Abstract
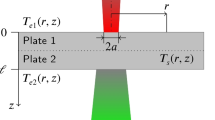
This paper introduces a novel method for the quality evaluation of resistance spot welds. The evaluation is based on computer vision methods, which allow non-destructive on-line real-time processing. The input of the system is the image of a weld imprint on a metal band which covers the electrodes against wear and soiling. The shape and size of the structures within the imprint correlate with the nugget area and, therefore, allow an accurate estimation of the quality of the spot weld. The system segments the electrode imprint and computes the nugget area from the minimum and maximum axis of a fitted ellipse. This method does not need training samples to perform reliable quality estimation. Additionally, the used algorithms are easy to implement and efficient, which guarantees real-time ability. Since there is only a single low-cost camera needed, the hardware can be placed directly on the gun arm, which makes a fast evaluation possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fitzgibbon A, Pilu M, Fisher R (1999) Direct least square fitting of ellipses. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 21(5):476–480
Sonka M, Hlavac V, Boyle R (1998) Image processing: analysis and machine vision, 2nd edn. International Thomson Publishing, London
Tsai CL, Jammal OA Papritan JC, Dickinson DW (1992) Modeling of resistance spot weld nugget growth. Weld J 71(2):47–54
Taylor JL, Xie P (1987) A new approach to the displacement monitor in resistance spot welding of mild steel sheet. Metal Constr 19(2):72–75
Howe P (1994) Spot weld spacing effect on weld button size. In: Proceedings of the AWS Sheet Metal Welding Conference VI, Detroit, Michigan, October 1994, paper C3
Dickinson DW, Franklin JE, Stanya A (1980) Characterization of spot welding behavior by dynamic electrical parameter monitoring. Weld J 59(6):170–176
Bhattacharya S, Andrews DR, Green LW (1975) In-process quality control of spot weld. Metal Constr, pp 227–229
Lee H-T, Wang M, Maev R, Maev E (2003) A study on using scanning acoustic microscopy and neural network techniques to evaluate the quality of resistance spot welding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 22(9–10):727–732
Cho YO, Rhee SE (2004) Quality estimation of resistance spot welding by using pattern recognition with neural networks. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 53(2):330–334
Cho YO, Rhee SE (2002) Primary circuit dynamic resistance monitoring and its application to the quality estimation during resistance spot welding. Weld J 81(6):104–111
Lin ZH, Zhang YA, Chen GU, Li YO (2004) Study on real-time measurement of nugget diameter for resistance spot welding using a neuro-fuzzy algorithm. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (IMTC 2004), Como, Italy, May 2004, pp 2230–2233
Lee SA, Choo YO (2001) A quality assurance technique for resistance spot welding using a neuro-fuzzy algorithm. J Manuf Syst 20(5):320–328
Dilthey UL, Dickersbach JO (1999) Application of neural networks for quality evaluation for resistance spot welds. ISIJ Int 39(10):1061–1066
Aravinthan A, Sivayoganathan K, Al-Dabass D, Balendran V (2001) A neural network system for spot weld strength prediction. In: Proceedings of the United Kingdom Simulation Society Conference (UKSim 2001), Cambridge, England, March 2001, pp 156–160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was carried out by the K-plus Competence Centre, Advanced Computer Vision GmbH, and was funded by the K-plus program.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruisz, J., Biber, J. & Loipetsberger, M. Quality evaluation in resistance spot welding by analysing the weld fingerprint on metal bands by computer vision. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 33, 952–960 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0522-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0522-6