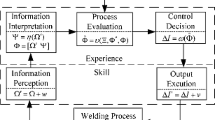
Abstract
In gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), the weld pool is the major source of information that can be used to assure the production of the desired weld penetration—the most critical factor determining the weld integrity. To meet this challenge, various sensing technologies, modeling methods, and control strategies have been studied, and artificial intelligence technologies were applied to improve system intelligence. The GTAW process analysis is given first. Then, a short introduction on weld pool sensing technologies is presented, where three-dimensional (3D) vision sensing is a very active orientation. Furthermore, weld pool description model and characteristic parameter model are also discussed, where intelligent algorithms were used generally. Besides, dynamic modeling and penetration control strategies, especially intelligent control strategies are presented. At last, the discussion about development of the GTAW penetration control product is analyzed briefly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Connor LP, O’Brien RL, Oates WR (2007) Welding handbook: welding processes, part 2. American Welding Society, Miami
Zhang YM (2008) Real-time weld process monitoring. Woodhead Publishing in Materials, ISBN 978-1-84569-268-1, Cambridge, England
Chen SB, Wu J (2008) Intelligentized methodology for arc welding dynamical processes: visual information acquiring, knowledge modeling and intelligent control. ISBN 3540856412, Sрringer
Wang XW (2014) Three-dimensional vision-based sensing of GTAW: a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 72:333–345
Wang XW (2013) Weld pool surface model establishment for GTAW based on 3D reconstruction technology. Proc 2013 Chin Intell Autom Conf Lect Notes Electr Eng 255:741–748
Zhang WJ, Liu YK, Wang XW, Zhang YM (2012) Characterization of three dimensional weld pool surface in GTAW. Weld J 91(7):195s–203s
Zhang WJ, Wang XW, Zhang YM (2013) Analytical real-time measurement of a three-dimensional weld pool surface. Meas Sci Technol 24:115011 (18pp)
Zhang WJ (2014) Modeling of human welder behavior in gas tungsten arc welding of stainless steel tubes. Weld World 58:601–617
Wang XW, Li RR (2014) Intelligent modelling of back-side weld bead geometry using weld pool surface characteristic parameters. J Intell Manuf 25(6):1301–1313
Zhang WJ, Zhang YM (2012) Modeling of human welder response to 3D weld pool surface: part I-principles. Weld J 91(11):310s–318s
Zhang WJ, Zhang YM (2012) Modeling of human welder response to 3D weld pool surface: part II-results and analysis. Weld J 91(12):329s–337s
Zhang WJ, Zhang YM (2012) Dynamic control of GTAW process using human welder response model. Weld J 92(5):154s–166s
Liu YK, Zhang YM (2014) Control of human arm movement in machine-human cooperative welding process. Control Eng Pract 32:161–171
Liu YK, Zhang YM (2013) Control of 3D weld pool surface. Control Eng Pract 21:1469–1480
Liu YK, Zhang WJ, Zhang YM (2013) Dynamic neuro-fuzzy-based human intelligence modeling and control in GTAW. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 99:1–12
Liu YK, Zhang YM (2013) Model-based predictive control of weld penetration in gas tungsten arc welding. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 22(3):955–966
Kovacevic R, Cao ZN, Zhang YM (1996) Roles of welding parameters in determining the geometrical appearance of weld pool. J Eng Mater Technol Trans ASME 118(4):589–596
Jou M (2003) Experimental study and modeling of GTA welding process. J Manuf Sci Eng 125:801–808
Zhao PC, Wu CS, Zhang YM (2004) Numerical simulation of dynamic characteristics of weld pool geometry with step-changes of welding parameters. Model Simul Mater Sci Eng 12(5):765–780
Zhang YM, Kovacevic R, Li (1996) Characterization and real-time measurement of geometrical appearance of weld pool. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 36(7):799–816
Zhang YM, Li L, Kovacevic R (1997) Dynamic estimation of full penetration using geometry of adjacent weld pools. J Manuf Sci Eng Trans ASME 119(4):631–643
Yasuo S (1999) Measurement of molten pool shape and penetration control applying neural network in TIG welding of thin steel plates. ISIJ Int 39(10):1075–1080
Tarng YS, Wu JL, Yen SS, Juang SC (1999) Intelligent modeling and optimization of the gas tungsten arc welding. J Intell Manuf 10:73–79
Wang B, Chen SB, Wang JJ (2005) Rough set based knowledge modeling for the aluminum alloy pulsed GTAW process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25(9):902–908
