Abstract
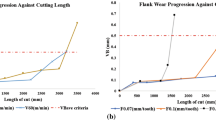
High-speed face milling of AISI H13 hardened steel is conducted in order to investigate the effects of cutting parameters on tool life and wear mechanisms of the cubic boron nitride (CBN) tools. Cutting speeds ranging from 400 to 1,600 m/min are selected. For each cutting speed, the metal removal rate and axial depth of cut are fixed, and different combinations of radial depth of cut and feed per tooth are adopted. The tool life, tool wear progression, and tool wear mechanisms are analyzed for different combinations of cutting parameters. It is found that for most of the selected cutting speeds, the tool life increases with radial depth cut and then decreases. For each cutting speed, the CBN tool life can be enhanced by means of adopting suitable combination of cutting parameters. When the cutting speed increases, the normal wear stage becomes shorter and the tool wear rate grows larger. Because of the variations of cutting force and tool temperature, the tool wear mechanisms change with different combinations of cutting parameters even at the same cutting speed. At relatively low cutting speed, in order to acquire high tool life of the CBN tool, the tool material should possess sufficient capability of resisting adhesion from the workpiece. When relatively high cutting speed is adopted, retention of mechanical properties to high cutting temperature and resistance to mechanical impact are crucial for the enhancement of the CBN tool life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maity SR, Chatterjee P, Chakraborty S (2012) Cutting tool material selection using grey complex proportional assessment method. Mater Des 36:372–378
Trent EM, Wright PK (2000) Metal cutting, 4th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Woburn
El-Wardany TI, Kishawy HA, Elbestawi MA (2000) Surface integrity of die material in high speed hard machining, Part 1: micrographical analysis. J Manuf Sci Eng Trans ASME 122:620–631
Chen W (2000) Cutting forces and surface finish when machining medium hardness steel using CBN tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 40:455–466
Huang Y (2002) Predictive modeling of tool wear rate with application to CBN hard turning. PhD Thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA
Özel T, Hsu TK, Zeren E (2005) Effects of cutting edge geometry, workpiece hardness, feed rate and cutting speed on surface roughness and forces in finish turning of hardened AISI H13 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25:262–269
Benga GC, Abrao AM (2003) Turning of hardened 100Cr6 bearing steel with ceramic and PCBN cutting tools. J Mater Process Technol 143–144(1):237–241
Dawson T (2002) Machining hardened steel with polycrystalline cubic boron nitride cutting tools. PhD Thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA
Huang Y, Liang SY (2003) Cutting forces modeling considering the effect of tool thermal property-application to CBN hard turning. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43(3):307–315
Huang Y, Liang SY (2005) Modeling of cutting forces under hard turning conditions considering tool wear effect. J Manuf Sci Eng Trans ASME 127(2):262–270
Barry J, Byrne G (2001) Cutting tool wear in the machining of hardened steels: part II: cubic boron nitride cutting tool wear. Wear 247:152–160
Huang Y, Liang SY (2004) Modelling of CBN tool crater wear in finish hard turning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 24(9–10):632–639
Arsecularatne JA, Zhang LC, Montross C, Mathew P (2006) On machining of hardened AISI D2 steel with PCBN tools. J Mater Process Technol 171:244–252
Chou YK, Evans CJ, Barash MM (2002) Experimental investigation on CBN turning of hardened AISI 52100 steel. J Mater Process Technol 124:274–283
Poulachon G, Moisan A, Jawahir IS (2001) Tool-wear mechanisms in hard turning with polycrystalline cubic boron nitride tools. Wear 250:576–586
Huang Y, Liang SY (2004) Modeling of CBN tool flank wear progression in finish hard turning. J Manuf Sci Eng Trans ASME 126(1):98–106
Iqbal A, He N, Li L, Dar NU (2007) A fuzzy expert system for optimizing parameters and predicting performance measures in hard-milling process. Expert Syst Appl 32:1020–27
Okada M, Hosokawa A, Tanaka R, Ueda T (2011) Cutting performance of PVD-coated carbide and CBN tools in hardmilling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 51:127–132
Braghini A, Coelho RT (2001) An investigation of the wear mechanisms of polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (PCBN) tools when end milling hardened steels at low/medium cutting speeds. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 17:244–251
Koshy P, Dewes RC, Aspinwall DK (2002) High speed end milling of hardened AISI D2 tool steel ( 58 HRC). J Mater Process Technol 127:266–273
Aslan E (2005) Experimental investigation of cutting tool performance in high speed cutting of hardened X210 Cr12 cold-work tool steel (62 HRC). Mater Des 26:21–27
Salomon CJ (1931) Process for machining metals of similar acting materials when being worked by cutting tools. German patent: Number 523594
Chen R (1992) Principle of metal cutting. China Machine, Beijing
Childs T, Maekawa K, Obikawa T, Yamane Y (2000) Metal machining: Theory and applications. Wiley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, X., Zhao, J. & Dong, Y. The effects of cutting parameters on tool life and wear mechanisms of CBN tool in high-speed face milling of hardened steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 66, 955–964 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4380-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4380-0