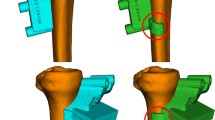
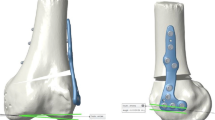
Abstract
Purpose
The accuracy of intraoperative control of correction commonly is achieved by K-wires or Schanz-screws in combination with goniometer in de-rotational osteotomies. The purpose of this study is to investigate the accuracy of intraoperative torsional control in de-rotational femoral and tibial osteotomies. It is hypothesized, that intraoperative control by Schanz-screws and goniometer in de-rotational osteotomies around the knee is a safe and well predictable method to control the surgical torsional correction intraoperatively.
Methods
55 consecutive osteotomies around the knee joint were registered, 28 femoral and 27 tibial. The indication for osteotomy was femoral or tibial torsional deformity with the clinical occurrence of patellofemoral maltracking or PFI. Pre- and postoperative torsions were measured according to the method of Waidelich on computed tomography (CT) scan. The scheduled value of torsional correction was defined by the surgeon preoperatively. Intraoperative control of torsional correction was achieved by 5 mm-Schanz-screws and goniometer. The measured values of torsional CT scan were compared to the preoperative defined and intended values and deviation was calculated separately for femoral and tibial osteotomies.
Results
The surgeon’s intraoperative measured mean value of correction in all osteotomies was 15.2° (SD 4.6; range 10–27), whereas the postoperatively measured mean value on CT scan was 15.6 (6.8; 5.0–28.5). Intraoperatively the femoral mean value measured 17.9° (4.9; 10–27) and 12.4° (1.9; 10–15) for the tibia. Postoperatively the mean value for femoral correction was 19.8 (5.5; 9.0–28.5) and 11.3 (5.0; 5.0–26.0) for tibial correction. When considering a deviation of plus or minus 3° to be acceptable femorally 15 osteotomies (53.6%) and tibially 14 osteotomies (51.9%) fell within these limits. Nine femoral cases (32.1.%) were overcorrected, four cases undercorrected (14.3%). Four tibial cases of overcorrection (14.8%) and 9 tibial cases of undercorrection (33.3%) were observed. However, the observed difference between femur and tibia regarding the distribution of cases between the three groups did not reach significance. Moreover, there was no correlation between the extent of correction and the deviation from the intended result.
Conclusion
The use of Schanz-screws and goniometer in de-rotational osteotomies as an intraoperative control of correction is an inaccurate method. Every surgeon performing derotational osteotomies must consider this and include postoperative torsional measurement in his postoperative algorithm until new tools or devices are available to guarantee a better intraoperative accuracy of torsional correction.
Study design
Observational study.
Level of evidence
III.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buly RL, Sosa BR, Poultsides LA, Caldwell E, Rozbruch SR (2018) Femoral derotation osteotomy in adults for version abnormalities. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 26:e416–e425
Cao Y, Zhang Z, Shen J, Song G, Ni Q, Li Y et al (2022) Derotational distal femoral osteotomy yields satisfactory clinical outcomes in pathological femoral rotation with failed medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30:1809–1817
Cohen J (1992) A power primer. Psychol Bull 112:155–159
Cooke TD, Price N, Fisher B, Hedden D (1990) The inwardly pointing knee. An unrecognized problem of external rotational malalignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 260:56–60
Dejour D, Reynaud P, Lecoultre B (1998) Douleurs et instabilité rotulienne. Essai Classif Med Hyg 56:1466–1471
Dejour DH, Mesnard G, Giovannetti de Sanctis E (2021) Updated treatment guidelines for patellar instability: “un menu à la carte.” J Exp Orthop 8:109–119
Dejour H, Walch G, Nove-Josserand L, Guier C (1994) Factors of patellar instability: an anatomic radiographic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2:19–26
Deng X, Li L, Zhou P, Deng F, Li Y, He Y et al (2021) Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction combined with biplanar supracondylar femoral derotation osteotomy in recurrent patellar dislocation with increased femoral internal torsion and genu valgum: a retrospective pilot study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 22:990
Dickschas J, Harrer J, Reuter B, Schwitulla J, Strecker W (2015) Torsional osteotomies of the femur. J Orthop Res 33:318–324
Dickschas J, Tassika A, Lutter C, Harrer J, Strecker W (2017) Torsional osteotomies of the tibia in patellofemoral dysbalance. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137:179–185
Hinz M, Cotic M, Diermeier T, Imhoff FB, Feuerriegel GC, Woertler K et al (2022) Derotational distal femoral osteotomy for patients with recurrent patellar instability and increased femoral antetorsion improves knee function and adequately treats both torsional and valgus malalignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-022-07150-9
