Abstract
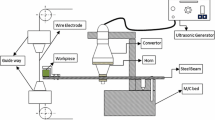
This paper presents the results of experimental research aimed to improve yield in the wire electrical discharge machining (W-EDM). These machines were equipped with special devices for ultrasonic activation of the wire electrode. During experiments, we noticed that the ultrasonic energy introduced into the working environment influenced the erosive capacity of machining process. Two ways of activating the wire electrode: in a single point or in two points after two rectangular directions in space, as well as the combining methods of vibrations along the wire electrode, having equal or different frequencies and amplitudes, were analyzed. Variation the erosive capacity for different materials, depending on how the technological parameters (current intensity for dielectric breakdown and the ultrasound generator power) are prescribing, is presented under graphic and tabular forms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikeda M (1972) The movement of a bubble in the gap depending on the single electrical discharge (first report). J Jpn Electr Mach Eng 6(11):12–26
Mironoff NL (1977) Thermal effects of erosive pulses. ISEM 5, Wolfsberg
Okada A, Uno Y, Nakazawa M, Yamauchi T (2010) Evaluation of spark distribution and wire vibration in wire EDM by high-speed observation. CIRP Ann 59(1):231–234
Kitamura T, Kunieda M (2014) Clarification of EDM gap phenomena using transparent electrodes. CIRP Ann 63(1):213–216
Miţkevici MK (1966) Ob elektroerozionnom effekte na vibrinuişcih elektrodah. Fiziceskie osnovi elektroiskrovoi obrabotki materiallov, Editura Nauka
Savii G, Nani VM, Militaru C, Muntean N (1989) Contributions on ultrasound activation of wire-cut electric discharge processing. ISEM 9, Nagoya
Wong Y, Rahman M, Lim H, Han H, Ravi N (2003) Investigation of micro-EDM material removal characteristics using RC-pulse discharges. J Mater Process Technol 140(1–3):303–307
Kazantsev V.A., Rosenberg L.D. The mechanism of ultrasonic cutting. Ultrasonics, vol. 3, SUA, 1965
Murti VSR, Philip PK (1987) An analysis of the debris in ultrasonic-assisted electrical discharge machining. Wear 117:241–250
Jun Q, Fei Y, Jun W, Bert L, Dominiek R (2015) Material removal mechanism in low-energy micro-EDM process. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 64:225–228
Inoue K., 1979. Procédé et dispositif pour le traitement par érosion électrique avec électrode filiforme vibrant. Brevet France, no. 2 350 919/07.10.1979
Savii Gh., Nani V.M., Militaru C., Muntean N. Method and device for ultrasonic activation wire electrode. Romanian Patent, no. 102596/12.12.1988, 1988
Chen Z, Huang Y, Huang H, Zhang Z, Zhang G (2015) Three-dimensional characteristics analysis of the wire-tool vibration considering spatial temperature field and electromagnetic field in WEDM. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 92:85–96
Hayakawa S, Sasaki Y, Itoigawa F, Nakamura T (2013) Relationship between occurrence of material removal and bubble expansion in electrical discharge machining. Procedia CIRP 6:174–179
Cetin S, Okada A, Uno Y (2004) Effect of debris accumulation on machining speed in EDM. Int J Electr Mach 9:9–14
Agarval S, Rao PV (2008) Experimental investigation of surface/subsurface damage formation and material removal mechanisms in SIC grinding. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48(6):698–710
SC STIMEL SA Timisoara, Romanian. Electrodischarge processing machine with wire electrode and numerical command by type ELEROFIL-10. Technical paper, 2002
Nani VM (2015) Ultrasonic activation of the wire electrode on EDM processing machine. LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, Germany
Nani VM (1992) Activation ultrasonic methods of wire electrode used in electrodischarge processing, vol 28, Copybook for acoustics. Romanian Academy, Bucharest, pp 41–44
Silaş G, Rădoi M, Brîndeu L, Klepp M, Hegedus A (1973) Collection of problems for mechanical vibrations. Technical Publishing House, Bucharest
Yamada H, Mohri N, Saito N, Magara T (1997) Modal analysis of wire electrode vibration in wire-EDM. Int J Electr Mach 19–24
Tomura S, Kunieda M (2009) Analysis of electromagnetic force in wire-EDM. Precis Eng 33(3):255–252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viorel-Mihai, N. Effect of wire electrode’s ultrasonic vibration on erosive capacity to W-EDM machines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88, 425–441 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8752-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8752-8