Abstract
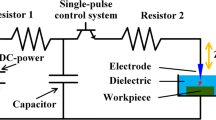
Machining fluid is a primary factor that affects the material removal rate, surface quality, and electrode wear of electrical discharge machining (EDM). Kerosene is the most commonly used working fluid in die sinking EDM, but it shows low ignition temperature and high volatility; if the improper operations are undertaken, it can cause conflagration. Using distilled water or pure water as the machining fluid in EDM, no fire hazard occurs, and the working environment is well; however, using distilled water or pure water as the machining fluid in EDM, the material removal rate of machining large surface is low, and the machine tool is easily eroded. Emulsion-1 and emulsion-2 used as working fluid in die sinking EDM are developed. The compositions of emulsion-1 and emulsion-2 are introduced. In comparison with kerosene, emulsion-1 and emulsion-2 used in EDM show high material removal rate, low surface roughness, high discharge gap, and good working environment. The electrode wear ratio in emulsion-1 is lower than that in kerosene. The electrode wear ratio in emulsion-2 is higher than that in kerosene. The effects of composition and concentration of emulsifier on the emulsion property and EDM performance have been investigated. The comparative tests of EDM performance with kerosene, emulsion-1, and emulsion-2 have been done.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rehbein W, Schulze HP, Mecke K, Wollenberg G, Storr M (2004) Influence of selected groups of additives on breakdown in EDM sinking. J Mater Process Technol 149(1–3):58–64
Khan AA (2008) Electrode wear and material removal rate during EDM of aluminum and mild steel using copper and brass electrodes. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 39(5–6):482–487
Lin C-T, Chow H-M, Yang L-D, Chen Y-F (2007) Feasibility study of micro-slit EDM machining using pure water. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 34(1–2):104–110
Peças P, Henriques E (2008) Effect of the powder concentration and dielectric flow in the surface morphology in electrical discharge machining with powder-mixed dielectric (PMD-EDM). Int J Adv Manuf Tech 37(11–12):1120–1132
Bai CY (2007) Effects of electrical discharge surface modification of superalloy Haynes 230 with aluminum and molybdenum on oxidation behavior. Corros Sci 49(10):3889–3904
Wu KL, Yan BH, Huang FY, Chen SC (2005) Improvement of surface finish on SKD steel using electro-discharge machining with aluminum and surfactant added dielectric. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45(10):1195–1201
Kumar S, Singh TP (2007) A comparative study of the performance of different EDM electrode materials in two dielectric media. J Inst Engrs India 87(3):3–8
Chen SL, Yan BH, Huang FY (1999) Influence of kerosene and distilled water as dielectrics on the electric discharge machining characteristics of Ti–6Al–4V. J Mater Process Technol 87(1–3):107–111
Chung DK, Kim BH, Chen CN (2007) Micro electrical discharge milling using deionized water as a dielectric fluid. J Micromech Microeng 17(5):867–874
Chow HM, Yang LD, Lin CT, Chen YF (2008) The use of SiC powder in water as dielectric for micro-slit EDM machining. J Mater Process Technol 195(1–3):160–170
Chow HM, Yan BH, Huang FY (1999) Micro slit machining using electro-discharge machining with a modified rotary disk electrode (RDE). J Mater Process Technol 91(1–3):161–166
Zhao SM (2005) The principle, composition, determination and application of the surfactant. China Petrochemical Press, Beijing
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Ji, R., Zhang, Y. et al. Investigation of emulsion for die sinking EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47, 403–409 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2209-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2209-2