Abstract
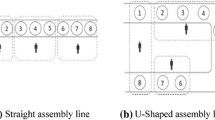
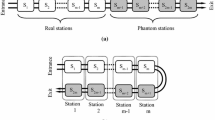
Recently, there is a growing interest in the industry to replace traditional straight assembly lines with U-shaped lines for more flexibility and higher productivity. Due to mathematical and computational complexity, assembly line balancing problems are known to be NP hard in nature. Therefore, many meta-heuristics have been proposed to find optimal solution for these problems. This paper presents a new hybrid evolutionary algorithm to solve stochastic U-type assembly line balancing problems, with the aim of minimizing the number of work stations, idle time at each station, and non-completion probabilities of each station (probability of the station time exceeding cycle time). The proposed algorithm is a combination of computer method for sequencing operations for assembly lines (COMSOAL), task assignment rules heuristic, and newly introduced imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA). Unlike the current evolutionary algorithms that are computer simulation of natural processes, ICA is inspired from socio-political evolution processes. Since appropriate design of the parameters has a significant impact on the algorithm efficiency, various parameters of the ICA are tuned by means of the Taguchi method. For the evaluation of the proposed hybrid algorithm, the performance of the proposed method is examined over benchmarks from the literature and compared with the best algorithm proposed before. Computational results demonstrate the efficiency and robustness of our algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park K, Park S, Kim W (1997) A heuristic for an assembly line balancing problem with incompatibility, range, and partial precedence constraints. Comput Ind Eng 32:321–332
Hautsch K, John H, Schürgers H (1972) Taktabstimmung bei FlieXarbeit mit dem Positionswert-Verfahren. REFANachrichten 25:451–464
Lapierre SD, Ruiz AB (2004) Balancing assembly lines: an industrial case study. J Oper Res Soc 55:589–597
Malakooti B (1991) A multiple criteria decision making approach for the assembly line balancing problem. Int J Prod Res 29:1979–2001
Boysen N, Fliedner M, Scholl A (2007) A classification of assembly line balancing problems. Eur J Oper Res 183:674–693
Urban TL, Chiang WC (2006) An optimal piecewise-linear program for the U-line balancing problem with stochastic task times. Eur J Operation Res 168(3):109–120
Baykasoğlu A, Özbakir L (2007) Stochastic U-line balancing using genetic algorithms. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32(1):139–147
Chiang WC, Urban TL (2006) The stochastic U-line balancing problem: a heuristic procedure. Eur J Oper Res 175(3):1767–1781
Hirano H (1988) JIT factory revolution. Productivity, Cambridge
Monden Y (1983) Toyota production system. Industrial Engineering and Management, Norcross
Sekine K (1992) One-piece flow. Productivity, Portland
Scholl A, Klein R (1999) ULINO: optimally balancing U-shaped JIT assembly lines. Int J Prod Res 37(4):721–736
Baybars I (1986) A survey of exact algorithms for the simple line balancing problem. Manage Sci 32:909–932
Erel E, Sarin SC (1998) A survey of the assembly line balancing procedures. Prod Plann Control 9:414–434
Ghosh S, Gagnon RJ (1989) A comprehensive literature review and analysis of the design, balancing and scheduling of assembly systems. Int J Prod Res 27:637–670
Scholl A, Becker C (2006) State-of-the-art exact and heuristic solution procedures for simple assembly line balancing. Eur J Oper Res 168:666–693
Miltenburg J, Wijngaard J (1994) The U-line line balancing problem. Manage Sci 40(10):1378–1388
Miltenburg GJ, Sparling D (1995) Optimal solution algorithms for the U-line balancing problem. Working Paper, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.
Urban T (1998) Optimal balancing of U-shaped assembly lines. Manage Sci 44(5):738–741
Ajenblit DA, Wainwright RL (1998) Applying genetic algorithms to the U-shaped assembly line balancing problem. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation, Anchorage, Alaska, pp. 96–101
Erel E, Sabuncuoglu I, Aksu BA (2001) Balancing of U-type assembly systems using simulated annealing. Int J Prod Res 39(13):3003–3015
Miltenburg J (1998) Balancing U-lines in a multiple U-line facility. Eur J Oper Res 109:1–23
Sparling D (1998) Balancing JIT production units: the N U-line balancing problem. Inf Syst Oper Res 36:215–237
Kim YK, Kim JY, Kim Y (2000) A coevolutionary algorithm for balancing and sequencing in mixed model assembly lines. Appl Intell 13:247–258
Sparling D, Miltenburg J (1998) The mixed-model U-line balancing problem. Int J Prod Res 36:485–501
Visich JK, Diaz-Saiz J, Khumawala BM (2002) Development of heuristics to reduce model imbalance for the mixed model, U-shaped assembly line. Proc Annu Meet Decis Sci Inst 2002:1786–1791
Kara Y, Özcan U, Peker A (2007) An approach for balancing and sequencing mixed-model JIT U-lines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32:1218–1231
Kara Y, Özcan U, Peker A (2007) Balancing and sequencing mixed-model just-in-time U-lines with multiple objectives. Appl Math Comput 184(2):566–588
Nakade K, Ohno K (1999) An optimal worker allocation problem for a U-shaped production line. Int J Prod Econ 60(1):353–358
