Abstract
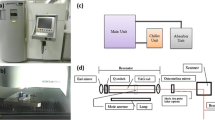
This study presents the investigation results of micro-channel fabrication in nickel-based super alloy (Inconel 718) by Nd:YAG laser beam machining. The effects of laser parameters on the machining performance characteristics over dimensional sizes are evaluated. Three number of laser parameters have been reserved as predictors to the naming of laser intensity, pulse frequency, and laser scanning speed. The channel’s top width, bottom width, depth, and taperness are considered as the process responses. Micrographs by SEM have been organized to study and measure the micro-sized dimensions of fabricated channels. The results showed that the selection of channel size is critical to achieve desired machining results. Wider-sized channels (for example 200 × 100 μm and 1000 × 500 μm) can more confidently be machined than narrower-sized channels (50 × 50 μm). The possible reasons behind the failure of narrow-sized micro-channel fabrication are identified. The appropriate combination of parameters that can yield the better results for 100 × 100 μm channel size are the laser intensity of 92.7 %, repetition rate of 30 kHz, and scan speed of 300 mm/s. At this combination, the channel geometries of wider-sized channels are more close to the designed geometries as compared to narrow-sized channels. Microstructures of the machined channels are also studied showing the recast layer with lamellar grain structure and phase transformation near the edges of micro-channels. The channel edges and their adjacent areas show variation in hardness relative to bulk material. This has been validated via micro-hardness profiles of the close vicinity of machined micro-channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teng J, Chu J-C, Liu C, Xu T, Lien Y-F, Cheng J-H, Huang S, Jin S, Dang T, Zhang C, Yu X, Lee M-T, Greif R (2012) Fluid dynamics in microchannels. In: Juarez LH (ed) Fluid dynamics, computational modeling and applications, InTech
Fujioka H, Grotberg JB (2005) The steady propagation of a surfactant-laden liquid plug in a two-dimensional channel. Phys Fluids 17(no. 8):082102
Kreutzer MT, Kapteijn F, Moulijn JA, Heiszwolf JJ (2005) Multiphase monolith reactors: chemical reaction engineering of segmented flow in microchannels. Chem Eng Sci 60(22):5895–5916
Haghbin N, Spelt JK, Papini M (2015) Abrasive waterjet micro-machining of channels in metals: comparison between machining in air and submerged in water. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 88:108–117
Nouraei H, Kowsari K, Spelt JK, Papini M (2014) Surface evolution models for abrasive slurry jet micro-machining of channels and holes in glass. Wear 309(1–2):65–73
Son SW, Lee MK, Oh KH, Jeong SH (2006) Fabrication of titanium microchannels using laser-assisted thermochemical wet etching. J Laser Appl 18(2):131–137
Vazquez E, Gomar J, Ciurana J, Rodríguez CA (2015) Analyzing effects of cooling and lubrication conditions in micromilling of Ti6Al4V. J Clean Prod 87:906–913
Dahotre NB, Harimkar SP (2008) Laser fabrication and machining of materials. Springer US, Boston
Kumar A, Gupta MC (2010) Laser machining of micro-notches for fatigue life. Opt Lasers Eng 48(6):690–697
Karazi SM, Issa A, Brabazon D (2009) Comparison of ANN and DoE for the prediction of laser-machined micro-channel dimensions. Opt Lasers Eng 47(9):956–964
Nieto D, Delgado T, Flores-Arias MT (2014) Fabrication of microchannels on soda-lime glass substrates with a Nd:YVO4 laser. Opt Lasers Eng 63:11–18
Suriano R, Kuznetsov A, Eaton SM, Kiyan R, Cerullo G, Osellame R, Chichkov BN, Levi M, Turri S (2011) Femtosecond laser ablation of polymeric substrates for the fabrication of microfluidic channels. Appl Surf Sci 257(14):6243–6250
Tam SC, Yeo CY, Jana S, Lau MWS, Lim LEN, Yang LJ, Noor YM (1993) Optimization of laser deep-hole drilling of Inconel 718 using the Taguchi method. J Mater Process Technol 37(1–4):741–757
