Abstract
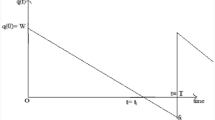
This paper discusses the optimal pricing and replenishment policies of an economic order quantity model for non-instantaneous deteriorating items with partial backlogging over an infinite time horizon. The model is studied under the replenishment policy starting with no shortages. The backlogging rate is any non-increasing function of the waiting time up to the next replenishment. The objective of this model is to maximize the total profit which includes the sales revenue, purchasing cost, set up cost, holding cost, shortage cost, and opportunity cost due to lost sales. Here, the selling price, replenishment quantity, replenishment cycle length, and the time duration of the positive inventory level are taken as decision variables to maximize the profit of the inventory system. The existence and the uniqueness of the solution of the proposed inventory system are examined. We suggest a solution procedure to find the optimal solution of the described model. Numerical examples are presented to determine the developed model and the solution procedure. Sensitivity analysis of the optimal solution with respect to major parameters is carried out and some useful managerial results are obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad PL (1996) Optimal pricing and lot sizing under conditions of perishability and partial backordering. Manage Sci 42(8):1093–1104. doi:10.1287/mnsc.42.8.1093
Chang HJ, Teng JT, Ouyang LY, Dye CY (2006) Retailer’s optimal pricing and lot sizing policies for deteriorating items with partial backlogging. Eur J Oper Res 168(1):51–64. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2004.05.003
Dye CY, Ouyang LY (2005) An EOQ model for perishable items under stock-dependent selling rate and time-dependent partial backlogging. Eur J Oper Res 163(3):776–783. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2003.09.027
Dye CY, Hsieh TP, Ouyang LY (2007) Determining optimal selling price and lot size with a varying rate of deterioration and exponential partial backlogging. Eur J Oper Res 181(2):668–678. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2006.06.029
Goyal SK, Giri BC (2001) Recent trends in modelling of deteriorating inventory. Eur J Oper Res 134(1):1–16. doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(00)00248-4
Hwang HS (1997) A study on an inventory model for items with Weibull ameliorating. Comput Ind Eng 33(3–4):701–704. doi:10.1016/S0360-8352(97)00226-X
Hwang HS (1999) Inventory models for both deteriorating and ameliorating items. Comput Ind Eng 37(1–2):257–260. doi:10.1016/S0360-8352(99)00068-6
Khouja M (2006) A joint optimal pricing, rebate value, and lot-sizing model. Eur J Oper Res 174(2):706–723. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2005.02.041
Kim JS, Hwang H, Shinn SW (1995) An optimal credit policy to increase supplier’s profit with price-dependent demand functions. Prod Plan Control 6(1):45–50. doi:10.1080/09537289508930252
Manna SK, Lee CC, Chiang C (2009) EOQ model for non-instantaneous deteriorating items with time-varying demand and partial backlogging. Int J Ind Syst Eng 4(3):241–254. doi:10.1504/IJISE.2009.023540
Ouyang LY, Teng JT, Chen LH (2006) Optimal ordering policy for deteriorating items with partial backlogging under permissible delay in payments. J Glob Optim 34(2):245–271. doi:10.1007/s10898-005-2604-7
Raafat F (1991) Survey of literature on continuously deteriorating inventory models. J Oper Res Soc 42:27–37. doi:10.1057/jors.1991.4 Review
Sana SS (2008) An EOQ model with a varying demand followed by advertising expenditure and selling price under permissible delay in payments: for a retailer. Int J Model Ident Control 5(2):166–172. doi:10.1504/IJMIC.2008.022022
Sana SS, Sarkar BK, Chaudhuri K, Purohit D (2009) The effect of stock, price and advertising on demand—an EOQ model. Int J Model Ident Control 6(1):81–88. doi:10.1504/IJMIC.2009.023533
San José LA, Sicilia J, García-Laguna J (2006) Analysis of an inventory system with exponential partial backordering. Int J Prod Econ 100(1):76–86. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2004.10.012
Skouri K, Konstantaras I, Papachristos S, Ganas I (2009) Inventory models with ramp type demand rate, partial backlogging and Weibull deterioration rate. Eur J Oper Res 192(1):79–92. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2007.09.003
Wee HM (1993) Economic production lot size model for deteriorating items with partial back-ordering. Comput Ind Eng 24(3):449–458. doi:10.1016/0360-8352(93)900405
Wee HM (1995) Joint pricing and replenishment policy for deteriorating inventory with declining market. Int J Prod Econ 40(2–3):163–171. doi:10.1016/0925-5273(95)00053-3
Wu KS, Ouyang LY, Yang CT (2006) An optimal replenishment policy for non-instantaneous deteriorating items with stock-dependent demand and partial backlogging. Int J Prod Econ 101(2):369–384. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2005.01.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valliathal, M., Uthayakumar, R. Optimal pricing and replenishment policies of an EOQ model for non-instantaneous deteriorating items with shortages. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 54, 361–371 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2913-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2913-y