Abstract
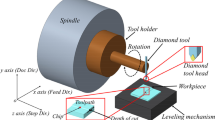
A ball endmill made of single-crystalline diamond was used for cutting micro-structures on two kinds of mold materials, oxygen-free copper, and reaction-bonded silicon carbide (RB-SiC). The cutting performance of the ball endmill was investigated by examining surface roughness and form accuracy of the machined workpiece as well as tool wear characteristics. Micro-dimple arrays, micro-grooves, and micro-pyramid arrays with extremely smooth surface and high-accuracy profile could be obtained on oxygen-free copper without remarkable tool wear. When machining RB-SiC, however, tool flank wear takes place, leading to a rough surface finish. After the tool has worn off, the cutting performance of the endmill significantly depended on the tool feed direction. The optimum tool feed direction for micro-grooving was experimentally investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evans C, Bryan J (1999) “Structured” “textured” or “engineered” surfaces. CIRP Ann 48:541–556
Lim C, Hong M, Lin Y, Chen G, Kumar A, Rahman M, Tan L, Fuh J, Lim G (2007) Sub-micron surface patterning by laser irradiation through microlens arrays. J Mater Process Technol 192–193:328–333
Däschner W, Long P, Stein R, Wu C, Lee S (1996) General aspheric refractive micro-optics fabricated by optical lithography using a high energy beam sensitive glass gray-level mask. J Vac Sci Technol B 14:3730–3733
Totsu K, Fujishiro K, Tanaka S, Esashi M (2006) Fabrication of three-dimensional microstructure using maskless gray-scale lithography. Sensor Actuator A 130–131:387–392
Weule H, Hüntrup V, Tritschler H (2001) Micro-cutting of steel to meet new requirements in miniaturization. CIRP Ann 50:61–64
Kim J, Kang Y (1997) High-spend machining of aluminium using diamond endmills. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 37:1155–1165
Torres C, Heaney P, Sumant A, Hamilton M, Carpick R, Pfefferkorn F (2009) Analyzing the performance of diamond-coated micro end mills. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49:599–612
Pan C, Wu T, Liu Y, Yamagata Y, Huang J (2009) Fabrication of aspheric surface using ultraprecision cutting and BMG molding. J Mater Process Technol 209:5014–5023
Yan J, Zhang Z, Kuriyagawa T (2009) Mechanism for material removal in diamond turning of reaction-bonded silicon carbide. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 49:366–374
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, J., Zhang, Z., Kuriyagawa, T. et al. Fabricating micro-structured surface by using single-crystalline diamond endmill. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51, 957–964 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2695-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2695-2