Abstract
Purpose
This study aims to (1) measure the kinematics of lower extremity alignment and the bony position relative to the ground during walking, focusing on the coronal plane, and (2) determine the correlation between the kinematics and coronal inclination of the medial tibial plateau (coronal inclination) for healthy and varus knee osteoarthritis (OA).
Methods
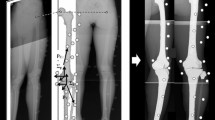
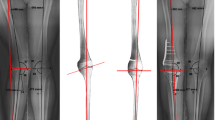
In this study, 43 women (non-OA, 9 knees; early OA, 13 knees; advanced OA, 21 knees; mean age 58 ± 17 years) were examined. The knee phenotypes in varus knee OA were varied. Three-dimensional (3D) knee kinematics were calculated in gait analysis by combining the motion capture system and the 3D lower extremity alignment assessment system via biplanar long-leg X-rays, applying the 3D–2D registration technique. The main parameters were the kinematics of the bony axes relative to the ground in the coronal plane during the stance phase of the gait. The differences in overall kinematics were assessed using repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. The association between kinematic parameters and coronal inclination was evaluated by multiple linear regression after univariate analysis.
Results
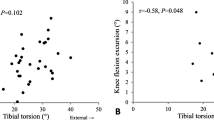
The tibia tilted laterally during the loading response, and a plateau area subsequently appeared until the terminal stance phase, whereas the femur slowly tilted laterally until the terminal stance phase. The dynamic alignment showed a relatively large varus angular change during the loading response in all groups. The trend of motion was similar among all groups (p = n.s.), although to varying degrees. The coronal inclination was the more dominant factor than the Kellgren–Lawrence (K–L) grades (β = − 0.423, p = 0.005) when the change in dynamic alignment was determined.
Conclusions
The TAA plateau area after the loading response implies that the tibial articular surface may become horizontal. The femur slowly tilted laterally until the terminal stance phase in response to the tibial motion. Consequently, the dynamic alignment showed a varus angular change, in which coronal MCT was more involved than K–L grades.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abid M, Mezghani N, Mitiche A (2019) Knee joint biomechanical gait data classification for knee pathology assessment: a literature review. Appl Bionics Biomech. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7472039
Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW (1988) Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol 16:494–502
Chang A, Hayes K, Dunlop D, Hurwitz D, Song J, Cahue S, Genge R, Sharma L (2004) Thrust during ambulation and the progression of knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:3897–3903
Farrokhi S, Tashman S, Gil AB, Klatt BA, Fitzgerald GK (2012) Are the kinematics of the knee joint altered during the loading response phase of gait in individuals with concurrent knee osteoarthritis and complaints of joint instability? A dynamic stereo X-ray study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 27:384–389
Graichen H, Lekkreusuwan K, Eller K, Grau T, Hirschmann MT, Scior W (2021) A single type of varus knee does not exist: morphotyping and gap analysis in varus OA. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-021-06688-4
Hess S, Moser LB, Robertson EL, Behrend H, Amsler F, Iordache E, Leclercq V, Hirschmann MT (2022) Functional knee phenotypes: a novel classification for phenotyping the coronal lower limb alignment based on the native alignment in young non-osteoarthritic patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30:407–418
Higano Y, Hayami T, Omori G, Koga Y, Endo K, Endo N (2016) The varus alignment and morphologic alterations of proximal tibia affect the onset of medial knee osteoarthritis in rural Japanese women: Case control study from the longitudinal evaluation of Matsudai Knee Osteoarthritis Survey. J Orthop Sci 21:166–171
Hirschmann MT, Hess S, Behrend H, Amsler F, Leclercq V, Moser LB (2019) Phenotyping of hip-knee-ankle angle in young non-osteoarthritic knees provides better understanding of native alignment variability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27:1378–1384
