Abstract
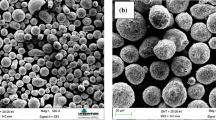
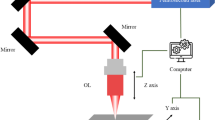
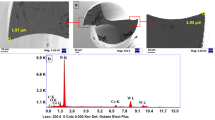
Sustainable manufacturing requires the extended usage of materials and reuse of hard metal tooling. In general, titanium nitride (TiN) coating gives enhanced hardness and wear resistance to the surfaces of engineering tools. However, the high hardness makes it difficult to re-grind or refurbish TiN-coated materials, especially TiN-coated cutting tools. This paper presents the results of laser decoating of TiN from TiN-coated tungsten carbide (WC) substrates. Laser decoating was performed using a KrF excimer laser. The effect of laser fluence, number of pulses, frequency, scanning speed and beam overlap on the decoating performance was investigated in detail. A two-dimensional symmetric finite element model (FEM) was established to elucidate the temperature and stress fields created during the laser decoating process. Successful laser decoating of TiN coating from the WC substrate was demonstrated. It was found that decoating with a laser fluence of 4 J/cm2, scanning speed of 2 mm/s, frequency of 25 Hz and a beam overlap of 91% gives best results for removing an area of TiN coating to its 3 μm thickness. The surface roughness of the best samples was found to be in the order of 0.8–0.9 μm Ra. The experimental and FEM investigation suggested that the decoating of TiN follows combined explosion and evaporation mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiedemann R, Oettel H, Bertram T, Weihnacht V (2001) Mechanical properties of TiN coatings. Adv Eng Mater 3:865–870. doi:10.1002/1527-2648(200111)3:11<865::AID-ADEM865>3.0.CO;2-X
Ghani JA, Choudhury IA, Masjuki HH (2004) Wear mechanism of TiN coated carbide and uncoated cermets tools at high cutting speed applications. J Mater Process Technol 153–154:1067–1073. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.04.352
Perry AJ (1981) The adhesion of chemically vapour-deposited hard coatings to steel—the scratch test. Thin Solid Films 78:77–94. doi:10.1016/0040-6090(81)90419-3
Hu SB, Tu JP, Mei Z, Li ZZ, Zhang XB (2001) Adhesion strength and high temperature wear behaviour of ion plating TiN composite coating with electric brush plating Ni–W interlayer. Surf Coat Tech 141:174–181. doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(01)01041-6
Nevyantseva RR, Gorbatkov SA, Parfenov EV, Bybin AA (2001) The influence of vapor–gaseous envelope behavior on plasma electrolytic coating removal. Surf Coat Tech 148:30–37. doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(01)01334-2
Hellriegel R, Albert M, Hintze B, Winzig H, Bartha JW (2007) Remote plasma etching of titanium nitride using NF3/argon and chlorine mixtures for chamber clean applications. Microelectronic Eng 84:37–41. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2006.08.002
Neves P, Arronte M, Vilar R, Botelho do Rego AM (2002) KrF excimer laser dry and steam cleaning of silicon surfaces with metallic particulate contaminants. Appl Phys A 74:191–199. doi:10.1007/s003390100868
Mateo MP, Nicolas G, Piñon V, Ramil A, Yañez A (2005) Laser cleaning: an alternative method for removing oil-spill fuel residues. Appl Surf Sci 247:333–339. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.01.086
Kim J, Na S (2007) Metal thin film ablation with femtosecond pulsed laser. Opt Laser Technol 39:1443–1448. doi:10.1016/j.optlastec.2006.10.001
Turner MW, Crouse PL, Li L (2006) Comparison of mechanisms and effects of Nd:YAG and CO2 laser cleaning of titanium alloys. Appl Surf Sci 252:4792–4797. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.06.050
Heitz J, Pedarnig JD, Bäuerle D, Petzow G (1997) Excimer-laser ablation and micro-patterning of ceramic Si3N4. Appl Phys A 65:259–261. doi:10.1007/s003390050575
Dyer PE, Farley RJ, Giedl R, Karnakis DM (1996) Excimer laser ablation of polymers and glasses for grating fabrication. Appl Surf Sci 96–98:537–549. doi:10.1016/0169-4332(95)00528-5
Lappalainen J, Frantti J, Moilanen H, Leppävuori S (1995) Excimer laser ablation of PZT thin films on silicon cantilever beams. Sens Actuators A Phys 46:104–109. doi:10.1016/0924-4247(94)00871-E
Paek UC, Kestenbaum A (1973) Thermal analysis of thin-film micromachining with lasers. J Appl Phys 44:2260–2268. doi:10.1063/1.1662547
Zaleckas VJ, Koo JC (1977) Thin-film machining by laser-induced explosion. Appl Phys Lett 31:615–617. doi:10.1063/1.89801
Veiko VP, Metez SM, Kaidanov AI, Libenson MN, Jakovlev EB (1980) Two-phase mechanism of laser-induced removal of thin absorbing films: I Theory. J Phys D Appl Phys 13:1565–1570. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/13/8/026
Kononenko TV, Garnov SV, Pimenov SM, Konov VI, Romano V, Borsos B, Weber HP (2000) Laser ablation and micropatterning of thin TiN coatings. Appl Phys A 71:627–631. doi:10.1007/s003390000572
Stallard J, Poulat S, Teer DG (2006) The study of the adhesion of a TiN coating on steel and titanium alloy substrates using a multi-mode scratch tester. Tribology Int 39:159–166. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2005.04.011
Geiger M, Popp U, Engel U (2002) Excimer laser micro texturing of cold forging tool surfaces—influence on tool life. CIRP Ann—Manuf Technol 51:231–234
Dong Y, Sakata H, Molian P (2005) Femtosecond pulsed laser ablation of diamond-like carbon films on silicon. Appl Surf Sci 252:352–357. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.01.008
Bishop GJ, Dyer PE (1985) Polymer film cutting and ablative etching using a 1-khz xecl laser. Appl Phys Lett 47:1229–1231. doi:10.1063/1.96337
Madenci E, Guven I (2005) The finite element method and applications in engineering using ANSYS. Springer, Berlin
Pierson HO (1996) Handbook of refractory carbides and nitrides. Noyes, New Jersey
Bauerle D (1996) Laser processing and chemistry. Springer, Berlin
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundar, M., Mativenga, P.T., Li, L. et al. Laser removal of TiN from coated carbide substrate. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 45, 1169 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2059-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2059-y