Abstract
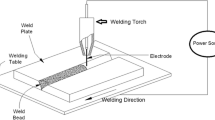
In this work, a pulsed metal inert gas welding (PMIGW) process is modeled by using a hybrid soft computing technique. Ant colony optimization (ACO) and back-propagation neural network (BPNN) models are combined to predict the ultimate tensile strength of butt-welded joints. A large number of experiments have been conducted, and comparative study shows that the hybrid neuro ant colony-optimized model produces faster and also better weld-joint strength prediction than the conventional back propagation model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin M (1983) Pulsed current parameters for stability and controlled metal transfer in arc welding. Met Constr 15(5):272–278
Sweet LM (1985) Sensor-based control systems for arc welding robots. Robot Comput-Integr Manuf 2:125–133
Sforza P, Blasiis DD (2002) On-line monitoring system for arc welding. NDT&E international 35:37–43. doi:10.1016/S0963-8695(01)00021-4
Munezane Y, Watanabe T, Iochi A, Sekino T (1987) A sensing system for arc welding. In: Lane JD (ed) Robotic welding. IFS, London, pp 265–274
Cook GE, Andersen K, Fernandez KR, Shepard ME, Wells AM (1987) Electric arc sensing for robot positioning control. In: Lane JD (ed) Robotic welding. IFS, London, pp 182–216
Hughes RV, Walduck RP (1987) Electromagnetic arc path control I plasma welding. In: Lane JD (ed) Robotic welding. IFS, London, pp 2244–2263
Nagarajan S, Chen WH, Chin BA (1989) Infrared sensing for adaptive arc welding. Weld J 68:462s–466s
Chen WH, Chin BA (1990) Monitoring weld penetration using infrared sensing techniques. Weld J 69:181s–185s
Guu AC, Rokhlin SI (1992) Arc weld process control using radiographic sensing. Mater Eval 50:1344–1348
International institute of welding (1985) Automation and robotisation in welding and allied processes. Pergamon, Oxford
Grad L, Grum J, Polajnar I, Slabe JM (2004) Feasibility study of acoustic signals for on-line monitoring in short circuit gas metal arc welding. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 44:555–561. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2003.10.016
Saini D, Floyd S (1998) An investigation of gas metal arc welding sound signature for on-line quality control. Weld J 77:172s–179s
Carlson NM, Johnson JA (1988) Ultrasonic sensing of weld pool penetration. Weld J 67:239s–246s
Li D, Yonglun S, Feng Y (2000) On line monitoring of weld defects for short-circuit gas metal arc welding based on the self-organize feature map neural networks. Proc int. joint. conf. neural networks 5:239–244
Siewert T, Samardzic I, Klaric S (2002) Application of an on-line weld monitoring system. Proceedings of the 1st int. conf. on advanced technologies for developing countries. Slavonski Brod, Croatia
Cook GE (1981) Feed back and adaptive control in automated arc welding systems. Met Constr 13:551–556
Quinn TP, Smith C, Mccowan CN, Blachowiak E, Madigan RB (1999) Arc sensing for defects in constant voltage gas metal arc welding. Weld J 79:322s–328s
Johnson JA, Carlson NM, Smartt HB, Clark DE (1991) Process control of GMAW: sensing of metal transfer mode. Weld J 70:91s–99s
Rajasekaran S, Kulkarni SD, Mallya UD, Chaturvedi RC (1998) Droplet detachment and plate fusion characteristics in pulsed current gas metal arc welding. Weld J 78:254s–269s
Adolfsson S, Bahrami A, Bolmsjo G, Claesson I (1999) On-line quality monitoring in short-circuit gas metal arc welding. Weld J 78:59s–73s
Wang J, Kusumoto K, Nezu K (2003) Microweld penetration monitoring techniques by arc sensing. Proc int. conf. on advanced intelligent mechatronics, IEEE/ASME1027–1030
Chu YX, Hu SJ, Hou WK, Wang PC, Marin SP (2004) Signature analysis for quality monitoring in short circuit GMAW. Weld J 83:336s–343s
Andersen K, Cook GE, Karsai G, Ramaswamy K (1990) Artificial neural networks applied to arc welding process modeling and control. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 26:824–830. doi:10.1109/28.60056
Cook GE, Barnett RJ, Andersen K, Strauss AM (1995) Welding modeling and controlling using artificial neural networks. Industry applications, IEEE Trans 31:1484–1491
Kang SI, Kim GH, Lee SB (1999) A study on the horizontal fillet welding using neural networks. 3rd Int. conf. on knowledge-based intelligent information. Eng Sys, Australia, pp 217–221
Lee J, Um K (2000) A comparison in a back-bead predication of gas metal arc welding using multiple regression analysis and artificial neural network. Optical and Laser in Eng 34:149–158. doi:10.1016/S0143-8166(00)00097-X
