Abstract
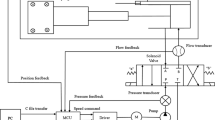
High response and high efficiency velocity control of a hydraulic injection molding machine (HIMM) is requested especially for the process of high-tech industries, such as CD and DVD disks, plastic optical lens, light guide plates, etc. Instead of the hydraulic valve-controlled systems that have the problem of low energy efficiency but have been used widely in today’s HIMMs, the paper develops a high response and high energy efficiency electro-hydraulic pump-controlled system driven by a variable rotational speed AC servo motor for achieving high response and high efficiency velocity control in HIMMs. A constant displacement axial piston pump combined with the AC servo motor is developed in this research as the high response electro-hydraulic pump-controlled system for the HIMMs. For that, the control strategy, signed-distance fuzzy sliding mode control (SD-FSMC) is developed to simplify the fuzzy rule base through the sliding surface for practical applications. The developed high response variable rotational speed electro-hydraulic pump-controlled system controlled by SD-FSMC is implemented and verified experimentally for velocity control with various velocity targets and external loading conditions. Furthermore, the energy efficiencies of different experiments are analyzed and compared precisely by the power quality recorder used to measure the electrical power consumed by the AC servo motor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murrenhoff H (1998) Servohydrualik (in German). Lecture notes, RWTH Aachen University, Germany
Backé W, Feigel H-J (1990) Neue Möglichkeiten beim Electro-hydraulischen load-Sensing (in German), O+P Ölhydraulik und Pneumatik 34, No.2, pp 106–114
Esders H (1994) Elektrohydraulisches Load-Sensing für Mobile Anwendungen, (in German), O+P Ölhydraulik und Pneumatik 36, Nr.8, pp 473–480
Kim S-D, Cho H-S, Lee C-O (1988) Stability analysis of a load-sensing hydraulic system. Proc Inst Mech Eng A Power Process Eng 202(No.A2):79–88 doi:10.1243/PIME_PROC_1988_202_012_02
Chiang M-H, Chien Y-W (2003) Parallel control of velocity control and energy-saving control on a hydraulic valve controlled system using self-organizing fuzzy sliding mode control. JSME Int J Ser C 46(1):224–231 doi:10.1299/jsmec.46.224
Chiang M-H, Lee L-W, Tsai J-J (2004) Concurrent implementation of high velocity control performance and high energy-efficiency for hydraulic injection moulding machines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 23(3–4):256–262 doi:10.1007/s00170-003-1652-8
Chiang M-H, Yang F-L, Chen Y-N, Yeh Y-P (2005) Integrated control of clamping force and energy-saving in hydraulic injection moulding machines using decoupling sliding-mode control. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 27(1–2):53–62 doi:10.1007/s00170-004-2138-z
Renn J-C, Tsai C (2005) Development of an unconventional electro-hydraulic proportional valve with fuzzy-logic controller for hydraulic presses. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 26(1):10–16 doi:10.1007/s00170-003-1973-7
Lovrec D, Kastrevc M, Ulaga S (2008) Electro-hydraulic load sensing with a speed-controlled hydraulic supply system on forming-machines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol doi:10.1007/s00170-008-1553-y
Helduser S (1995) Moderne hydraulische Antriebe und Steuerungen am Beispiel von Kunststoff-Spritgiessmaschinen (in German). O+P Ölhydraulik und Pneumatik 39, No.10
Ruhlicke I (1997) Elektro-hydraulische Antriebssysteme mit drehzahlveränderbarer Doppelpumpe (in German). O+P Ölhydraulik und Pneumatik 41, No.10
Kazmeier B, Feldmann D-G (1998) Ein neues Konzept füreinen kompakten elektrohydraulischen Linearantrieb (in German). Proc. of 1. International Fluid Power Conference (1.IFK), Aachen, Germany, Band 1, pp 345–358.
Bildstein A (1998) Application of electro-hydrostatic actuators (EHA) for future aircraft primary flight control. Proc. of the 1. International Fluid Power Conference (1.IFK), Aachen, Germany, Band 1, pp 93–105
Helduser S (1999) Electric-hydrostatic drive—an innovative energy-saving power and motion control system. Proc Inst Mech Eng 213(Part I):427–439
Habibi S, Goldenberg A (1999) Design of a new high performance electro-hydraulic actuator. Proc. of the 1999 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Mechatroics, Atlanta, USA, pp 227–232
Helbig A (2002) Injection moulding machine with electric-hydrostatic drives. Proc. of the 3. International Fluid Power Conference (3. IFK), Aachen, Germany, Vol.1, pp 67–82
Kim S-W, Lee J-J (1995) Design of a fuzzy controller with fuzzy sliding surface. Fuzzy Sets Syst 71(3):359–367 doi:10.1016/0165-0114(94)00276-D
Choi B-J, Kwak S-W, Kim B-K (1999) Design of a single-input fuzzy logic controller and its properties. Fuzzy Sets Syst 106:299–308 doi:10.1016/S0165-0114(97)00283-2
Tzafestas S-G, Rigatos G-G (1999) A simple robust sliding mode fuzzy-logic controller of the diagonal type. J Intell Robot Syst 26(3–4):353–388 doi:10.1023/A:1008161815798
Wu J-C, Liu T-S (1996) A sliding-mode approach to fuzzy control design. IEEE Trans Contr Syst Technol 4(2):141–151 doi:10.1109/87.486340
Choi B-J, Kwak S-W, Kim B-K (2000) Design and stability analysis of single-input fuzzy logic controller. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern, Part B Cybern 30(2):303–309 doi:10.1109/3477.836378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiang, MH., Chen, CC. & Kuo, CF.J. The high response and high efficiency velocity control of a hydraulic injection molding machine using a variable rotational speed electro-hydraulic pump-controlled system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 43, 841–851 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1759-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1759-z