Abstract
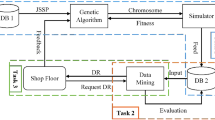
For most shop floors, consideration of more than one criterion would be likely to provide more realistic scheduling of a given set of jobs. The present paper considers this aspect of scheduling and uses an algorithm proposed by the authors in their previous work for implementing several criteria simultaneously in a shop of dynamic nature. The algorithm considers several dispatching rules simultaneously for selecting a job for processing and continuously monitors the attained values of performance measures. The selection of dispatching rules is made by identifying the worst performing criterion. A rule that can improve system performance for the worst-performing criterion is selected to dispatch the part under consideration. In this paper, several case studies have been attempted to evaluate the efficiency of the algorithm. The results of the taken case studies indicate that in a dynamic system the system performance improves by changing the dispatching rules corresponding to the worst-performance criterion at the appropriate deterioration in the performance measures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith WE (1956) Various optimizers for single-stage production. Nav Res Logist Q 3(1):59–66
Heck H, Roberts S (1972) A note on the extension of a result on scheduling with secondary criteria. Nav Res Logist Q 19:403–405
Sen T, Gupta SK (1983) A branch and bound to solve a bi-criteria scheduling problem. IIE Trans 15:84–88
Miyazaki S (1981) One-machine scheduling problem with dual criteria. J Oper Res Soc Jpn 24(1):37–50
Shanthikumar JG (1983) Scheduling n jobs on one machine to minimize the maximum tardiness with minimum number tardy jobs. Comput Oper Res 10(3):255–266
Su LH, Chou FD (2001) Heuristic for scheduling in a bi-criteria single-machine problem. J Chin Inst Ind Eng 18(5):39–46
Koksalan M, Keha AB (2003) Using genetic algorithms for single-machine bicriteria scheduling problems. Eur J Oper Res 145(3):543–556
Kao EPC (1980) A multiple objective decisions theoretic approach to one-machine scheduling problems. Comp Oper Res 7(4):251–259
Ignizio JP (1984) A generalized goal programming approach to the minimal interface, multicriteria, N×1 scheduling problem. IIE Trans 16(4):316–322
Daniel RM (1990) A multi-objective approach to resource allocation in scheduling. Eur J Oper Res 48(2):226–241
Norbis MI, Smith JM (1988) A multi-objective multi-level heuristics for dynamic resource constrained scheduling problems. Eur J Oper Res 33(1):30–41
Rajendran C (1992) Two-stage flow shop scheduling problems with bi-criteria. J Oper Res Soc 43(9):871–884
Lio C-J, Yu W-C, Joe C-B (1997) Bi-criterion scheduling in the two-machine flowshop. J Oper Res Soc 48(9):929–935
Gupta JND, Ho Jc, Webster S (2000) Bi-criteria optimization of the make span and mean flow time on two identical parallel machines. J Oper Res Soc 51(11):1330–1339
Ho JC, Wong JS (1979) Makespan minimization for parallel identical processors. Nav Res Logist 42:935–948
Teghem J, Tuyttens D, Ulungu EL (2000) An interactive heuristic method for multi-objective combinatorial optimization. Comput Oper Res 27:621–634
Loukil T, Teghem J, Tuyttens D (2005) Solving multi-objective production scheduling problems using metaheuristics. Eur J Oper Res 161(1):42–61
Allahverdi A, Aldowaisan T (2002) No-wait flow shop with bi-criteria of make span and total completion time. J Oper Res Soc 53(9):1004–1015
Hoogeveen H (2005) Multicriteria scheduling. Eur J Oper Res 161(3):592–623
Liu J, MacCarthy BL (1996) The classification of FMS scheduling problems. Int J Prod Res 34(3):647–656
Muhlemann AP, Lockett AG, Farn CK (1982) Job-shop scheduling heuristics and frequency of scheduling. Int J Prod Res 20(2):227–241
Holthaus O (1999) Scheduling in job-shop with machine breakdowns: an experimental study. Comput Ind Eng 36(1):137–162
Blackstone JH, Phillips DT, Hogg GL (1982) A state-of-the-art survey of dispatching rules for manufacturing job-shop operations. Int J Prod Res 20(1):27–45
Singh A, Mehta NK, Jain PK (2004) A multi-criterion scheduling approach in a dynamic manufacturing environment. 15th International DAAAM Symposium -DAAAM 2004. Intelligent manufacturing & automation: globalizations- technology-men-nature. 3-6th November 2004, Vienna, Austria, pp 419–420
Law AM, Kelton WD (2000) Simulation modeling and analysis, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Singh A, Mehta NK, Jain PK (2004) Performance analysis of flow-time-based dispatching rules with unreliable machines. Int J Sim Model 3(4):109–120
Jayamohan MS, Rajendran C (2000) New dispatching rules for shop scheduling: a step forward. Int J Prod Res 38(3):563–586
Holthaus O, Rajendran C (1997) Efficient dispatching rules for scheduling in a job shop. Int J Prod Econ 48(1):87–105
Singh A, Mehta NK, Jain PK (2005) Tardiness-based new dispatching rules for shop scheduling with unreliable machines. Int J Sim Modell 4(1):5–16
Conway RW, Maxwell WL, Miller LW (1967) Theory of scheduling. Addition-Wesley Publishing Company
Kanet JJ, Hayya JG (1981) Priority dispatching with operation due dates in a job shop. J Oper Manage 2(3):167–176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A., Mehta, N.K. & Jain, P.K. Multicriteria dynamic scheduling by swapping of dispatching rules. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34, 988–1007 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0674-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0674-4