Abstract
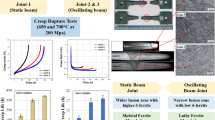
The influence of beam oscillations on the microstructure and mechanical properties of low-carbon steels, subjected to electron beam welding, was investigated. Beam oscillations created a dynamic distribution of power around the stationary position of the beam resulting in the enhanced flow of heat inside the keyhole and yielded wider fusion and heat-affected zones. A reduction in the undercutting at the weld root was also achieved through beam oscillation. The weld microstructure consisted of large columnar grains in the fusion zone and equiaxed grains of varying sizes in the heat-affected zone. The variation in grain size across the weld joint was attributed to the steep temperature gradients produced during electron beam welding. High hardness was seen in the fusion and heat-affected zones due to the occurrence of martensite. Weld samples fabricated using beam oscillations showed lower microhardness compared with joints produced by stationary beam welding. This decrease in hardness arose from enhanced grain growth and additional diffusion of carbon out of the austenite lattice due to beam oscillations. Beam oscillations did not introduce any significant morphological changes to the weld microstructure, but resulted in enhanced tensile strength and lower microhardness in the weld joints.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang P, Chen X, Pan Q, Madigan B, Long J (2016) Laser welding dissimilar materials of aluminum to steel: an overview. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(9):3081–3090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8725-y
Williams E, Lavery N (2017) Laser processing of bulk metallic glass: A review. J Mater Process Technol 247(Supplement C):73–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.03.034. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924013617301279
Verma J, Taiwade RV (2017) Effect of welding processes and conditions on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steel weldments - A review. J Manuf Process 25 (Supplement C):134–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.11.003. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S152661251630158X
David SA, DebRoy T (1992) Current issues and problems in welding science. Science 257(5069):497–502. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.257.5069.497. http://science.sciencemag.org/content/257/5069/497
Jebaraj AV, Ajaykumar L, Deepak C, Aditya K (2017) Weldability, machinability and surfacing of commercial duplex stainless steel AISI2205 for marine applications - a recent review. J Adv Res 8(3):183–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2017.01.002. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2090123217300115
Chiumenti M, Cervera M, Dialami N, Wu B, Jinwei L, de Saracibar CA (2016) Numerical modeling of the electron beam welding and its experimental validation. Finite Elem Anal Des 121(Supplement C):118–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2016.07.003. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168874X16301378
Kaur A, Ribton C, Balachandaran W (2015) Electron beam characterisation methods and devices for welding equipment. J Mater Process Technol 221(Supplement C):225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.02.024. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924013615000679
Wȩglowski M, Bacha S, Phillips A (2016) Electron beam welding–techniques and trends–review. Vacuum 130(Supplement C):72–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2016.05.004. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0042207X16301245
International electron beam welding conference: Lectures of the 2nd IEBW conference taking place in aachen on march 26-30 (2012) vol 285, DVS Media GmbH, Dusseldorf
Alali M, Todd I, Wynne B (2017) Through-thickness microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded 20mm thick aisi 316l austenitic stainless steel. Mater Des 130(Supplement C):488–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.05.080. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264127517305610
Wang Y, Fu P, Guan Y, Lu Z, Wei Y (2013) Research on modeling of heat source for electron beam welding fusion-solidific ation zone. Chin J Aeron 26(1):217– 223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2012.12.023. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1000936112000313
Ziolkowski M, Brauer H (2009) Modelling of seebeck effect in electron beam deep welding of dissimilar metals. COMPEL - Int J Comput Math Electr Electron Eng 28(1):140–153. https://doi.org/10.1108/03321640910918940
Rai R, Burgardt P, Milewski JO, Lienert T, DebRoy T (2009) Heat transfer and fluid flow during electron beam welding of 21cr–6ni–9mn steel and ti–6al–4v alloy. J Phys D: Appl Phys 42(2):025503. http://stacks.iop.org/0022-3727/42/i=2/a=025503
Chiumenti M, Cervera M, Dialami N, Wu B, Jinwei L, de Saracibar CA (2016) Numerical modeling of the electron beam welding and its experimental validation. Finite Elements Anal Des 121:118–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2016.07.003. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168874X16301378
Huang B, Chen X, Pang S, Hu R (2017) A three-dimensional model of coupling dynamics of keyhole and weld pool during electron beam welding. Int J Heat Mass Transf 115:159–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.08.010. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0017931017310608
Kar J, Roy SK, Roy GG (2016) Effect of beam oscillation on electron beam welding of copper with aisi-304 stainless steel. J Mater Process Technol 233(Supplement C):174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.03.001. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924013616300577
Babu NK, Raman SGS, Murthy CVS, Reddy GM (2007) Effect of beam oscillation on fatigue life of ti–6al–4v electron beam weldments. Mater Sci Eng: A 471(1):113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.03.040. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921509307005357
