Abstract
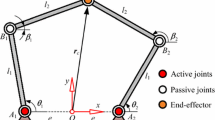
One of the key problems in high speed motion control of a flexible parallel mechanism (PM) is to damp out the mechanical vibration arising from high inertial force acting on the linkages and other components. In this paper, the dynamic equations of a 2 degree-of-freedom (DOF) planar PM with flexible links are established by taking the singular perturbation approach (SPA). Thus the model of the mechanism can be separated into slow time-scale and fast time-scale subsystems. Based on the feedback linearization theory and input shaping technique, the large range rigid motion controller and the flexible link vibration controller can be designed separately. A composite control with the two separate controllers can then be applied in the PM to achieve the desired fast and accurate positioning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellezza F, Lanari L, Ulivi G (1990) Exact modeling of the flexible slewing link. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Cincinnati, OH, pp 734–739
Luca AD, Giovanni GD (2001) Rest-to-rest motion of a two-link robot with a flexible forearm. In: IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics Proceedings. Como, Italy, pp 929–935
Book WJ (1990) Modeling, design and control of flexible manipulator arm: a tutorial review. In: 29th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Honolulu, HI, 1990, pp 500–506
Guo MH, Zhang RJ, Sun ZQ (1998) Modeling and control of a flexible manipulator-A survey. Control Decis 13(1):16 (in Chinese)
Merlet JP (2000) Parallel robots. Kluwer, The Netherlands
Geng Z, Haynes LS (1992) On the dynamics model and kinematics analysis of a class of Stewart platforms. Robot Auton Syst 9:237–254
Tsai KY, Kohli D (1990) Modified Newton Euler computational scheme for dynamic analysis and simulation of parallel manipulators with applications to configuration based on R-l actuators. In: Proceedings of ASME Design Engineering Technical Conference. Boston, MA, USA (24):111–117
Bindzi I, Richard MJ, Gosselin CM (1992) Dynamic analysis of robotic manipulators with closed kinematic chains. In: IEEE Region 10 Conference Tencon 92, Tencon, Melbourne, Australia, pp 639–643
Ma O, Angeles J (1989)Direct kinematics and dynamics of a three-dof planar manipulator. ASME Design and Automation Conference, Montréal (3):313–320
Kock S, Schumacher W (2000) A mixed elastic and rigid-body dynamic model of an actuation redundant parallel robot with high-reduction gears. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, pp 1918–1923
Kang B, Mills JK (2003) Study on piezoelectric actuators in vibration control of a planar parallel manipulator. In: IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Port Island, Kobe, Japan, pp 1268–1273
Kock S, Schumacher W (1998) A parallel X-Y manipulator with actuation redundancy for high-speed and active-stiffness applications. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation, Leuven, Belgium (3):2295–2300
Tse FS, Morse EE, Hinkle RT (1978) Mechanical vibrations: theory and applications, 2nd ed. Allyn and Bacon, Boston, MA
Siciliano B, Prasad JVR, Calise AJ (1992) Output feedback two-time scale control of multilink flexible arms. Trans ASME J Dyn Syst Meas Control 114(1):70–77
Siciliano B, Book WJ (1988) A singular perturbation approach to control of lightweight flexible manipulators. Int J Robot Res 17(4):79–90
Singer NC, Seering WP (1990) Preshaping command inputs to reduce system vibration. J Dyn Syst Meas Control 112(1):76–81
Singh T, Heppler GR (1993) Shaped input control of a system with multiple modes. J Dyn Syst Meas Control 115(3):341–347
Singhose WE, Seering WP, Singer NC (1994) Residual vibration reduction using vector diagrams to generate shaped inputs. J Dyn Syst Meas Control 116(2):654–659
Bing Z, Honghua Z (2001) A closed loop implementation of square wave form control for the space flexible manipulator. Control Theory Appl 18(5):765768 (in Chinese)
Zhang TM (1996) Vibration control theory and experimental research on flexible manipulator. Dissertation, Tian Jin University (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, L., Wang, S., Mo, J. et al. On the modeling and composite control of flexible parallel mechanism. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 29, 786–793 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-005-2554-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-005-2554-8