Abstract
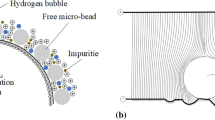
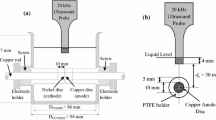
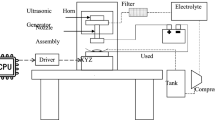
In this study, a composite processing technique that combines ultrasonic vibration and electroforming process was utilised to investigate the machining performance of copper electroforming. Supersonic agitation mechanisms were mounted on a cathode and electrolyte separately to evaluate the processing performance of electroforming. Results revealed that a copper deposit speed can be raised by cathode agitation of ultrasonic-aided electroforming. Processed copper surface of cathode agitation is better than no agitation. An array multi-mould microstructure is fabricated by cathode agitation of ultrasonic-aided copper electroforming .
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Kan JA, Sanchez IL, Xu B, Osipowicz T, Watt F (1999) Micromachining using focused high energy ion beams: Deep Ion Beam Lithography. Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res B 148:1085–1089
Yang H, Pan CT, Chou MC (2001) Ultra-fine machining tool/molds by LIGA technology. J Micromech Microeng 11(2)94–99, 2001
Pei ZJ, Ferreira PM, Kapoor SG, Hasekorn M (1995) Rotary ultrasonic machining for face milling of ceramics. Int J Tools Manuf 35(7)1033–1046
Zhang JH, Lee TC, Wu CL, Tang CY (2002) Surface integrity and modification of electro-discharge machined alumina-based ceramic composite. J Mater Process Technol 123:75–79
Zhang QH, Zhang JH, Jia ZX, Sun JL (1999) Material removal-rate analysis in the ultrasonic machining of engineering ceramics. J Mater Process Technol 88:180–184
Yan BH, Wang AC, Hang CY, Huang FY (2002) Study of precision micro-holes in borosilicate glass using micro EDM combined with micro ultrasonic vibration machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42:1105–1112
Guo ZN, Lee TC, Yue TM, Lau WS (1997) A study of ultrasonic-aided wire electrical discharge machining. J Mater Process Technol 63:823–828
Roetzel W, Spang B, Luo X, Das SK (1998) Propagation of the third sound wave in fluid: hypothesis and theoretical foundation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 41:2769–2780
Weng FT, Hsu CS, Shyu RF, Ho CT (2003) Manufacturing of micro electrodes using ultra sonic aided electrochemical machining. Proceedings of the MEMS/MOEMS 2003 Design, Test, Integration & Packaging Conference, pp 399–401
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, FT. A study of cathode agitation in ultrasonic-aided microelectroforming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25, 909–912 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-003-1918-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-003-1918-1