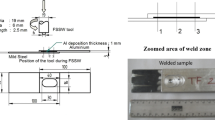
Abstract
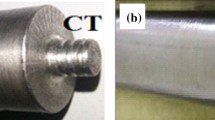
Double-sided friction stir spot welding (FSSW) of dissimilar Al/steel alloy sheets was developed, and the effects of different tool rotational directions and plunge forces on the welding quality were investigated and compared with single-sided FSSW. Experimental results show that the fracture load increases with the increasing of plunge force, and double-sided FSSW can sustain higher fracture load than single-sided FSSW regardless of the plunge force. Two rotational directions result in similar fracture load of the welded part if the plunge force is less than 1.16 kN. If the plunge force is larger than 1.16 kN, opposite rotational direction achieves higher fracture load of the welding point. The formation of intermetallic compounds under different welding conditions at the welding joint was analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anawa EM, Olabi AG (2008) Using Taguchi method to optimize welding pool of dissimilar laser-welded components. Opt Laser Technol 40:379–388
Hsieh MJ, Lee RT, Chiou YC (2017) Friction stir spot fusion welding of low-carbon steel to aluminum alloy. J Mater Process Technol 240:118–125
Piccini JM, Svoboda HG (2017) Tool geometry optimization in friction stir spot welding of Al-steel joints. J Manuf Process 26:142–154
Habibnia M, Shakeri M, Nourouzi S, Givi MKB (2015) Microstructural and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 5050 Al alloy and 304 stainless steel plates. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 76:819–829
Fereiduni E, Movahedi M, Kokabi A (2015) Aluminum/steel joints made by an alternative friction stir spot welding process. J Mater Process Technol 224:1–10
Bozkurt Y, Bilici MK (2013) Application of Taguchi approach to optimize of FSSW parameters on joint properties of dissimilar AA2024-T3 and AA5754-H22 aluminum alloys. Mater Des 51:513–521
Bozzi S, Helbert-Etter AL, Baudin T, Klosek V, Kerbiguet JG, Criqui B (2010) Influence of FSSW parameters on fracture mechanisms of 5182 aluminium welds. J Mater Process Technol 210:1429–1435
Liyanage T, Kilbourne J, Gerlich A, North T (2009) Joint formation in dissimilar Al alloy/steel and Mg alloy/steel friction stir spot welds. Sci Technol Weld Join 14:500–508
Li W, Li J, Zhang Z, Gao D, Wang W, Dong C (2014) Improving mechanical properties of pinless friction stir spot welded joints by eliminating hook defect. Mater Des 62:247–254
Tozaki Y, Uematsu Y, Tokaji K (2010) A newly developed tool without probe for friction stir spot welding and its performance. J Mater Process Technol 210:844–851
Chiou Y-C, Liu C-T, Lee R-T (2013) A pinless embedded tool used in FSSW and FSW of aluminum alloy. J Mater Process Technol 213:1818–1824
Garg A, Bhattacharya A (2017) Strength and failure analysis of similar and dissimilar friction stir spot welds: influence of different tools and pin geometries. Mater Des 127:272–286
Yuan X, Li C, Chen J, Li X, Liang X, Pan X (2017) Resistance spot welding of dissimilar DP600 and DC54D steels. J Mater Process Technol 239:31–41
Xie X, Shen J, Gong F, Wu D, Zhang T, Luo X, Li Y (2016) Effects of dwell time on the microstructures and mechanical properties of water bath friction stir spot-welded AZ31 magnesium alloy joints. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82:75–83
Tier M, Rosendo T, Mazzaferro J, Mazzaferro C, dos Santos J, Strohaecker T (2017) The weld interface for friction spot welded 5052 aluminium alloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90:267–276
Song X, Ke L, Xing L, Liu F, Huang C (2014) Effect of plunge speeds on hook geometries and mechanical properties in friction stir spot welding of A6061-T6 sheets. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71:2003–2010
Cox CD, Gibson BT, DeLapp DR, Strauss AM, Cook GE (2014) A method for double-sided friction stir spot welding. J Manuf Process 16:241–247
Cox CD, Gibson BT, Strauss AM, Cook GE (2014) Energy input during friction stir spot welding. J Manuf Process 16:479–484
Hsieh MJ, Chiou YC, Lee RT (2015) Friction stir spot welding of low-carbon steel using an assembly-embedded rod tool. J Mater Process Technol 224:149–155
Sun Y, Fujii H, Takaki N, Okitsu Y (2013) Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar Al alloy/steel joints prepared by a flat spot friction stir welding technique. Mater Des 47:350–357
Lee C-Y, Choi D-H, Yeon Y-M, Jung S-B (2009) Dissimilar friction stir spot welding of low carbon steel and Al–Mg alloy by formation of IMCs. Sci Technol Weld Join 14:216–220
Bozzi S, Helbert-Etter A, Baudin T, Criqui B, Kerbiguet J (2010) Intermetallic compounds in Al 6016/IF-steel friction stir spot welds. Mater Sci Eng A 527:4505–4509
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China through grant no. 51675332.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, X., Li, M., Li, X. et al. Double-sided friction stir spot welding of steel and aluminum alloy sheets. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96, 2875–2884 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1710-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1710-x