Miltenburg J (2000) The effect of breakdowns on U-shaped production lines. Int J Prod Res 38:353–364
Miltenburg J (2001) One-piece flow manufacturing on U-shaped production lines: a tutorial. IIE Trans 33:303–321
Nakade K, Ohno K (2003) Separate and carousel type allocations of workers in a U-shaped production line. Eur J Oper Res 145:403–424
Aase GR, Schniederjans MJ, Olson JR (2003) U-OPT: an analysis of exact U-shaped line balancing procedures. Int J Prod Res 41(17):4185–4210
Aase GR, Olson JR, Schniederjans MJ (2004) U-shaped assembly line layouts and their impact on labor productivity: an experimental study. Eur J Oper Res 156:698–711
Martinez U, Duff WS (2004) Heuristic approaches to solve the U-shaped line balancing problem augmented by genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 2004 Systems and Information Engineering Design Symposium (SIEDS 2004), Charlottesville, Virginia, April 2004, pp. 287–293
Gökçen H, Ağpak K, Gencer C, Kizilkaya E (2005) A shortest route formulation of simple U-type assembly line balancing problem. Appl Math Model 29:373–380
Gökçen H, Ağpak K (2006) A goal programming approach to simple U-line balancing problem. Eur J Oper Res 171:577–585
Baykasoğlu A (2006) Multi-rule multi-objective simulated annealing algorithm for straight and U type assembly line balancing problems. J Intell Manuf 17:217–232
Hwang RK, Katayama H, Gen M (2007) U-shaped assembly line balancing problem with genetic algorithm. Int J Prod Res 46(16):3797–3822
Becker C, Scholl A (2006) A survey on problems and methods in generalized assembly line balancing. Eur J Oper Res 168(3):694–715
Toklu B, Özcan U (2008) A fuzzy goal programming model for the simple U-line balancing problem with multiple objectives. Eng Optim 40(3):191–204
Boysen N, Fliedner M (2008) A versatile algorithm for assembly line balancing. Eur J Oper Res 184:39–56
Toksari MD, Isleyen SK, Guner E, Baykoc OF (2008) Simple and U-type assembly line balancing problems with a learning effect. Appl Math Model 32(12):2954–2961
Özcan U, Toklu B (2008) A new hybrid improvement heuristic approach to simple straight and U-type assembly line balancing problems. J Intell Manuf 20(1):123–136
Sabuncuoglu I, Erel E, Alp A (2009) Ant colony optimization for the single model U-type assembly line balancing problem. Int J Prod Econ 120(2):287–300
Baykasoğlu A, Dereli T (2009) Simple and U-type assembly line balancing by using an ant colony based algorithm. Math Comput Appl 14(1):1–12
Hwang R, Katayama H (2009) A multi-decision genetic approach for workload balancing of mixed-model U-shaped assembly line systems. Int J Prod Res 47(14):3797–3822
Simaria AS, Zanella M, de Sá M, Vilarinho PM (2009) Meeting demand variation using flexible U-shaped assembly lines. Int J Prod Res 47(14):3937–3955
Zhang Z, Cheng Z, Song L, Yu O (2009) A heuristic approach for fuzzy U-shaped Line balancing problem. Sixth International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery 4:228–232
Chand S, Zeng T (2001) A comparison of U-line and straightline performances under stochastic task times. Manuf Serv Oper Manage 3(2):138–150
Ağpak K, Gökçen H, Saray N, Özel S (2002) A heuristic for single model U-line assembly line balancing with stochastic task time. J Fac Eng Arch Gazi Univ 17(4):115–124
Chiang WC, Urban TL (2002) A hybrid heuristic for the stochastic U-line balancing problem. Working Paper, University of Tulsa, Oklahoma
Guerriero F, Miltenburg J (2003) The stochastic U-line balancing problem. Nav Res Logist 50(1):31–57
Erel E, Sabuncuoglu I, Sederci H (2005) Stochastic assembly line balancing using beam search. Int J Prod Res 43:1411–1426
Arcus AL (1966) COMSOAL: a computer method of sequencing operations for assembly lines. Intell J Prod Res 4(4):259–277
Atashpaz-Gargari E, Lucas C (2007) Imperialist competitive algorithm: an algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Singapore
Bautista J, Suarez R, Mateo M, Companys R (2000) Local search heuristics for the assembly line balancing problem with incompatibilities between tasks. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2000), San Francisco, California, April 2000, pp. 2404–2409
Carraway RL (1989) A dynamic programming approach to stochastic assembly line balancing. Manage Sci 35(4):459–470
Cochran WG, Cox GM (1992) Experimental designs, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Taguchi G (1986) Introduction to quality engineering. Asian Productivity Organization/UNIPUB, White Plains
Tsai JT, Ho WH, Liu TK, Chou JH (2007) Improved immune algorithm for global numerical optimization and job-shop scheduling problems. Appl Math Comput 194:406–424
Al-Aomar R (2006) Incorporating robustness into genetic algorithm search of stochastic simulation outputs. Simul Model Pract Theory 14:201–223
Phadke MS (1989) Quality engineering using robust design. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagher, M., Zandieh, M. & Farsijani, H. Balancing of stochastic U-type assembly lines: an imperialist competitive algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 54, 271–285 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2937-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2937-3