Imhoff FB, Beitzel K, Zakko P, Obopilwe E, Voss A, Scheiderer B et al (2018) Derotational osteotomy of the distal femur for the treatment of patellofemoral instability simultaneously leads to the correction of frontal alignment: a laboratory cadaveric study. Orthop J Sports Med 6:232596711877566
Imhoff FB, Cotic M, Liska F, Dyrna FGE, Beitzel K, Imhoff AB et al (2019) Derotational osteotomy at the distal femur is effective to treat patients with patellar instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27:652–658
Imhoff FB, Funke V, Muench LN, Sauter A, Englmaier M, Woertler K et al (2020) The complexity of bony malalignment in patellofemoral disorders: femoral and tibial torsion, trochlear dysplasia, TT-TG distance, and frontal mechanical axis correlate with each other. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28:897–904
Imhoff FB, Schnell J, Magaña A, Diermeier T, Scheiderer B, Braun S et al (2018) Single cut distal femoral osteotomy for correction of femoral torsion and valgus malformity in patellofemoral malalignment—proof of application of new trigonometrical calculations and 3D-printed cutting guides. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 19:215
Kaiser P, Konschake M, Loth F, Plaikner M, Attal R, Liebensteiner M et al (2020) Derotational femoral osteotomy changes patella tilt, patella engagement and tibial tuberosity trochlear groove distance. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28:926–933
Leite CBG, Santos TP, Giglio PN, Pecora JR, Camanho GL, Gobbi RG (2021) Tibial tubercle osteotomy with distalization is a safe and effective procedure for patients with patella alta and patellar instability. Orthop J Sports Med 9:232596712097510
Liße J, Perl M, Dickschas J (2022) Double-level torsional osteotomy a treatment for the ‘inwardly pointing knee’ syndrome. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04446-w
Metcalfe AJ, Clark DA, Kemp MA, Eldridge JD (2017) Trochleoplasty with a flexible osteochondral flap: results from an 11-year series of 214 cases. Bone Joint J 99B:344–350
Mückley T, Lerch C, Gonschorek O, Marintschev I, Bühren V, Hofmann GO (2005) Compression nailing for posttraumatic rotational femoral deformities: open versus minimally invasive technique. Int Orthop 29:168–173
Müller M, Strecker W (2008) Arthroscopy prior to osteotomy around the knee? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128:1217–1221
Nelitz M, Wehner T, Steiner M, Dürselen L, Lippacher S (2014) The effects of femoral external derotational osteotomy on frontal plane alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:2740–2746
Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Tetsworth K, McKie J, Bhave A (1994) Deformity planning for frontal and sagittal plane corrective osteotomies. Orthop Clin North Am 25:425–465
Portney LG, Watkins MP (2009) Foundations of clinical research: applications to practice, vol 892. Pearson/Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Sanchis-Alfonso V, Domenech-Fernandez J, Ferras-Tarrago J, Rosello-Añon A, Teitge RA (2022) The incidence of complications after derotational femoral and/or tibial osteotomies in patellofemoral disorders in adolescents and active young patients: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30:3515–3525
Schmeling A, Frings J, Akoto R, Frosch KH (2020) Patellar dislocation: causes and treatment. Unfallchirurg 123:969–983
Schneider B, Laubenberger J, Jemlich S, Groene K, Weber HM, Langer M (1997) Measurement of femoral antetorsion and tibial torsion by magnetic resonance imaging. Br J Radiol 70:575–579
Strecker W, Dickschas J (2015) Torsional osteotomy: operative treatment of patellofemoral maltracking. Oper Orthop Traumatol 27:505–524
Strecker W, Keppler P, Gebhard F, Kinzl L (1997) Length and torsion of the lower limb. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:1019–1023
Waidelich HA, Strecker W, Schneider E (1992) Computed tomographic torsion-angle and length measurement of the lower extremity. The methods, normal values and radiation load. Rofo 157:245–251
Zhang Z, Cao Y, Song G, Li Y, Zheng T, Zhang H (2021) Derotational femoral osteotomy for treating recurrent patellar dislocation in the presence of increased femoral anteversion: a systematic review. Orthop J Sports Med 9:232596712110571
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
There is no funding source.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ferner, F., Klinder, A., Woerner, M. et al. Intraoperative control by Schanz-screws is inaccurate to achieve the exact amount of correction in de-rotational osteotomies. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 31, 4319–4326 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-023-07485-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-023-07485-x