Abstract
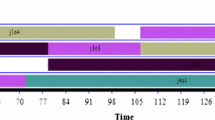
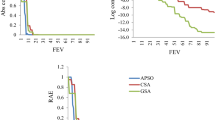
In this paper, a stochastic group shop scheduling problem with a due date-related objective is studied. The group shop scheduling problem provides a general formulation including two other shop scheduling problems, the job shop and the open shop. Both job release dates and processing times are assumed to be random variables with known distributions. Moreover, earliness and tardiness of jobs are penalized at different rates. The objective is to minimize the expected maximum completion cost among all jobs. A lower bound on the objective function is proposed, and then, a hybrid approach following a simulation optimization procedure is developed to deal with the problem. An ant colony optimization algorithm is employed to construct good feasible solutions, while a discrete-event simulation model is used to estimate the performance of each constructed solution that, taking into account its lower bound, may improve the best solution found so far. The proposed approach is then evaluated through computational experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
http://www.win.tue.nl/whizzkids/1997. Accessed 2010
Blum C, Sampels M (2004) An ant colony optimization algorithm for shop scheduling problems. J Math Modell Algorithms 3:285–308
Liu SQ, Ong HL, Ng KM (2005) A fast tabu search algorithm for the group shop scheduling problem. Adv Eng Softw 36:533–539
Ahmadizar F, Ghazanfari M, Fatemi Ghomi SMT (2009) Application of chance-constrained programming for stochastic group shop scheduling problem. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 42:321–334
Ahmadizar F, Ghazanfari M, Fatemi Ghomi SMT (2010) Group shops scheduling with makespan criterion subject to random release dates and processing times. Comput Oper Res 37:152–162
Pinedo M (2008) Scheduling: theory, algorithms, and systems. Springer, New York
Hardy GH, Littlewood JE, Polya G (1952) Inequalities. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rubinstein RY (1986) Monte Carlo optimization, simulation and sensitivity of queuing networks. Wiley, New York
Colorni A, Dorigo M, Maniezzo V (1991) Distributed optimization by ant colonies. Paris, Elsevier Publishing, Proceedings of the first European conference on artificial life, pp 134–142
Dorigo M, Stutzle T (2004) Ant colony optimization. London, Cambridge
Stutzle T, Hoos HH (1997) The max-min ant system and local search for the traveling salesman problem. New York, IEEE Press, Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation, pp 308–313
Giffler B, Thompson GL (1960) Algorithms for solving production scheduling problems. Oper Res 8(4):487–503
Essafi I, Mati Y, Dauzère-Pérès S (2008) A genetic local search algorithm for minimizing total weighted tardiness in the job-shop scheduling problem. Comput Oper Res 35:2599–2616
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadizar, F., Rabanimotlagh, A. Group shop scheduling with uncertain data and a general cost objective. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70, 1313–1322 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5353-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5353-7