Abstract
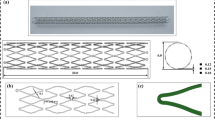
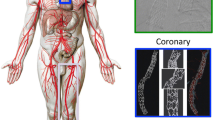
In this paper, we develop reliability and condition-based maintenance models for a multi-component system of stents implanted in human arteries that is subject to both delayed and instantaneous failures. Considering the physics of failure and probability of failure, we develop a system-level reliability model and maintenance strategy by merging fracture mechanics and stochastic process approaches. In our new system-level reliability model, due to the exposure of stents to the same shocks, the component failure times are probabilistically dependent. Two patient groups with different activity levels are considered, and their corresponding system-level reliability functions are derived. We further develop a new condition-based maintenance policy, in which the replacement is either a preventive or corrective action performed depending on the condition of the system. Numerical examples using data from the literature are presented to analyze the reliability of implanted multi-stent systems and investigate the effectiveness of the proposed condition-based maintenance policy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allie DE, Hebert CJ, Walker CM (2004) Nitinol stent fractures in the SFA. Endovasc Today 7:22–34
Amico F, Geraci S, Tamburino C (2013) Acute coronary syndrome Due to early multiple and complete fractures in sirolimus-eluting stent: a case report and brief literature review. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 81(1):52–56
Arab A, Keedy E, Feng Q, Song S, Coit DW (2013) Reliability analysis for implanted multi-stent systems with stochastic dependent competing risk processes. Proceedings of Industrial and Systems Engineering Research Conference, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 18-22 May 2013
Ayuso JR, de Caralt TM, Pages M, Riambau V, Ayuso C, Sanchez M, Real MI, Montaña X (2004) MRA is useful as a follow-up technique after endovascular repair of aortic aneurysms with nitinol endoprostheses. J Magn Reson Imaging 20:803–810
Cho DI, Parlar M (1991) A survey of maintenance models for multi-unit systems. Eur J Oper Res 51(1):1–23
Daly S, Miller A, Ravichandran G, Bhattacharya K (2007) An experimental investigation of crack initiation in thin sheets of nitinol. Acta Mater 55(18):6322–6330
Dekker R, Wildeman RE, Duyn Schouten FA (1997) A review of multi-component maintenance models with economic dependence. Math Meth Oper Res 45(3):411–435
Ferreira M, Lanziotti L, Monteiro M, Abuhadba G, Capotorto LF, Nolte L, Fearnot N (2007) Superficial femoral artery recanalization with self-expanding nitinol stents: long-term follow-up results. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 34(6):702–708
Keedy E, Feng Q (2012) A physics-of-failure based reliability and maintenance modeling framework for stent deployment and operation. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 103:94–101
Keedy E, Feng Q (2013) Reliability analysis and customized preventive maintenance policies for stents with stochastic dependent competing risk processes. IEEE Trans Reliab 62(4):887–897
Lagarias JC, Reeds JA, Wright MH, Wright PE (1998) Convergence properties of the Nelder-Mead simplex method in low dimensions. SIAM J Optim 9(1):112–147
Marrey RV, Burgermeister R, Grishaber RB, Ritchie RO (2006) Fatigue and life prediction for cobalt-chromium stents: a fracture mechanics analysis. Biomaterials 27(9):1988–2000
Mewissen MW (2009) Primary nitinol stenting for femoropopliteal disease. J Endovasc Ther 16(2 Suppl 2):II63–II81
Nakazawa G, Finn AV, Vorpahl M, Ladich E, Kutys R, Balazs I, Kolodgie FD, Virmani R (2009) Incidence and predictors of drug-eluting stent fracture in human coronary artery a pathologic analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 54(21):1924–1931
Pelton AR, Schroeder V, Mitchell MR, Gong X-Y, Barney M, Robertson SW (2008) Fatigue and durability of nitinol stents. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 1(2):153–164
Peng H, Feng Q, Coit DW (2010) Reliability and maintenance modeling for systems subject to multiple dependent competing failure processes. IIE Trans 43(1):12–22
Räber L, Jüni P, Löffel L, Wandel S, Cook S, Wenaweser P, Togni M, Vogel R, Seiler C, Eberli F, Lüscher T, Meier B, Windecker S (2010) Impact of stent overlap on angiographic and long-term clinical outcome in patients undergoing drug-eluting stent implantation. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(12):1178–1188
Riepe G, Heintz C, Kaiser E, Chakfé N, Morlock M, Delling M, Imig H (2002) What can we learn from explanted endovascular devices? Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 24(2):117–122
Robertson SW, Ritchie RO (2007) In vitro fatigue-crack growth and fracture toughness behavior of thin-walled superelastic nitinol tube for endovascular stents: a basis for defining the effect of crack-like defects. Biomaterials 28(4):700–709
Sachs NW (2005) Understanding the surface features of fatigue fractures: how they describe the failure cause and the failure history. J Fail Anal Prev 5(2):11–15
Thomas LC (1986) A survey of maintenance and replacement models for maintainability and reliability of multi-item systems. Reliab Eng 16(4):297–309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Q., Rafiee, K., Keedy, E. et al. Reliability and condition-based maintenance for multi-stent systems with stochastic-dependent competing risk processes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 80, 2027–2040 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7182-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7182-3