Teixidor D, Ferrer I, Ciurana J, Özel T (2013) Optimization of process parameters for pulsed laser milling of micro-channels on AISI H13 tool steel. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 29(1):209–218
Gilbert T, Krstic VD, Zak G (2007) Machining of aluminium nitride with ultra-violet and near-infrared Nd:YAG lasers. J Mater Process Technol 189(1–3):409–417
Biffi CA, Lecis N, Previtali B, Vedani M, Vimercati GM (2010) Fiber laser microdrilling of titanium and its effect on material microstructure. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 54(1–4):149–160
Zhao X, Chen J, Lin X, Huang W (2008) Study on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser rapid forming Inconel 718. Mater Sci Eng A 478(1–2):119–124
Kumar SA, Sundar R, Raman SGS, Kumar H, Kaul R, Ranganathan K, Oak SM, Kukreja LM, Bindra KS (2014) Influence of laser peening on microstructure and fatigue lives of Ti–6Al–4V. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 24(10):3111–3117
Chikarakara E, Naher S, Brabazon D (2012) High speed laser surface modification of Ti–6Al–4V. Surf Coat Technol 206(14):3223–3229
Yang J, Sun S, Brandt M, Yan W (2010) Experimental investigation and 3D finite element prediction of the heat affected zone during laser assisted machining of Ti6Al4V alloy. J Mater Process Technol 210(15):2215–2222
Yilbas BS, Akhtar SS, Karatas C (2010) Laser surface treatment of Inconel 718 alloy: thermal stress analysis. Opt Lasers Eng 48(7–8):740–749
Yang X, Richard Liu C (1999) Machining titanium and its alloys. Mach Sci Technol 3(1):107–139
Prakash S, Kumar S (2015) Fabrication of microchannels on transparent PMMA using CO2 Laser (10.6 μm) for microfluidic applications: an experimental investigation. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 16(2):361–366
Metals M Magellan Industrial Trading Company, Inc. (dba Magellan Metals), 227 Wilson Avenue. South Norwalk, CT 06854 U.S.A.” [Online]. Available: http://www.magellanmetals.com/
Lee SW, Shin HS, Chu CN (2013) Fabrication of micro-pin array with high aspect ratio on stainless steel using nanosecond laser beam machining. Appl Surf Sci 264:653–663
Metallography of superalloys. Vander voort metallography, failure analysis & archeometallography consulting. [Online]. Available: http://www.georgevandervoort.com/metallography/general/nickel-alloys/20001279-metallography-of-superalloys.html. Accessed 24 Apr 2015
Dehmas M, Lacaze J, Niang A, Viguier B (2011) TEM study of high-temperature precipitation of delta phase in inconel 718 alloy. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2011:e940634
Kuo C-M, Yang Y-T, Bor H-Y, Wei C-N, Tai C-C(2009) Aging effects on the microstructure and creep behavior of Inconel 718 superalloy. Mater Sci Eng A 510–511:289–294
Aliou Niang BV (2010) Some features of anisothermal solid-state transformations in alloy 718. Mater Character - Mater Charact 61(5):525–534
Ghosh S, Yadav S, Das G (2008) Study of standard heat treatment on mechanical properties of Inconel 718 using ball indentation technique. Mater Lett 62(17–18):2619–2622
Wiley: superalloys II: high-temperature materials for aerospace and industrial power - Chester T. Sims, Norman S. Stoloff, William C. Hagel.” [Online]. Available: http://eu.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-0471011479.html. Accessed 26 Apr 2015
Suryanarayana C (2011) Experimental techniques in materials and mechanics. CRC Press
E04 Committee (2011) Test method for knoop and vickers hardness of materials. ASTM International
Ghassemali E, Tan M-J, Wah CB, Jarfors AEW, Lim SCV (2013) Grain size and workpiece dimension effects on material flow in an open-die micro-forging/extrusion process. Mater Sci Eng A 582:379–388
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, N., Darwish, S., Alahmari, A.M. et al. Micro-channels by Nd:YAG laser beam machining: fabrication, microstructures, and micro-hardness profiles. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85, 1955–1968 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7257-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7257-1