Dinda SK, Sk MB, Roy GG, Srirangam P (2016) Microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded dissimilar steel to fe–al alloy joints. Mater Sci Eng: A 677(Supplement C):182–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.09.050. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921509316311108
Kar J, Dinda SK, Roy GG, Roy SK, Srirangam P (2018) X-ray tomography study on porosity in electron beam welded dissimilar copper–304ss joints. Vacuum 149:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.12.038. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0042207X17314896
Trushnikov D, Koleva E, Mladenov G, Belenkiy VY (2013) Effect of beam deflection oscillations on the weld geometry. J Mater Process Technol 213(9):1623–1634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.03.028. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924013613001209
Wang L, Gao M, Zhang C, Zeng X (2016) Effect of beam oscillating pattern on weld characterization of laser welding of aa6061-t6 aluminum alloy. Mater Des 108(Supplement C):707–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.07.053. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264127516309534
Kar J, Roy SK, Roy GG (2017) Effect of beam oscillation on microstructure and mechanical properties of aisi 316l electron beam welds. Metall and Mater Trans A 48(4):1759–1770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-3976-2
RajaKumar G, Janaki Ram GD, Koteswara Rao SR (2015) Effect of beam oscillation on borated stainless steel electron beam welds. Mater Test 57(6):489–494. https://doi.org/10.3139/120.110740
Ferreño D., Carral JP, Calderón RL, Álvarez JA, Gutiérrez-Solana F (2017) Development and experimental validation of a simplified finite element methodology to simulate the response of steel beams subjected to flame straightening. Construct Build Mater 137(Supplement C):535–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.001. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950061817301769
Lacalle R, Álvarez J, Ferreño D, Portilla J, Ruiz E, Arroyo B, Gutiérrez-Solana F. (2013) Flame straightening application on structural steels: Effects on mechanical and fracture properties, 0. https://doi.org/10.1201/b15963-76
Sun X, Choi K, Liu W, Khaleel M (2009) Predicting failure modes and ductility of dual phase steels using plastic strain localization. Int J Plast 25(10):1888–1909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2008.12.012. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0749641908001897
Ramazani A, Mukherjee K, Schwedt A, Goravanchi P, Prahl U, Bleck W (2013) Quantification of the effect of transformation-induced geometrically necessary dislocations on the flow-curve modelling of dual-phase steels. Int J Plast 43:128–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2012.11.003. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0749641912001684
Tasan C, Hoefnagels J, Diehl M, Yan D, Roters F, Raabe D (2014) Strain localization and damage in dual phase steels investigated by coupled in-situ deformation experiments and crystal plasticity simulations. Int J Plast 63:198–210. deformation Tensors in Material Modeling in Honor of Prof. Otto T. Bruhns. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijplas.2014.06.004. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0749641914001260
Minami H, Nakayama K, Morikawa T, Higashida K, Toji Y, Hasegawa K (2011) Effect of tempering conditions on inhomogeneous deformation behavior of ferrite-martensite dual-phase steels. Tetsu-to-Hagane 97(9):493–500. https://doi.org/10.2355/tetsutohagane.97.493
Hasegawa K, Toji Y, Minami H, Ikeda H, Morikawa T, Higashida K (2012) Effect of martensite fraction on tensile properties of dual-phase steels. Tetsu-to-Hagane 98(6):320–327. https://doi.org/10.2355/tetsutohagane.98.320
Tasan C, Diehl M, Yan D, Bechtold M, Roters F, Schemmann L, Zheng C, Peranio N, Ponge D, Koyama M, Tsuzaki K, Raabe D (2015) An overview of dual-phase steels: Advances in microstructure-oriented processing and micromechanically guided design. Annu Rev Mater Res 45(1):391–431. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-matsci-070214-021103
Zheng C, Raabe D (2013) Interaction between recrystallization and phase transformation during intercritical annealing in a cold-rolled dual-phase steel: A cellular automaton model. Acta Mater 61(14):5504–5517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.05.040. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1359645413004187
EN-5173:2010+A1:2011 (2010) Destructive tests on welds in metallic materials. bend tests, European committee for Standardization
Han R, Lu S, Dong W, Li D, Li Y (2015) The morphological evolution of the axial structure and the curved columnar grain in the weld. J Cryst Growth 431(Supplement C):49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2015.09.001. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022024815005473
Lienert T, Siewert T, Babu S, Acoff V (2011) ASM handbook, vol 6A. ASM International, Ohio
Komerla K, Naumov A, Mertin C, Prahl U, Bleck W (2018) Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded aa6016-t4 and dc04 alloy joints. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94 (9):4209–4219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1022-6
Sadowski AJ, Rotter JM, Stafford PJ, Reinke T, Ummenhofer T (2017) On the gradient of the yield plateau in structural carbon steels. J Construct Steel Res 130(Supplement C):120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2016.11.024. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0143974X16304771
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the German Research Foundation (DFG) for their continued support of our research in the Collaborative Research Centre SFB1120 ‘Precision Melt Engineering’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komerla, K., Gach, S., Vossel, T. et al. The effect of beam oscillations on the microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded steel joints. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 102, 2919–2931 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03355-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03355-4