Abstract
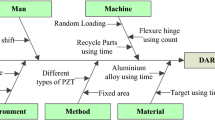
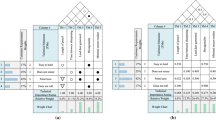
Quality function deployment (QFD) has attracted much attention in not only the quality management field but also other engineering fields. The original concept of QFD is focused only on the voice of customers, which means that the needs of customers should be satisfied from the design stage of products. However, some problems were found in using subjective and qualitative data when constructing a house of quality (HOQ). To solve the problems, Wasserman presented a methodology to consider correlation weights on the top matrix of HOQ, but the weights are subjective data and can not guarantee consistency and objectivity. The Wasserman’s weights are randomly determined under subjective conditions. This research applies Taguchi’s robust design method as another method for obtaining the HOQ top matrix weights. With the new weights, S/N-QFD is deployed, and the result of S/N-QFD is compared with W-QFD. As an application example, with a real process and quality data of a representative company product, the relationship and the correlation between the process characteristics and the quality characteristics are analyzed. Finally, this paper presents a new QFD processing methodology to determine the weights with more consistent and objective data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kang JH (1999) Evaluation method of design quality in deployment of quality functions. Dissertation, Myong Ji University
Kang JH, Park MK (2000) A study for method to determine the quality characteristics through deployment of quality functions. Safety Manage J 2(4):113–124
Kim HS, Yang HJ, Lim KT, Cheon TJ, Cheong CB, Madhav SP (1992) Quality Engineering With Robust Designs. Min Young Sa, Seoul, Korea
Armacost RL, Componation PJ, Mullens MA, WW Swart (1994) An AHP framework for prioritizing customer requirements in QFD: an industrialized housing application. IIE Trans 26(4):72–79
Govers CPM (1996) What and how about quality function deployment (QFD). Int J Prod Econ 46–47:575–585
Govers CPM (2001) QFD not just a tool but a way of quality management. Int J Prod Econ 69:151–159
Partovi FY (1999) A qulity function deployment approach to strategic capital budgeting. Eng Econ 44(3):239–260
Wasserman GS (1993) On How to Prioritize Design Requirements During the QFD Planning Process. IIE Transaction 25(3):59–65
Sullivan LP (1986) Quality function deployment. Qual Prog 19(6):39–50
Saaty TL (1980) The Analytic Hierarchy Process (Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation). McGraw-Hill, USA
German Standard DIN 70 907, Goetze ag, D-5093 Buchscheid
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Yang, K. & Kang, K. A quality function deployment methodology with signal and noise ratio for improvement of Wasserman’s weights. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 26, 631–637 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-003-2036-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-003-2036-9