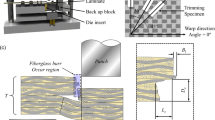
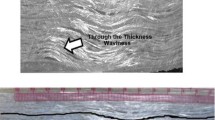
Abstract
The effects of resin infusion process parameters on the mechanical properties of stitched or non-stitched composite laminates out of autoclave were studied using the design of experiment method. This method was chosen due to the complexity of the problem. The preforms used were laminates of multi-axial quasi-isotropic non-crimp fabric (NCF), either stitched or non-stitched. A literature review identified nine parameters as the key design-of-experiment factors: sewing; the number of NCFs; the number of high-porous media; the interaction between the number of NCFs and the number of high-porous media; the mould temperature, injection temperature and cure temperature; the position of the preform; and, finally, the vacuum level. The mechanical properties studied and the morphological analysis carried out concerned the resistance in tension, compression and shear, the glass transition temperature, the thickness of the finished laminate, and the fibre volume fraction and porosity. The study revealed the best suited manufacturing conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takeda F, Nishiyama S, Hayashi K and al., Research in the application of the VaRTM technique to the fabrication of primary aircraft composite structures. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Technical Review Vol. 42 (No. 5), 2005. http://www.mhi.co.jp/technology/review/pdf/e425/e425220.pdf. Accessed 10 May 2012
Beckwith SW (2006) Resin infusion liquid molding vacuum infusion processing numerous other names. An alphabet soup of expanding technologies. SAMPE Journal 42(1):4
Teemer L, Okoli O, Liang Z (2006) The effect of processing parameters on the mechanical properties of components manufactured using the resin infusion between double flexible tooling process. SAMPE ’06 Long Beach 51:9
Mattsson D, Joffe R, Varna J (2007) Methodology for characterization of internal structure parameters governing performance in NCF composites. Compos Part B: Eng 38(1):44–57
Lundström (2000) The permeability of non-crimp stitched fabrics. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manuf 31(12):1345–1353
Timms, Mulchandani, Govignon Q and Bickerton S (2008) Identifying sources of variability in the mechanical performance of resin infused textile composites. The 9th international conference on textile composites (TexComp9), Newark, DE
Dransfield K, Baillie C, Mai YW (1994) Improving the delamination resistance of CFRP by stitching—a review. Compos Sci Technol 50(3):305–317
Govignon Q, Bickerton S, Morris J et al (2008) Full field monitoring of the resin flow and laminate properties during the resin infusion process. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manuf 39:1412–1426
Olivier P, Cottu JP, Ferret B (1995) Effects of cure cycle pressure and voids on some mechanical properties of carbon/epoxy laminates. Composites 26(7):509–515
Ruiz, Achim EV et al (2006) Optimization of injection flow rate to minimize micro/macro-voids formation in resin transfer molded composites. Compos Sci Technol 66(3–4):475–486
Breard J, Saouab A, Bouquet G (2003) Numerical simulation of void formation in LCM. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manuf 34(6):517–523
Lawrence, Neacsu V, Advani S (2009) Modeling the impact of capillary pressure and air entrapment on fibre tow saturation during resin infusion in LCM. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manuf 40(8):1053–1064
Ledru Y, Bernhart G, Piquet R, Schmidt F, Michel L (2010) Coupled visco-mechanical and diffusion void growth modelling during composite curing. Compos Sci Technol 70(15):2139–2145
Berthet F (2008) Calcul et expériences sur le profil du front de résine en infusion. Rev Compos Matér Avancés 18(3):375–391
Sutherland LS, Shenoi RA, Lewis SM (1999) Size and scale effects in composites: II. Unidirectional laminates. Compos Sci Technol 59:221–233
Nakouzi S, Pancrace J, Schmidt F et al (2011) Simulations of an infrared composite curing process. Adv Eng Mater 13(7 and SI):604–608. doi:10.1002/adem.201000344
Yenilmez B, Senan M, Sozer EM (2008) Variation of part thickness and compaction pressure in vacuum infusion process. Compos Sci Technol 69(11-12):28
Donadon MV, Iannucci L, Falzon BG et al (2007) Intralaminar toughness characterisation of unbalanced hybrid plain weave laminates. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manuf 38(6):1597–1611
Klunker F, Aranda S, Ziegmann G et al. (2008) Permeability and compaction models for non crimped fabrics to perform 3D filling simulations of vacuum assisted resin infusion. The 9th International Conference on Flow Processes In Composite Materials, Montréal (Québec), Canada
Chang SH, Hwang JR, Doong JL (2008) Optimization of the injection molding process of short glass fiber reinforced polycarbonate composites using grey relational analysis. J Mater Process Technol 97(1-3):186–193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Njionhou, A., Berthet, F. & Castanié, B. Effects of process parameters on the mechanical properties and morphology of stitched and non-stitched carbon/epoxy liquid resin-infused NCF laminate, out of autoclave and out of oven. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 65, 1289–1302 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4257-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4257-2