Abstract.
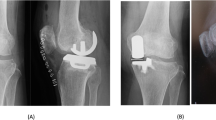
We report a case of dislocation of the polyethylene inlay in revision total knee arthroplasty. Eight days after revision arthroplasty due to a previous infection, the polyethylene inlay of a PCL- retaining cemented total knee arthroplasty dislocated at about 80° of flexion on the CPM machine. Lateral X-ray examination revealed an anterior slope of the tibial cut of 5°. Correction of the tibial slope to a posterior tibial slope of 7° reduced the forces on the posterior aspect of the inlay and no redislocation occurred. The mechanisms causing tibial inlays to dislocate in TKA are analyzed and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waelchli, B., Romero, J. Dislocation of the polyethylene inlay due to anterior tibial slope in revision total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Art 9, 296–298 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001670100203
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001670100203