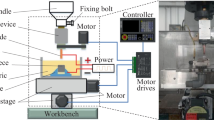
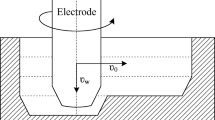
Abstract
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a nonconventional machining process widely applied for the manufacture of intricate shapes in hard materials which are not easily machined by conventional machining processes. The production of geometrically complex EDM electrodes is difficult, time consuming, and it can account for about 50 % of the total process costs. Selective laser sintering (SLS) can be an alternative technique to produce EDM electrodes in a faster way. This work conducted an experimental study on the performance of EDM electrodes made by SLS using pure copper, bronze–nickel alloy, copper/bronze–nickel alloy, and steel alloy powders. Important EDM performance measures such as material removal rate and volumetric relative wear were investigated and discussed for finishing, semifinish, and roughing regimes. This work contributes with an insight into the production of EDM electrodes via selective laser sintering, as an alternative technique to conventional machining processes, as well as to evaluate the performance of the electrodes, and also provide directions for future research on this field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
König W, Klocke F, Lenzen R (1996) The electrical machining processes—what demands will they face in the future? Proc Int J Electr Mach 1:3–7
Ho KH, Newman ST (2003) State of the art electrical discharge machining (EDM). Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43:1287–1300
Amorim FL, Weingaertner WL (2004) Die-sinking electrical discharge machining of a high-strength copper- based alloy for injection molds. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 26(2):137–144
Rosochowski A, Matuszak A (2000) Rapid tooling: the state of the art. J Mater Process Technol 106(1–3):191–198
Das S, Beaman JJ, Wohlert M, Bourell DL (1998) Direct freeform fabrication of high performance metal components. Rapid Prototyp J 4(3):112–117
Dürr H, Pilz R, Eleser NS (1999) Rapid tooling of EDM electrodes by means of selective laser sintering. Comput Ind 39(1):35–45
Williams JD, Deckard CR (1998) Advances in modeling the effects of selected parameters on the SLS process. Rapid Prototyp J 2(4):90–100
König W, Klocke F (1997) Fertigungsverfahren—vol. 3: Abtragen Und Generieren. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Tolochko NK, Laoui T, Khlopkov YV, Mozzharov SE, Titov VI, Ignatiev MB (2000) Absorptance of powder materials suitable for laser sintering. Rapid Prototyp J 6(3):155–160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amorim, F.L., Lohrengel, A., Müller, N. et al. Performance of sinking EDM electrodes made by selective laser sintering technique. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 65, 1423–1428 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4267-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4267-0