Abstract
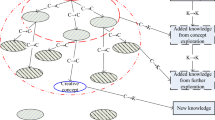
In a knowledge-intensive engineering product design process, case retrieval based on partial problem descriptions (PPDs) becomes more important than the general case retrieval in normal conditions for product design and acts as a crucial role in decision-making. Within the consultation mechanism, similarity knowledge can be acquired expediently and effectively in the product case base described with partial and incomplete information and knowledge. At one time, PPDs can interact with domain knowledge in an appropriate manner to serve the acquisition of similarity knowledge based on consultation (SKC) and case retrieval based on PPDs effectively. So, the consultation approach to case knowledge retrieval is provided to support engineering product design in this paper and the consultation hierarchy is analyzed and discussed from the viewpoint of knowledge transfer. The similarity transformation matrix for similarity measures is presented to handle the relationship between the partial unknown features and the related features, and the determination of weights found on the semantic knowledge of the design domain. As the complementarities of the domain knowledge, explanation knowledge is utilized to explain design requirements for case knowledge reuse and to assist the acquisition of similarity knowledge. Finally, the PPD of an oil pump design is employed to demonstrate the above viewpoints.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goel AK, Craw S (2005) Design, innovation and case-based reasoning. Knowl Eng Rev 20(3):271–276
Gilboa I, Schmeidler D (2000) Case-based knowledge and induction. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part A—Syst Hum 30(2):85–95
Yap WP, Fok SC (2002) A case-based design system for the conceptual design of electrical connectors. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 20(11):787–798
Bogaerts S, Leake DB (2004) Facilitating CBR for incompletely-described cases: distance metrics for partial problem descriptions. In: Funk P, González-Calero PA (eds) Advances in case-based reasoning. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 62–76
Richter MM (1998) Introduction. In: Lenz M, Bartsch-Spörl B, Burkhard H-D, Wess S (eds) Case-based reasoning technology: from foundations to applications. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 1–16
Lee KS, Luo C (2002) Application of case-based reasoning in die-casting die design. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 20(4):284–295
Chang GA, Su CC, Priest JW (2005) Retrieving assembly part design using case-based reasoning and genetic algorithms. Am Soc Mech Eng Manuf Eng Div (MED) 16(1):547–554
Gomes P, Pereira FC, Paiva P, Seco N, Carreiro P, Ferreira JL, Bento C (2005) Rebuilder: a case-based reasoning approach to knowledge management in software design. Eng Intell Syst 13(4):269–276
Stahl A, Gabel T (2003) Using evolution programs to learn local similarity measures. In: Ashley KD, Bridge DG (eds) Case-based reasoning research and development. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 537–551
Leake DB, Smyth B, Wilson DC, Yang Q (2001) Introduction to the special issue on maintaining case-based reasoning systems. Comput Intell 17(2):193–195
Sanin C, Szczerbicki E (2006) Extending set of experience knowledge structure into a transportable language extensible markup language. Cybern Syst 37(2–3):97–117
Jovanović J, Gašević D (2005) Achieving knowledge interoperability: an XML/XSLT approach. Expert Sys Appl 29(3):535–553
McSherry D (2003) Similarity and compromise. In: Ashley KD, Bridge DG (eds) Case-based reasoning research and development. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 291–305
Roth-Berghofer TR (2004) Explanations and case-based reasoning: foundational issues. In: Funk P, González-Calero PA (eds) Advances in case-based reasoning. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 389–403
Jones MC (2005) Tacit knowledge sharing during ERP implementation: a multi-site case study. Inf Resour Manage J 18(2):1–23
Barb AS, Shyu C-R, Sethi YP (2005) Knowledge representation and sharing using visual semantic modeling for diagnostic medical image databases. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 9(4):538–553
Núñez H, Sànchez-Marrè M, Cortés U (2003) Improving similarity assessment with entropy-based local weighting. In: Ashley KD, Bridge DG (eds) Case-based reasoning research and development. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 377–391
Tsang ECC, Lee JWT, Yeung DS (2002) Tuning certainty factor and local weight of fuzzy production rules by using fuzzy neural network. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 32(1):91–98
Kontkanen P, Lathinen J, Myllymäki P, Tirri H (2000) An unsupervised Bayesian distance measure. In: Blanzieri E, Portinale L (eds) Advances in case-based reasoning. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 148–160
Schank RC (1986) Explanation patterns: understanding mechanically and creatively. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, New Jersey
Spieker P (1991) Natürlichsprachiche Erklärungen in technischen Expertensystemen. PhD dissertation, University of Kaiserslautern, Kaiserslautern, Germany
Coyle L, Doyle D, Cunningham P (2004) Representing similarity for CBR in XML. In: Funk P, González-Calero PA (eds) Advances in case-based reasoning. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp 389–403
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, J., Jiang, Z.H., Zhao, Y.S. et al. The acquisition and application of similarity knowledge based on consultation in engineering product design. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37, 1–14 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-0938-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-0938-7