Abstract
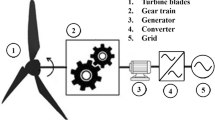
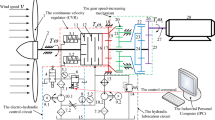
The demerits of traditional wind power generation system-equipped gearbox transmission and direct-drive transmission are becoming more and more obvious; a new hydraulic-type wind power generation system has aroused the attention of both theoretical and industrial circles. In order to accurately reveal the general characteristics and efficiency of the new system, we built an 8-kW hydraulic wind power generation system, mainly to investigate the generating efficiency of the hydraulic motor in varied frequencies under different input pressures and flow conditions. The results show that under a low-frequency (10 Hz) condition, the generator has a low efficiency, near 0.2, while under a high-frequency (50 Hz) condition, the efficiency dramatically increases to 0.73. Meanwhile, with the increase of the frequency, both the output power and total efficiency of the system rise obviously. The total efficiency can reach up to 0.51 at a high frequency of 50 Hz, which is quite desirable. We find that the accomplishments of this study would provide a theoretical basis for the application and promotion of the hydraulic-type wind power generation system and offer a valuable research method on current energy, wave energy, and other new energy resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou SX, Lu ZX (2011) Wind power and power system, vol 7. China Electric Power Press, Beijing, pp 4–7
Zhang DH, Wei L, Lin YG (2009) Simulation of generation system of marine current turbine with pressure-maintaining storage based on hydraulic transmission. Power Syst Autom 33(7):70–74
Khalid M, Savkin AV (2010) A model predictive control approach to the problem of wind power smoothing with controlled battery storage. Renew Energy 35(7):1520–1526
Bhuiyan FA, Yazdani A (2010) Reliability assessment of a wind-power system with integrated energy storage. IET Renew Power Gener 4(3):211–220
Zhang GX (2012) A new generation of wind turbines with full hydraulic transmission. Hydraul Pneum Seals 1:59–62
Bian YM, Niu X (2009) Applying hydraulic energy storage for wind turbine generators. Chin J Constr Mach 7(4):488–493
Zhang H, Zhang GF, Xiong ZQ (2012) Motor speed characteristics of hydraulic transmission wind power equipment. J Liaoning Tech Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 31(4):536–539
Liu BL, Li J, Xu YY (2010) The model design of a new wave energy power generation with hydraulic system. Mach Tool Hydraul 38(10):38–39
Chen XF, Li JM, Cheng H (2011) Research and application of condition monitoring and fault diagnosis technology in wind turbines. J Mech Eng 47(9):45–52
Beng XF, Qi DQ (2011) The state of investigation on structural decomposition and overall design of offshore wind turbines. Struct Eng 27(3):140–141
Wang ZX (2010) New modern wind power technology and engineering application. Electronic Industry Press, Beijing
Ye HY (2010) The design of wind turbine system, operation and maintenance. Electronic Industry Press, Beijing
Ciprian V, Iulian M, Antoneta IB, Emil C (2010) Output power maximization of low-power wind energy conversion systems revisited: possible control solutions. Energy Convers Manag 51:305–310
Liu X, Zhang XM, Chen Y (2008) The dynamic simulation of the monitoring press in variable speed and pitch wind turbine. J Sol Energy 29(8):1008–1013
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fangwei, X., Xianjun, Z., Cuntang, W. et al. Experimental research on hydraulic-type wind power generation system and its efficiency. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73, 1237–1242 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5878-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5878-4