Abstract
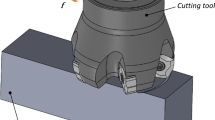
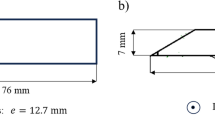
In the present study, high-speed face milling of AISI H13 hardened steel was conducted to investigate the cutting performance of coated carbide tools. The characteristics of chip morphology, tool life, tool wear mechanisms, and surface roughness were analyzed and compared for different cutting conditions. It was found that as the cutting speed increased, the chip morphology evolved in different ways under different milling conditions (up, down, and symmetric milling). Individual saw-tooth segments and sphere-like chip formed at the cutting speed of 2,500 m/min. Owing to the relatively low mechanical load, longest tool life can be obtained in up milling when the cutting speed was no more than 1,000 m/min. As the cutting speed increased over 1,500 m/min, highest tool life existed in symmetric milling. When the cutting speed was 500 m/min, owing to the higher mechanical load, the flaked region on the tool rake face in symmetric milling was much larger than that in up and down milling. There was no obvious wear on the tool rake face at the cutting speed of 2,500 m/min due to the short tool-chip contact length. In symmetric milling, the delamination of tool material, which did not occur in up and down milling, was caused by the relatively large cutting force. Abrasion had great effect on the tool flank wear in symmetric milling. With the increment of cutting speed, surface roughness decreased first and then increased rapidly. Lowest surface roughness can be obtained at the cutting speed of about 1,500 m/min.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salomon CJ (1931) Process for machining metals of similar acting materials when being worked by cutting tools. German patent, number 523594
Nelson S, Schueller JK, Tlusty J (1998) Tool wear in milling hardened die steel. J Manuf Sci Eng 120(4):669–673
Iqbal A, He N, Li L, Dar NU (2007) A fuzzy expert system for optimizing parameters and predicting performance measures in hard-milling process. Expert Syst Appl 32(4):1020–1027
Toh CK (2006) Cutter path orientations when high-speed finish milling inclined hardened steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 27(5–6):473–480
Koshy P, Dewes RC, Aspinwall DK (2002) High speed end milling of hardened AISI D2 tool steel (similar to 58 HRC). J Mater Process Technol 127(2):266–273
Aslan E (2005) Experimental investigation of cutting tool performance in high speed cutting of hardened X210 Cr12 cold-work tool steel (62 HRC). Mater Des 26(1):21–27
Fallböhmer P, Rodríguez CA, Özel T, Altan T (2000) High-speed machining of cast iron and alloy steels for die and mold manufacturing. J Mater Process Technol 98(1):104–115
Urbanski JP, Koshy P, Dewes RC, Aspinwall DK (2000) High speed machining of moulds and dies for net shape manufacture. Mater Des 21(4):395–402
Ghani JA, Choudhury IA, Masjuki HH (2004) Wear mechanism of TiN coated carbide and uncoated cermets tools at high cutting speed applications. J Mater Process Technol 153–154:1067–1073
Okada M, Hosokawa A, Tanaka R, Ueda T (2011) Cutting performance of PVD-coated carbide and CBN tools in hardmilling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51(2):127–132
Pu Z, Singh A (2013) High speed ball nose end milling of hardened AISI A2 tool steel with PCBN and coated carbide tools. J Manuf Process 15(4):467–473
Camuşcu N, Aslan E (2005) A comparative study on cutting tool performance in end milling of AISI D3 tool steel. J Mater Process Technol 170(1–2):121–126
Siller HR, Vila C, Rodríguez CA, Abellán JV (2009) Study of face milling of hardened AISI D3 steel with a special design of carbide tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40(1–2):12–25
Cui X, Zhao J, Dong Y (2013) The effects of cutting parameters on tool life and wear mechanisms of CBN tool in high-speed face milling of hardened steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 66(5–8):955–964
Cui X, Zhao J, Tian X (2013) Cutting forces, chip formation, and tool wear in high-speed face milling of AISI H13 steel with CBN tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64(9–12):1737–1749
Elbestawi MA, Chen L, Becze CE, El-Wardany TI (1997) High-speed milling of dies and molds in their hardened state. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 46(1):57–62
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, X., Zhao, J. Cutting performance of coated carbide tools in high-speed face milling of AISI H13 hardened steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71, 1811–1824 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5611-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5611-3