Katsumi R, Mochizuki T, Sato T, Kobayashi K, Watanabe S, Tanifuji O, Endo N (2018) Contribution of sex and body constitution to three-dimensional lower extremity alignment for healthy, elderly, non-obese humans in a Japanese population. J Exp Orthop 5(1):32
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1957) Radiological assessment of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 6:494–502
Kobayashi K, Sakamoto M, Tanabe Y, Ariumi A, Sato T, Omori G, Omori G, Koga Y (2009) Automated image registration for assessing three-dimensional alignment of entire lower extremity and implant position using bi-plane radiography. J Biomech 42:2818–2822
Mochizuki T, Koga Y, Tanifuji O, Sato T, Watanabe S, Koga H, Kobayashi K, Omori G, Endo N (2019) Effect on inclined medial proximal tibial articulation for varus alignment in advanced knee osteoarthritis. J Exp Orthop 6:14
Mochizuki T, Koga Y, Mori T, Nishino K, Kobayashi K, Tanifuji O, Sato T, Katsumi R, Koga H, Omori G, Tanabe Y (2019) Articular surface of the medial proximal tibia is aligned parallel to the ground in three-dimensional space under weight-bearing conditions in healthy and varus osteoarthritic knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28:3232–3239
Mochizuki T, Omori G, Nishino K, Tanaka M, Tanifuji O, Koga H, Mori T, Koga Y, Kawashima H (2022) The medial inclination of the proximal tibia is associated with the external knee adduction moment in advanced varus knee osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30:574–583
Nishino K, Omori G, Koga Y, Kobayashi K, Sakamoto M, Tanabe Y, Tanaka M, Arakawa M (2015) Three-dimensional dynamic analysis of knee joint during gait in medial knee osteoarthritis using loading axis of knee. Gait Posture 42:127–132
Okazaki K, Miura H, Matsuda S, Takeuchi N, Mawatari T, Hashizume M, Iwamoto Y (2006) Asymmetry of mediolateral laxity of the normal knee. J Orthop Sci 11:264–266
Omori G, Koga Y, Tanaka M, Nawata A, Watanabe H, Narumi K, Endoh K (2013) Quadriceps muscle strength and its relationship to radiographic knee osteoarthritis in Japanese elderly. J Orthop Sci 18:536–542
Perry J, Burnfield JM (2010) Normal and pathological function. Gait Analysis: NJ: Slack Inc
Ro DH, Lee J, Lee J, Park JY, Han HS, Lee MC (2019) Effects of knee osteoarthritis on hip and ankle gait mechanics. Adv Orthop 24:9757369
Sato T, Koga Y, Omori G (2004) Three-dimensional lower extremity alignment assessment system: application to evaluation of component position after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 19:620–628
Sato T, Mochizuki T, Katsumi R, Takahashi Y (2020) Functionally oriented alignment of the lower extremity reflecting the direction of gait for healthy elderly, knee osteoarthritis, and total knee arthroplasty subjects. J Med Biol Eng 40:887–898
Sharma L, Chang AH, Jackson RD, Nevitt M, Moisio KC, Hochberg M, Eaton C, Kwoh CK, Almagor O, Cauley J, Chmiel JS (2017) Varus thrust and incident and progressive knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 69:2136–2143
Skoyles R (2006) Human balance, the evolution of bipedalism and dysequilibrium syndrome. Med Hypotheses 66:1060–1068
Takagi S, Omori G, Koga H, Endo K, Koga Y, Nawata A, Endo N (2018) Quadriceps muscle weakness is related to increased risk of radiographic knee OA but not its progression in both women and men: the Matsudai Knee Osteoarthritis Survey. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26:2607–2614
Winter DA (2009) Processing of raw kinematic data. In: Winter DA (ed) Biomechanics and Motor Control of Human Movement, 4th edn. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York, pp 64–75
Funding
This study received KAKENHI from grants–in–aid for scientific research in Japan society for the promotion of science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors received and will not receive any benefits or funding from any commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mochizuki, T., Tanifuji, O., Omori, G. et al. The coronal inclination of the medial tibial plateau affects coronal gait kinematics for varus osteoarthritic knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30, 4162–4172 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-022-07019-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-022-07019-x