Abstract
Purpose
Telehealth rehabilitation (telerehab) is an increasingly popular cost-saving alternative to traditional rehabilitation after total joint arthroplasty. We compared the safety and efficacy of an institutional telerehab program to conventional “face-to-face” rehabilitation in a sample of patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
Methods
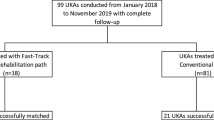
A retrospective matched cohort study was performed. Medicare patients who utilized telerehab following unilateral TKA were matched in a 1:3 ratio to those utilizing conventional rehabilitation. Patients were matched on sex, body mass index (BMI, ± 5 kg/m2), preoperative extension (± 10 degrees), preoperative flexion (± 10 degrees), and Risk Assessment and Prediction Tool (RAPT) score (± 2 points). Ninety-day unplanned healthcare encounters, 120-day manipulations under anesthesia (MUAs), and 6-week and 3-month changes in the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score for Joint Replacement (KOOS-JR), pain visual analog scale (VAS), Veterans RAND 12 (VR-12), and Lower-Extremity Activity Scale (LEAS) were compared between groups.
Results
Eighty-two telerehab patients and 244 conventional rehab patients were included. After matching, there were no differences in 90-day unplanned healthcare encounters or 120-day MUA rates between groups. There were no differences in 6-week or 3-month changes in KOOS-JR, VAS pain, or VR-12 mental or physical sub-scores between groups. Telerehab patients had a greater improvement in LEAS score at 3 months compared to the conventional group (mean difference 1.9, P = 0.03).
Conclusion
In a matched cohort study of 326 TKA patients, telerehab patients had similar rates of unplanned healthcare encounters and MUAs and similar patient-reported outcomes compared to conventional PT patients, suggesting that telerehab can be an equally effective alternative to conventional PT following TKA.
Level of evidence
III
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourne RB (2008) Measuring tools for functional outcomes in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:2634–2638
Chugtai M, Kelly J, Newman J, Sultan A, Khlopas A, Sodhi N, Bhave A, Kolczun M, Mont M (2019) The role of virtual rehabilitation in total and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg 32:105–110
Correia FD, Nogueira A, Magalhães I, Guimarães J, Moreira M, Barradas I, Molinos M, Teixeira L, Tulha J, Seabra R, Lains J, Bento V (2019) Medium-term outcomes of digital versus conventional home-based rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty: prospective, parallel-group feasibility study. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol 6:e13111
Davidovitch RI, Anoushiravani AA, Feng JE, Chen KK, Karia R, Schwarzkopf R, Iorio R (2018) Home health services are not required for select total hip arthroplasty candidates: assessment and supplementation with an electronic recovery application. J Arthroplasty 33:S49–S55
Fisher C, Biehl E, Titmuss MP, Schwartz R, Gantha CS (2019) HSS@Home, physical therapist-led telehealth care navigation for arthroplasty patients: a retrospective case series. HSS J 15:226–233
Fusco F, Turchetti G (2016) Telerehabilitation after total knee replacement in Italy: cost-effectiveness and cost-utility analysis of a mixed telerehabilitation-standard rehabilitation programme compared with usual care. BMJ Open 6:1–10
Kort NP, Barrena EG, Bédard M, Donell S, Epinette JA, Gomberg B, Hirschmann MT, Indelli P, Khosravi I, Karachalios T, Liebensteiner MC, Stuyts B, Tandogan R, Violante B, Zagra L, Thaler M (2020) Resuming elective hip and knee arthroplasty after the first phase of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: the European hip society and European knee associates recommendations. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28:2730–2746
Kuether J, Moore A, Kahan J, Martucci J, Messina T, Perreault R, Sembler R, Tarutis J, Zazulak B, Rubin LE, O’Connor MI (2019) Telerehabilitation for total hip and knee arthroplasty patients: a pilot series with high patient satisfaction. HSS J 15:221–225
McKeon JF, Alvarez PM, Vajapey AS, Sarac N, Spitzer AI, Vajapey SP (2021) Expanding role of technology in rehabilitation after lower-extremity joint replacement. JBJS Rev 9:1–17
Moffet H, Tousignant M, Nadeau S, Merette C, Boissy P, Corriveau H, Marquis F, Cabana F, Belzile E, Ranger P, Dimentberg R (2017) Patient satisfaction with in-home telerehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty: results from a randomized controlled trial. Telemed J E Heal 23:80–87
Piqueras M, Marco E, Coll M, Escalada F, Ballester A, Cinca C, Belmonte R, Muniesa JM (2013) Effectiveness of an interactive virtual telerehabilitation system in patients after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Rehabil Med 45:392–396
Prvu Bettger J, Green CL, Holmes DN, Chokshi A, Iii RCM, Hoch BT, De LAJ, Aluisio F, Seyler TM, Del GDJ, Chiavetta J, Webb L, Miller V, Smith JM, Peterson ED (2020) Effects of virtual exercise rehabilitation in-home therapy compared with traditional care after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 102:101–109
Russell TG, Buttrum P, Wootton R, Jull GA (2011) Internet-based outpatient telerehabilitation for patients following total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93:113–120
Tousignant M, Moffet H, Nadeau S, Mérette C, Boissy P, Corriveau H, Marquis F, Cabana F, Ranger P, Belzile ÉL, Dimentberg R (2015) Cost analysis of in-home telerehabilitation for post-knee arthroplasty. J Med Internet Res 17:e83
Williams BR, Smith LC, Only AJ, Parikh HR, Swiontkowski MF, Cunningham BP (2021) Unplanned emergency and urgent care visits after outpatient orthopaedic surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev 5:1–10
Windsor EN, Sharma AK, Gkiatas I, Elbuluk AM, Sculco PK, Vigdorchik JM (2021) An Overview of Telehealth in Total Joint Arthroplasty. HSS J 17:51–58
Zachwieja E, Theosmy EG, Yacovelli SJ, Beatty EW, McGrath ME, Lonner JH (2020) Web-based self-directed exercise program is cost-effective compared to formal physical therapy after primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 35:2335–2341
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY, USA.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LeBrun, D.G., Martino, B., Biehl, E. et al. Telerehabilitation has similar clinical and patient-reported outcomes compared to traditional rehabilitation following total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30, 4098–4103 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-022-06931-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-022-06931-6