Chi SC, Hsu LC (2001) A fuzzy radial basis function neural network for predicting multiple quality characteristics of plasma arc welding. IFSA/NAFIPS, Vancouver Canada, pp 2807–2812
Di L, Srikanthan T, Chandel RS, Katsunori I (2001) Neural-network based self-organized fuzzy logic control for arc welding. Eng Appl Artif Intell 14:115–124
Nagesh DS, Datta GL (2002) Prediction of weld bead geometry and prenetration in shielded metal-arc welding using artifical neural networks. J Mater Process Technol 123:303–312. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00101-2
Kim IS, Son JS, Lee SH, Yarlagadda PKDV (2004) Optimal design of neural networks for control in robotics arc welding. Robot Comput-Integr Manuf 20:57–63
Lightfoot MP, Bruce GJ, McPherson NA, Woods K (2005) The application of artificial neural networks to weld-induced deformation in ship plate. Weld J 84:23s–30s
Pal S, Pal SK, Samantaray AK (2007) Radial basis function neural network model based prediction of weld-plate distortion due to pulsed metal inert gas welding. Sc Tech Welding and Joining 12:725–731. doi:10.1179/174329307X249351
Kim IS, Jeong YJ, Lee CW, Yarlagadda PKDV (2003) Prediction of welding parameters for pipeline welding using an intelligent system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 22:713–719
Quero JM, Millan RL, Franquelo LG (1994) Neural network approach to weld quality monitoring. Proc. 20th int. conf. on industrial electronics, control and instrumentation. IEEE 2:1287–1291
Ohshima K, Yabe M, Akita K, Kugai K, Kubota T, Yamane S (1995) Sensor fusion using neural network in robotic welding. Industry Applications Conf., IEEE 2:1764–1769
Jang GB, Kim HK, Kang SS (2001) The effects of root opening on mechanical properties, deformation and residual stress of weldments. Weld J 81:80–89
Canyurt OE (2005) Estimation of welded joint strength using genetic algorithm approach. Int J Mech Sc 47:1249–1261. doi:10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2005.04.001
Cool T, Bhadeshia HKDH, Mackay DJC (1997) The yield and ultimate tensile strength of steel welds. J Mater Sc Engg A 223:186–200. doi:10.1016/S0921-5093(96)10513-X
Pal S, Pal SK, Samantaray AK (2008) Artificial neural network modeling of weld joint strength prediction of a pulsed metal inert gas welding process using arc signals. J Mater Pro Tech 202:464–474. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.09.039
Takeshita K (2000) Model equation for predicting the tensile strength of resistance-brazed joints. Weld J 80:261s–265s
Engelbrecht AP (2005) Fundamentals of computational swarm intelligence. Wiley, New York
Su-bing Z, Ze-min L (2001) Neural network training using ant algorithm in ATM traffic control. Proceedings of the IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems, Australia 3:157–160
Blum C, Socha K (2005) Training feed-forward neural networks with ant colony optimization: an application to pattern classification. Fifth IEEE international conference on hybrid intelligent systems 233–238
Liu YP, Wu MG, Qian JX (2007) Predicting coal ash fusion temperature based on its chemical composition using ACO-BP neural network. Thermochimica Acta 454:64–68. doi:10.1016/j.tca.2006.10.026
Haykin S (2003) Neural Networks: a comprehensive foundation. 2nd edn, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Dorigo M, Maniezzo V, Colorni A (1996) The ant system: optimization by a colony of co-operating agents. IEEE Transaction on Systems, Man and Cybernatics- Part B 26(1):29–41
Johnson S (2001) Emergence: the connected lives of ants, brains, cities, and software. Scribner, New York
Applegate DL, Bixby RE, Chvátal V, Cook WJ (2006) The traveling salesman problem: a computational study. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Montgomery DC (1976) Design and analysis of experiments. Wiley, New York
Minitab Inc., User manual of MINITAB™ statistical software, Release 13.31, State College, PA 16801 USA, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raghavendra, N., Koranne, R., Pal, S. et al. Joint strength prediction in a pulsed MIG welding process using hybrid neuro ant colony-optimized model. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 41, 694–705 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1517-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1517-2