Abstract
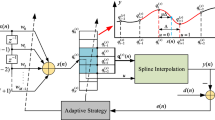
To meet the requirement of exploring a new generation of CNC systems based on STEP-NC, NURBS interpolation has been studied. In contrast to existing NURBS interpolation based on the Taylor’s expansion, this paper proposes a new method for NURBS interpolation which is based on exponential smoothing forecasting. The new method is very simple; it decreases the computational load observably, and speed and precision control are also achieved. This paper presents relative formulas and main computational processes, including speed and precision control, computation of real-time mapping, computation of real-time track, etc. The simulation results indicate that the method is feasible and has high-precision and better real-time performance, which is sufficient for the STEP-NC system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suh SH, Cho JH, Hong HD (2002) On the architecture of intelligent STEP compliant CNC. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 15(2):168–177
Tsai MC, Cheng CW (2003) A real-time predictor-corrector interpolator for CNC machining. J Manuf Sci Eng 125:449–460
Zhang QG, Greenway RB (1998) Development and implementation of a NURBS curve motion interpolator. Robot Comput-Integr Manuf 14:27–36
Yeh SS, Hsu PL (1999) The speed-controlled interpolator for machining parametric curves. Comput Aided Des 31:349–357
Huang JT, Yang DCH (1992) Precision command generation for computer controlled machines. ASME Precision Machining: Technology and Machine Development and Improvement, PED-58, pp. 89–104
Xu HY, Tam HY, Zhou Z, Tse PW (2001) Variable feedrate CNC interpolation for planar implicit curves. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 18:794–800
Xu ZM, Jincheng C, Zhengjin F (2002) Performance evaluation of real-time interpolation algorithm for NURBS curves. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 20:270–276
Yeh SS, Hsu PL (2002) Adaptive-feedrate interpolation for parametric curves with a confined chord error. Comput Aided Des 34:229–237
Park J, Nam S, Yang M (2005) Development of a real-time trajectory generator for NURBS interpolation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 26:359–365
Koren Y, Lo CC (1992) Advanced controllers for feed drives. Ann CIRP 41(2):689–699
Golden EH (1990) Next generation controller. Modern Machine Shop 63(7):148–152
Lo CC (2002) A tool-path control scheme for five-axis machine tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42:79–88
Chen YD, Ni J (1993)Real-time CNC tool path generation for machining IGES surfaces. J Eng Ind 115(11):480–486
Lo CC, Hsiao CY (1998) CNC machine tool interpolator with path compensation for repeated contour machining. Comput Aided Des 30(1):55–62
Sun MX (1998) Theory of modern forecasting (in Chinese). Press of Zhejiang Education Publishing House, Hangzhou, PR China
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kai, Z., Guanjun, W., Houzhong, J. et al. NURBS interpolation based on exponential smoothing forecasting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39, 1190–1196 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1297-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1297-0