Abstract
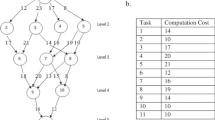
A successful implementation of a mixed-model U-line requires solutions for balancing and sequencing problems. This study proposes an approach for simultaneously solving the balancing and sequencing problems of mixed-model U-lines. The primary goal of the proposed approach is to minimize the number of workstations required on the line (Type I). To meet this aim, the proposed approach uses such a methodology that enables the minimization of the absolute deviation of workloads among workstations as well. In terms of minimizing the number of workstations required on the mixed-model U-line, as well as minimizing the absolute deviation of workloads among workstations, the proposed approach is the first method in the literature dealing with the balancing and sequencing problems of mixed-model U-lines. The newly developed neighborhood generation method employed in the simulated annealing (SA) method is another significant feature of the proposed approach. An illustrative example to clarify the solution methodology is presented. Some problem factors and algorithm parameters that may affect the performance of the approach are also tested by a comprehensive experimental study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts E, Korst J (1989) Simulated annealing and Boltzman machines. Wiley, New York
Aase GR, Schniederjans MJ, Olson JR (2003) U-OPT: an analysis of exact U-shaped line balancing procedures. Int J Prod Res 41(17):4185–4210
Bard JF, Dar-El E, Shtub A (1992) An analytic framework for sequencing mixed model assembly lines. Int J Prod Res 30(1):35–48
Baybars I (1986) A survey of exact algorithms for the simple line balancing problem. Manage Sci 32:909–932
Bukchin J, Dar-El EM, Rubinovitz J (2002) Mixed model assembly line design in a make-to-order environment. Comput Ind Eng 41(4):405–421
Dar-El EM, Cother RF (1975) Assembly line sequencing for model mix. Int J Prod Res 13(5):463–477
Duplaga EA, Bragg DJ (1998) Mixed-model assembly line sequencing heuristics for smoothing component parts usage: a comparative analysis. Int J Prod Res 36(8):2209–2224
Erel E, Sabuncuoglu I, Aksu BA (2001) Balancing of U-type assembly systems using simulated annealing. Int J Prod Res 39(13):3003–3015
Erel E, Sarin SC (1998) A survey of the assembly line balancing procedures. Prod Plan Control 9(5):414–434
Ghosh S, Gagnon RJ (1989) A comprehensive literature review and analysis of the design, balancing and scheduling of assembly systems. Int J Prod Res 27(4):637–670
Gokcen H, Erel E (1997) A goal programming approach to mixed-model assembly line balancing problem. Int J Prod Econ 48(2):177–185
Hall R (1983) Zero inventories. American Production and Inventory Control Society/Dow Jones-Irwin, Homewood, Illinois
Jin M, Wu SD (2002) A new heuristic method for mixed model assembly line balancing problem. Comput Ind Eng 44(1):159–169
Karabati S, Sayin S (2003) Assembly line balancing in a mixed-model sequencing environment with synchronous transfers. Eur J Oper Res 149(2):417–429
Kim YK, Kim JY, Kim Y (2000) A coevolutionary algorithm for balancing and sequencing in mixed model assembly lines. Appl Intell 13(3):247–258
Kim YK, Kim SJ, Kim JY (2000) Balancing and sequencing mixed-model U-lines with a co-evolutionary algorithm. Prod Plan Control 11(8):754–764
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt CD, Veechi MP (1983) Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 220(4598):671–680
Macaskill JLC (1972) Production-line balances for mixed-model lines. Manage Sci 19(4):423–434
Merengo C, Nava F, Pozzetti A (1999) Balancing and sequencing manual mixed-model assembly lines. Int J Prod Res 37(12):2835–2860
Miltenburg J (2002) Balancing and scheduling mixed-model U-shaped production lines. Int J Flex Manuf Syst 14(2):119–151
Miltenburg J (2001) U-shaped production lines: a review of theory and practice. Int J Prod Econ 70:201–214
Miltenburg J (1998) Balancing U-lines in a multiple U-line facility. Eur J Oper Res 109(1):1–23
Miltenburg J, Sparling D (1995) Optimal solution algorithms for the U-line balancing problem. Working paper, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Miltenburg J, Sinnamon G (1995) Revisiting the mixed-model multi-level just-in-time scheduling problem. Int J Prod Res 33(7):2049–2052
Miltenburg J, Wijngaard J (1994) The U-line balancing problem. Manage Sci 40(10):1378–1388
Miltenburg J (1989) Level schedules for mixed-model assembly lines in just-in-time production systems. Manage Sci 35(2):192–207
Miltenburg J, Sinnamon G (1989) Scheduling mixed model multi-level just-in-time production systems. Int J Prod Res 27(9):1487–1509
Miltenburg J, Sinnamon G (1992) Algorithms for scheduling multi-level just-in-time production systems. IIE Trans 24(2):121–130
Monden Y (1993) Toyota production system, 2nd edn. Engineering and Management Press, Norcross, Georgia
McMullen PR, Frazier GV (2000) A simulated annealing approach to mixed-model sequencing with multiple objectives on a just-in-time line. IIE Trans 32(8):679–686
McMullen PR, Frazier GV (1998) Using simulated annealing to solve a multiobjective assembly line balancing problem with parallel workstations. Int J Prod Res 36(10):2717–2741
Salveson ME (1955) The assembly line balancing problem. J Ind Eng 6:18–25
Scholl A, Klein R (1999) ULINO: optimally balancing U-shaped JIT assembly lines. Int J Prod Res 37(4):721–736
Sparling D, Miltenburg J (1998) The mixed-model U-line balancing problem. Int J of Prod Res 36(2):485–501
Sridhar J, Rajendran C (1993) Scheduling in a cellular manufacturing system: a simulated annealing approach. Int J Prod Res 31:2927–2945
Talbot FB, Patterson H (1984) An integer programming algorithm with network cuts for solving the single model assembly line balancing problem. Manage Sci 30:85–99
Thomopoulos NT (1970) Mixed model line balancing with smoothed station assignments. Manage Sci 16(9):593–603
Thomopoulos NT (1967) Line balancing-sequencing for mixed-model assembly. Manage Sci 14(2):59–75
Urban TL (1998) Optimal balancing of U-shaped assembly lines. Manage Sci 44(5):738–741
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kara, Y., Ozcan, U. & Peker, A. An approach for balancing and sequencing mixed-model JIT U-lines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32, 1218–1231 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0437-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-006-0437-2