Abstract
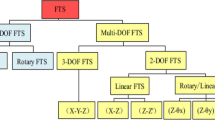
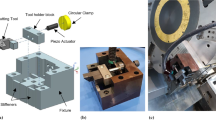
Piezoelectric actuators have wide applications because of their indefinite resolution and high stiffness, for use in optical devices, measurement systems and ultra-precision machine tools. In noncircular turning, the tools feeding servo should be long-travel, high-frequency and high-precision. In order to meet these requirements, a new flexure-hinge structure is used to amplify the output displacement of piezoelectric actuators. A hybrid of feed-forward control in the disturbance channel, repetitive control and Proportion and Integration control (PI) are also employed to better the tracking precision and robustness of the system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldfarb M, Celnovic N (1997) Modeling piezoelectric stack actuators for control of micromanipulation. IEEE Cont Syst 17(3):69–79
Dow TA, Miller MH, Falter PJ (1991) Application of a fast tool servo for diamond turning of non-rotationally symmetric surface. Precis Eng 13(4):243–250
Zhong Z, Nakagawa T (1992) Development of a micro-displacement table for ultra-precision machining and grinding for curved surfaces by use of it. J Japan Soc Precis Eng 26(2):102–107
Jung SB, Kim SW (1994) Improvement of scanning accuracy of PZT piezoelectric actuators by feed-forward model-reference control. Precis Eng 16(1):49–55
Huixing Z, Linna Z, Xiankui W, Jinling L (1994) Repetitive control and application to linear servo unit for CNC machining of elliptical pistons. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology 12:630–633
Alter DM, Tsao TC (1993) Implementation of a direct drive linear motor actuator for dynamic control of the turning process. In: Proceedings of the 1993 American Control Conference Part 6:1971–1975
Toshiro H, Yamaguchi T (1996) Development of a high speed non-circular machining NC lathe for cutting a piston head of a reciprocating engine by use of a new servomechanism actuated by electromagnetic attractive force. J Japan Soc Precis Eng 62(3):453–457
Tsao TC, Masayoshi T (1994) Robust adaptive and repetitive digital tracking control and application to a hydraulic servo for noncircular machining. J Dyn Systems Measure Cont Trans ASME 116(3):24–32
Reddy RG, DeVor RE, Kapoor SG, Sun Z (2001) A mechanistic model-based force-feedback scheme for voice-coil actuated radial contour turning. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 41(8):1131–1147
Kazuhiko S, Yoichi Y, Norio S (1992) Development of a noncircular high speed generating mechanism by hybrid system with VCM and PZT. J Japan Soc Precis Eng 58(9):1503–1508
Pahk HJ, Lee DS, Park JH (2001) Ultra precision positioning system for servo motor-piezo actuator using the dual servo loop and digital filter implementation. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 41(1):51–63
Kim BS (2001) Control of multiple degree of freedom fast tool stages for noncircular turning progress. Dissertation, University of Illinois
Ge P, Jouaneh M (1995) Modeling hysteresis in piezoelectric actuators. Precis Eng 17(3):211–221
Yu Y, Naganathan N, Dukkipati R (2002) Preisach modeling of hysteresis for piezoceramic actuator system. Mechan Mach Theory 37(1):49–59
H. Richter, E.A. Misawa, D.A. Lucca, and H. Lu. Modeling nonlinear behavior in a piezoelectric actuator. Precis Eng 25(2):128–137
Kim JD, Nam SR (1997) Development of a micro-depth control system for an ultra-precision lathe using a piezo-electric actuator. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 37(4):495–509
Tzou HS (1991) Design of a piezoelectric exciter/actuator for micro-displacement control. Theory Exp 13(2):104–110
Francis BA, Wonham WM (1976) The internal model principle of control theory. Automatica 12(5):457–465
Inoue T, Nakano M, Iwai S (1981) High accuracy control of servomechanism for repeated contouring. In: Proceedings of the 8th World Congress of IFAC, pp 285–292
Hara S, Yamamoto Y, Omata T (1988) Repetitive control system: a new type servo system for periodic exogenous signals. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 33(7):659–667
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, H., Hu, D. & Zhang, K. A fast tool feeding mechanism using piezoelectric actuators in noncircular turning. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 27, 254–259 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-004-2168-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-004-2168-6