Abstract
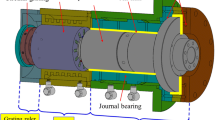
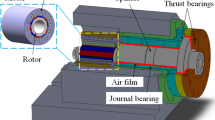
In this paper, the design and fabrication of a rotational electrostatic motor with air bearing is presented. Electrostatic motors have many advantages such as convenient fabrication and compact size. In this study, the rotor is a Plexiglas disc with 38-mm diameter and 1-mm thickness and stator is a round set of electrodes etched by standard printed circuit board technique. Plexiglas was used in laser disc optical media and has been developed for use in CDs and DVDs. To reduce the friction between the rotor and the stator, an air bearing is used. Also, in this paper, kinetics of the motion, design, and fabrication process of a prototype is described and then some parameters influencing motor operation are experimentally investigated; experimental results show successful motor operation. In addition, high rotational velocity and optimum acceleration are achieved throughout the operation of the motor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ubink J (1969) Optimization of the rotor surface resistance of the asynchronous electrostatic motor. Appl Sci Res 22:161–172
Kooy C (1969) Torque on a resistive rotor in a quasi electrostatic rotating field. Appl Sci Res 20:161–172 doi:10.1007/BF00382390
Bollee B (1969) Electrostatic motors. Philips Tech Rev 30:178–194
Jeon JU, Higuchi T (1998) Induction motors with electrostatic suspension. J Electrost 45:157–173 doi:10.1016/S0304-3886(98)00043-6
Moser R, Higuchi T (2002) Electrostatic rotation of glass disc. J Electrost 55:97–108 doi:10.1016/S0304-3886(01)00186-3
Cubric D, Lencova B, Read FH (1997) Comparison of the finite difference, finite element and surface charge methods for electrostatic charges particle optics, electron microscopy and analysis. Inst Phys Conf Ser 153:91–94
Melcher JR, Warren EP, Kotwal RH (1987) Theory for finite-phase traveling-wave boundary-guided transport of tribo-electrified particles. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 25(5):949–955 doi:10.1109/28.41263
Masuda S, Kamimura T (1975) Approximation methods for calculating a non-uniform traveling field. J Electrost 1:351–370 doi:10.1016/0304-3886(75)90030-3
Modabberifar M, Hojjat Y, Dadkhah M (2006) Numerical method for calculating a non-uniform traveling field. In: The 2nd Nordic ESD Conference, September 5–6, 2006, Karlskoga, Sweden
Moser R, Higuchi T (2002) Precise positioning using electrostatic glass motor. Precis Eng 26:162–167
Jeon JU, Jin J, Higuchi T (1996) Rotary actuators with electrostatic suspension. In: Fifth International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings, Kanazawa, Japan, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dadkhah, M., Hojjat, Y., Modabberifar, M. et al. Experimental investigation of parameters influencing electrostatic motor’s performance with air bearing operation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 43, 211–216 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1710-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1710-3