Abstract
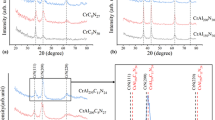
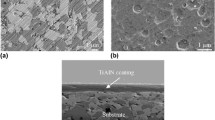
For micro replication, the base of a die should be ductile and the surface layer that will undergo processing should have a good machining response to various tool-making processes. At the same time, the resulting working surfaces of the tooling cavities should be hard; having low roughness, low wettability and high erosion resistance. To achieve such diverse properties, nano-crystalline CrC coatings deposited onto 12% Cr tool steel were investigated in this research. To verify the properties of such coatings various metallographic techniques were applied. In particular, the corrosion resistance was studied by means of potentiodynamic anodic polarisation. A scanning transmission electron microscopy analysis of the structure was performed on samples prepared with focused ion beam (FIB) machining. The mechanical properties and grain size distribution were determined and statistically analysed. In addition, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy were used in studying the surface properties of these coatings. To investigate the response of the CrC coatings to micro- and nano-structuring technologies with high specific energy, a series of rectangular trenches were produced by FIB milling. The effects of the ion beam current, exposure time and ion fluence on the sputtering yield and roughness of the produced micro-structures were especially investigated. Some essential parameter windows for performing FIB milling with relatively high sputtering rates, higher than 1 µm/min, and at the same time achieving the best possible surface integrity were determined during the experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shishkov R et al (2004) Journal of Material Processing and Technology 157 - 158:410–414
Shishkov R, Lisichkova E (1995) A general model for vacuum condensates and vacuum diffusive coatings. Vacuum 46(11):1337–1346. doi:10.1016/0042-207X(95)00026-7
Restrepo E et al (2004) Braz J Phys 34(no.4B):1748–1751. doi:10.1590/S0103-97332004000800043
Lamastra FR et al (2006) Surf Coat Tech 200:6172–6175. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.11.013
Gomez MA et al (2005) Surf Coat Tech 200:1819–1824. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.08.060
Li G et al (2005) Tsinghua Sci Technol 10(6):690–698. doi:10.1016/S1007-0214(05)70137-1
Barshilia HC, et al (2004) v. 72:241-248
Yang O et al (2004) Surf Coat Tech 177–178:204–208. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2003.09.033
Braic M et al (2003) J Optoelectronics Adv Mater 5:1399–1404
Mendibide C et al (2006) Surf Coat Tech 201:4119–4124. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.08.013
Suresha SJ et al (2006) Mater Sci Eng A 429:252–260. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2006.05.068
Gorokhovsky V et al (2006) Surf Coat Tech 201:3732–3747. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.09.007
Kayani A et al (2006) Surf Coat Tech 201:4460–4466. doi:10.1016/jsurfcoat.2006.08.049
Ducros C, et al (2005) 4 M Conference, Karlsruhe. pp. 177-180
Ochiai C et al (2001) High resolution organic resists for charged particle lithography. J Vac Sci Technol B 19:933. doi:10.1116/1.1349205
Loeschner H et al (2002) Large-field ion optics for projection and proximity printing and for maskless lithography (ML2). Proc SPIE 4688:595–606. doi:10.1117/12.472336
Lalev G et al (2008) Data preparation for FIB machining of complex 3D structures. Proc. IMechE. Part B 222(1):67–76
Gomez MA et al (2005) Surf. & Coat. Tech. 200(5-6):1819–1824
Li W. et al (2007) Patterning of amorphous and polycrystalline Ni78B14Si8 with a focused ion beam. Appl Surf Sci, issue 12:5404-5410, 15 April
Popov K et al (2006) Micromilling: material microstructure effects. IMechE Part B 220(11):1807–1813
Platzgummer E et al (2006) Simulation of ion beam direct structuring for 3D nanoimprint template fabrication. Microelectron. Eng. 83:936–939. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2006.01.140
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minev, R., Ilieva, M., Kettle, J. et al. Deposition and focused ion beam milling of anticorrosive CrC coatings on tool steel substrates. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47, 29–35 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2078-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2078-8