Kong M, Chen SB (2009) Al alloy weld pool control of welding robot with passive vision. Sens Rev 29(1):28–37
Zhao DB, Chen SB, Wu L, Dai M, Chen Q (2001) Intelligent control for the shape of the weld pool in pulsed GTAW with filler metal. Weld Res Suppl 80(11):253s–260s
Wu CS, Gao JQ (2006) Vision-based neuro-fuzzy control of weld penetration in gas tungsten arc welding of thin sheets. Int J Model Identif Control 1(2):126–132
Subashini L, Vasudevan M (2012) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS)-based models for predicting the weld bead width and depth of penetration from the infrared thermal image of the weld pool. Metall Mater Trans B 43B(2):145–154
Zhang YM, Wu L, Walcott B, Chen DH (1993) Determining joint penetration in GTAW with vision sensing of weld-face geometry. Weld J 72(10):463s–469s
Chokkalingham S, Chandrasekhar N, Vasudevan M (2012) Predicting the depth of penetration and weld bead width from the infrared thermal image of the weld pool using artificial neural network modeling. J Intell Manuf 23:1995–2001
Giridharan PK, Murugan N (2009) Optimization of pulsed GTA welding process parameters for the welding of AISI 304L stainless steel sheets. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40(5–6):478–489
Lu W, Zhang YM, Emmerson J (2004) Sensing of weld pool surface using non-transferred plasma charge sensor. Meas Sci Technol (15):991–999
Lu W, Zhang YM (2006) Robust sensing and control of the weld pool surface. Meas Sci Technol 17:2437–2446
Zhang YM, Kovacevic R (1998) Neurofuzzy model based predictive control of weld fusion zone geometry. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 6(3):389–401
Zhang YM, Kovacevic R, Wu L (1996) Dynamic analysis and identification of gas tungsten arc welding process for full penetration control. J Eng Ind Trans ASME 118(1):123–136
Zhang YM, Kovacevic R, Li L (1996) Adaptive control of full penetration GTA welding. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 4(4):394–403
Luo H, Devanathan R, Wang J, Chen X, Sun Z (2002) Vision based neurofuzzy logic control of weld pool geometry. Sci Technol Weld Join 7(5):321–325
Fan CJ, Lv FL, Chen SB (2009) Visual sensing and penetration control in aluminum alloy pulsed GTA welding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 42(1–2):126–137
Chen SB, Wu J, Du QY (2011) Non-linear modeling and compound intelligent control of pulsed gas tungsten arc welding dynamics. Proc Inst Mech Eng I J Syst Control Eng 225:113–124
Zhang YM, Kovacevic R (1997) Robust control of interval plants: a time domain approach. IEE Proc Control Theory Appl 144(4):347–353
Tsai CH, Hou KH, Chuang HT (2006) Fuzzy control of pulsed GTA welds by using real-time root bead image feedback. J Mater Process Technol 176(6):158–167
Servo-Robot http://www.meta-mvs.com/index.htm
Meta vision system http://www.servorobot.com/
Chen SB, Lv N (2014) Research evolution on intelligentized technologies for arc welding process. J Manuf Process 16:109–122
Xu YL, Lv N, Zhong JY, Chen HB, Chen SB (2012) Research on the real-time tracking information of three-dimension welding seam in robotic GTAW process based on composite sensor technology. J Intell Robot Syst 68:89–103
Fang HC, Ong SK, Nee AYC (2013) Orientation planning of robot end-effector using augmented reality. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67(9–12):2033–2049
Nee AYC, Ong SK, Chryssolouris G, Mourtzis D (2012) CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 61(2):657–679
Chen CJ, Hong J, Wang SF (2015) Automated positioning of 3D virtual scene in AR-based assembly and disassembly guiding system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-014-6321-6
Chen SJ, Huang N, Liu YK, Zhang YM (2015) Machine-assisted travel speed control in manual welding torch operation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-014-6310-9
Li GY, Xu FX, Sun GY, Li Q (2014) Identification of mechanical properties of the weld line by combining 3D digital image correlation with inverse modeling procedure. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74(5–8):893–905
Wang XW, Huang Y, Zhang YM (2013) Droplet transfer model for laser enhanced GMAW. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64(1):207–217
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X. Three-dimensional vision applications in GTAW process modeling and control. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 80, 1601–1611 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7063-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7063-9