual stress. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94(1–4):381–395
Tanikella NG, Wittbrodt B, Pearce JM (2017) Tensile strength of commercial polymer materials for fused filament fabrication 3D printing. Addit Manuf 15:40–47
Kuznetsov VE, Solonin AN, Urzhumtsev OD, Schilling R, Tavitov AG (2018) Strength of PLA components fabricated with fused deposition technology using a desktop 3D printer as a function of geometrical parameters of the process. Polymers 10(3):313
Wittbrodt B, Pearce JM (2015) The effects of PLA color on material properties of 3-D printed components. Additive Manufacturing 8:110–116
Chacón JM, Caminero MA, García-Plaza E, Núñez PJ (2017) Additive manufacturing of PLA structures using fused deposition modelling: effect of process parameters on mechanical properties and their optimal selection. Mater Des 124:143–157
Torres J, Cotelo J, Karl J, Gordon AP (2015) Mechanical property optimization of FDM PLA in shear with multiple objectives. Jom 67(5):1183–1193
Balderrama-Armendariz CO, MacDonald E, Espalin D, Cortes-Saenz D, Wicker R, Maldonado-Macias A (2018) Torsion analysis of the anisotropic behavior of FDM technology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol:1–11
Uddin MS, Sidek MFR, Faizal MA, Ghomashchi R, Pramanik A (2017) Evaluating mechanical properties and failure mechanisms of fused deposition modeling acrylonitrile butadiene styrene parts. J Manuf Sci Eng 139(8):081018
Upadhyay K, Dwivedi R, Singh AK (2017) Determination and comparison of the anisotropic strengths of fused deposition modeling P400 ABS. In: Advances in 3D Printing & Additive Manufacturing Technologies. Springer, Singapore, pp 9–28
Sood AK, Ohdar RK, Mahapatra SS (2012) Experimental investigation and empirical modelling of FDM process for compressive strength improvement. J Adv Res 3(1):81–90
Lee CS, Kim SG, Kim HJ, Ahn SH (2007) Measurement of anisotropic compressive strength of rapid prototyping parts. J Mater Process Technol 187:627–630
Martín-Doñate, C; Rubio-Paramio M. A ; Gómez-García J. J., García Tamargo J. González Lozano I. Toledano Rama I. .Mechanical device for the displacement of collection sheets for olive harvesting Patent Request Number P201831047. 2018
Funding
This work has been supported by the University of Jaen through the project titled “Design of a mechanical plastic device for the displacement of collection sheets for olive harvesting” Project Code (AC20/2016-10) and (ID228-R2 A8 2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mercado-Colmenero, J.M., Rubio-Paramio, M.A., la Rubia-Garcia, M.D. et al. A numerical and experimental study of the compression uniaxial properties of PLA manufactured with FDM technology based on product specifications. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103, 1893–1909 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03626-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03626-0