Abstract
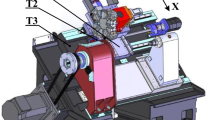
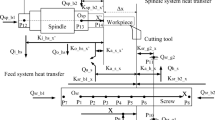
The demand for high-speed/high-precision machine tools is rapidly increasing in response to the development of production technology that requires high-precision parts and high productivity. The thermal deformation of the machine tool structure plays a critical role on the accuracy of machining. Heat generation in the bearings, chucking cylinder, and motor coil are the major sources of thermal deformation. This paper addresses the issues of the thermal displacements in the headstock assembly of a slant bed two-axis CNC lathe. Experimental and numerical investigations were carried out to gain insights into the extent of contribution made by the elements of the headstock assembly on the transient temperature rise and the resulting thermal deformation characteristics. The outcome of the work could be effectively used to improve the machine performance either by making suitable design changes or developing a robust error model for resorting to error compensation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krulewich DA (1998) Temperature integration model and measurement point selection for thermally induced machine tool errors. Mechatronics 8:395–412
Srinivasa N, Ziegert JC (1996) Automated measurement and compensation of thermally induced error map. Precis Eng 19:112–132
Lee J-H, Yang S-H (2002) Statistical optimization and assessment of a thermal error model for CNC machine tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42:147–155
Wang C, Griffin B (2001) A noncontact laser technique for circular contouring accuracy measurement. Rev Sci Instrum 72:1594–1596
Srinivasa N, Ziegert JC, Mize CD (1996) Spindle thermal drift measurement using the laser ball bar. Precis Eng 18:118–128
Yang S-H, Kim K-H, Park YK (2004) Measurement of spindle thermal errors in machine tool using hemispherical ball bar test. Int J Machine Tools 44:333–340
Ko TJ, Gim T-W, Ha J-Y (2003) Particular behavior of spindle thermal deformation by thermal bending. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43:17–23
Haitao Z, Jianguo Y, Jinhua S (2007) Simulation of thermal behavior of a CNC machine tool spindle. Int J Mach Tools Manufact 47:1003–1010
Harris TA (1991) Rolling bearing analysis. Wiley Sons, New York, pp 540–560
Bossmanns B, Tu JF (1999) A thermal model for high speed motorized spindles. Int J Mach Tools & Manufact 39:1345–1366
Li H, Shin YC (2004) Integrated dynamic thermo-mechanical modeling of high speed spindles, Part 1: model development, transactions of the ASME. J Manuf Sci Eng 126:148–158
Choi JK, Lee DG (1998) Thermal characteristics of the spindle bearing system with a gear located on the bearing span. Int J Mach Tools & Manufact 38:1017–1030
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, S.R., Raja, V.P., Thyla, P.R. et al. Prediction of transient thermo-mechanical behavior of the headstock assembly of a CNC lathe. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74, 17–24 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5916-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5916-2