Abstract
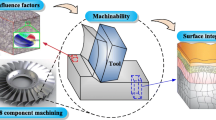
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided surgical robots are becoming a hotspot owing to the good quality of MR image and stability of robot. For the MR-compatible robot, machinability influences assembly accuracy and kinematic accuracy directly. At the same time, the cutting force plays a vital role in evaluating machinability and machining process. This paper presents the machinability evaluation on five kinds of MR-compatible materials and an improved mechanistic force model. The model takes shearing and edge forces of flank and bottom edge combined with tool runout into consideration. Experimental results show that the prediction error is within 9 %. The effects that chip shape imposes on the machining stability and surface roughness are analyzed and then involved in the machinability evaluation. Digraph and matrix method are applied to evaluate the material machinability based on cutting force, roughness, and the chip shape. Relative importance between the three components is analyzed and taken into the evaluation. At last, polyformaldehyde is proved to have the best machinability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dai J (2010) Surgical robotics and its development and progress. Robotica 28(3):161
Larson BT, Erdman AG, Tsekos NV, Yacoub E, Tsekos PV, Koutlas IG (2004) Design of an MRI-compatible robotic stereotactic device for minimally invasive interventions in the breast. J Biomech Eng-T ASME 126(4):458–465
Krieger A, Susil RC, Ménard C, Coleman JA, Fichtinger G, Atalar E, Whitcomb LL (2005) Design of a novel MRI compatible manipulator for image guided prostate interventions. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52(2):306–313
Chinzei K, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA (1999) MR compatibility of mechatronic devices: design criteria. In Proc. of MICCAI 1999 Conf. Cambridge, England, 1999: 1020–1030
Chinzei K, Hata N, Jolesz FA, Kikinis R (2000) MR compatible surgical assist robot: system integration and preliminary feasibility study. In Proc. of MICCAI 2000 Conf. Pittsburgh, 2000: 921–930
Stoianovici D (2005) Multi-imager compatible actuation principles in surgical robotics. Int J Med Robot Comput 1(2):86–100
Hu F, Li D (2012) Modelling and simulation of milling forces using an arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian finite element method and support vector regression. J Optim Theory Appl 153(2):461–484
Mounayri HEI, Badar MA, Rengifo GA (2008) Multi-parameter ANN model for flat-end milling. Trans Can Soc Mech Eng 32(3–4):523–536
Gonzalo O, Jauregi H, Uriarte LG, Lacalle LN (2009) Prediction of specific force coefficients from a FEM cutting model. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 43(3–4):348–356
Özel T, Altan T (2000) Process simulation using finite element method—prediction of cutting forces, tool stresses and temperatures in high speed flat end milling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 40(5):713–738
Gradisek J, Kalveram M, Weinert K (2004) Mechanistic identification of specific force coefficients for a general end mill. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44(4):401–414
Lamikiz A, Lacalle LN, Sánchez JA, Salgado MA (2004) Cutting force estimation in sculptured surface milling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44(14):1511–1526
Dang JW, Zhang WH, Yang Y, Wan M (2010) Cutting force modeling for flat end milling including bottom edge cutting effect. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 50(11):986–997
Ehmann KF, Kapoor SG, Devor RE, Lazoglu I (1997) Machining process modeling: a review. Trans ASME J Manuf Sci Eng 119(4B):655–663
Oscar G, Jokin B, Haritz J (2010) A method for the identification of the specific force coefficients for mechanistic milling simulation. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50(9):765–774
Roth D, Ismail F, Bedi S (2005) Mechanistic modelling of the milling process using complex tool geometry. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25(1–2):140–144
Engin S, Altintas Y (2001) Mechanics and dynamics of general milling cutters. Part I: helical end mills. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 41(15):2195–2212
Rivière-Lorphèvre E, Filippi E (2009) Mechanistic cutting force model parameters evaluation in milling taking cutter radial runout into account. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 45(1–2):8–15
Kumar A, Choi SK, Goksel L (2011) Tolerance allocation of assemblies using fuzzy comprehensive evaluation and decision support process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 55(1–4):379–391
Leon T, Liern V, Ruiz JL, Sirvent I (2003) A fuzzy mathematical programming approach to the assessment of efficiency with DEA models. Fuzzy Sets Syst 139(2):407–419
Rao RV, Gandhi OP (2002) Digraph and matrix methods for the machinability evaluation of work materials. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42(3):321–330
Jangra K, Grover S, Chan FTS, Aggarwal A (2011) Digraph and matrix method to evaluate the machinability of tungsten carbide composite with wire EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 56(9–12):959–974
Lee B, Tarng Y, Li H (2000) An investigation of modeling of the machining database in turning operations. J Mater Process Technol 105(1–2):1–6
Li X, Hong W, Wang J, Song J, Kang J (2006) Research on the radar chart theory applied to the indoor environmental comfort level evaluation. In Proc. of WCICA 2006 Conf. Dalian, China, 2006: 5214–5217
Altintas Y (2000) Manufacturing automation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Cifuentes ED, Garcia HP, Villasenor MG (2010) Dynamic analysis of runout correction in milling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 50(8):709–717
Seethaler RJ, Yellowley I (1999) The identification of radial runout in milling operations. Trans ASME J Manuf Sci Eng 121(3):524–531
Karpat Y, Bahtiyar O, Deger B (2012) Mechanistic force modeling for milling of unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced polymer laminates. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 56:79–93
Budak E, Altintas Y, Armarego EJA (1996) Prediction of milling force coefficients from orthogonal cutting data. Trans ASME J Manuf Sci Eng 118(2):216–224
Irene BJ, Joan VC, Hernan GR (2011) Influence of feed, eccentricity and helix angle on topography obtained in side milling processes. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51(12):889–897
Jurkat WB, Ryser HJ (1966) Matrix factorization of determinants and permanents. J Algebra 3:1–27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, S., Ren, Z. & Wu, Z. Mechanistic force modeling and machinability evaluation on MR-compatible materials. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74, 151–161 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5980-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5980-7