Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the effect of varus alignment of the tibial component on the outcomes with a minimum follow-up of 10 years. The hypothesis was that varus alignment of the tibial component might not affect the outcomes and survival of a neutrally aligned primary TKA.
Methods
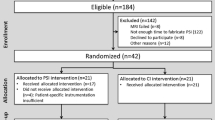
A matched case–control study was designed between 66 patients with varus alignment of the tibial component and 66 with neutral alignment with a minimum follow-up of 10 years. Functional outcome was assessed with the knee surgery scores (KSS) and reduced Western Ontario and MacMaster Universities questionnaire (WOMAC). Patient satisfaction was evaluated by a 0–10 visual analog scale. Radiological evaluation was performed at early postoperative and at final follow-up.
Results
The mean follow-up was 11.9 (SD 2.6) years for both groups. The mean postoperative proximal tibial angle in the varus group was 85.0° (SD 0.9) and 88.8° (SD 0.9) in control group. At the final follow-up, there were no significant differences in KSS, WOMAC, range of motion or patient satisfaction. There were no differences in the coronal anatomical alignment of the TKA between groups. Revision of TKA was performed in four knees in the varus group, and one in control group, due to aseptic loosening of the tibial component in all cases. TKA survival at 10 years was not significantly different between groups.
Conclusion
The alignment of the tibial component up to 7° varus did not negatively affect implant survival, patient satisfaction, and function of a well-aligned TKA, with a minimum postoperative follow-up of 10 years.
Level of evidence
III.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Authors ensure that all data and materials, as well as software application or custom code, support their published claims, meeting field standards. The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdel MP, Ollivier M, Parrate S, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ, Pagnano MW (2018) Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on survival and functional outcomes of modern total knee arthroplasties with cement: a concise follow-up at 20 years. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 100A:472–478
Abdel MP, Oussedik S, Paratte S, Lustig S, Haddad FS (2014) Coronal alignment in total knee replacement: historical review, contemporary analysis, and future direction. Bone Joint J 96B:857–862
Asif S, Choon DS (2005) Midterm results of cemented Press Fit Condylar Sigma total knee arthroplasty system. J Orthop Surg 13:280–284
Bellemans J, Colyn W, Vandenneucker H, Victor J (2012) The Chitranjan Ranawat award: is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:45–53
Berend ME, Ritter MA, Meding JB, Faris PM, Keating EM, Redelman R, Faris GW, Davis KE (2004) Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:26–34
Bonner TJ, Eardley WG, Patterson P, Gregg PJ (2011) The effect of post-operative mechanical axis alignment on the survival of primary total knee replacements after a follow-up of 15 years. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 93B:1217–1222
Charnley J (1972) The long-term results of low-friction arthroplasty of the hip performed as a primary intervention. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 54B:61–76
Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD (2009) Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 24:560–569
Cinotti G, Sessa P, D’Arino A, Ripani FR, Giannicola G (2015) Improving tibial component alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23:3563–3570
Davis JA, Hogan C, Dayton M (2015) Postoperative coronal alignment after total knee arthroplasty: does tailoring the femoral valgus cut angle really matter? J Arthroplasty 30:1444–1448
Ewald FC (1989) The Knee Society total knee arthroplasty roentgenographic evaluation and scoring system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:9–12
Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE (2009) Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty 24:39–43
Faschingbauer M, Hacker S, Seitz A, Dürselen L, Boettner F, Reichel H (2020) The tibial cut in total knee arthroplasty influences the varus alignment, the femoral roll-back and the tibiofemoral rotation in patients with constitutional varus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-020-05996-5
Green GV, Berend KR, Berend ME, Glisson RR, Vail TP (2012) The effects of varus tibial alignment on proximal tibial surface strain in total knee arthroplasty. The posteromedial hot spot. J Arthroplasty 17:1033–1039
Hirschmann MT, Moser LB, Amsler F, Behrend H, Leclerq V, Hess S (2019) Functional knee phenotypes: a novel classification for phenotyping the coronal lower limb alignment based on the native alignment in young non-osteoarthritic patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27:1394–1402
Howell SM, Shelton TJ, Hull ML (2018) Implant survival and function ten years after kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 33:3678–3684
Huang NF, Dowsey MM, Ee E, Stoney JD, Babazadeh S, Choong PF (2012) Coronal alignment correlates with outcome after total knee arthroplasty: five-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty 27:1737–1741
Innocenti B, Bellemans J, Catani F (2016) Deviations from optimal alignment in TKA: is there a biomechanical difference between femoral or tibial component alignment? J Arthroplasty 31:295–301
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN (1989) Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:13–14
Kim YH, Park JW, Kim JS, Park SD (2014) The relationship between the survival of total knee arthroplasty and postoperative coronal, sagittal and rotational alignment of knee prosthesis. Int Orthop 38:379–385
Lee SA, Choi SH, Chang MJ (2015) How accurate is anatomic limb alignment in predicting mechanical limb alignment after total knee arthroplasty? BMC Musculoskelet Disord 16:323–330
Lizaur-Utrilla A, González-Parreño S, Martínez-Méndez D, Miralles-Muñoz FA, López-Prats FA (2020) Minimal clinically important differences and substantial clinical benefits for Knee Society Scores. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 28:1473–1478
Magnussen RA, Weppe F, Demey G, Servien E, Lustig S (2011) Residual varus alignment does not compromise results of TKAs in patients with preoperative varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:3443–3450
Matziolis G, Adam J, Perka C (2010) Varus malalignment has no influence on clinical outcome in midterm follow-up after total knee replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130:1487–1491
Meneghini RM, Grant TW, Ishmael MK, Ziemba-Davies M (2017) Leaving residual varus alignment after total knee arthroplasty does not improve patient outcomes. J Arthroplasty 32(9S):S171–S177
Morgan SS, Bonshahi A, Pradhan N, Gregory A, Gambhir A, Porter ML (2008) The influence of postoperative coronal alignment on revision surgery in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 32:639–642
Ng VY, DeClaire JH, Berend KR, Gulick BC, Lombardi AV Jr (2012) Improved accuracy of alignment with patient-specific positioning guides compared with manual instrumentation in TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:99–107
Nishida K, Matsumoto T, Takayama K, Ishida K, Nakano N, Matsushita T, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2017) Remaining mild varus alignment leads to better clinical outcome in total knee arthroplasty for varus osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25:3488–3494
Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ (2010) Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 92A:2143–2149
Patil S, D’Lima DD, Fait JM, Colwell CW Jr (2007) Improving tibial component coronal alignment during total knee arthroplasty with use of a tibial planing device. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 89:381–387
Park A, Stambough JB, Nunley RM, Barrack RL, Nam D (2016) The inadequacy of short knee radiographs in evaluating coronal alignment after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 31:878–882
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement: its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:153–156
Scuderi GR, Bourne RB, Noble PC, Bejamin JB, Lonner JH, Scott WN (2012) The new Knee Society Knee Scoring System. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:3–19
Sikorski JM (2008) Alignment in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 90B:1121–1127
Slevin O, Amsler F, Hirschmann MT (2017) No correlation between coronal alignment of total knee arthroplasty and clinical outcomes: a prospective clinical study using 3D-CT. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25:3892–3900
Srivastava A, Lee GY, Steklov N, Colwell CW Jr, Ezzet KA, D’Lima DD (2012) Effect of tibial component varus on wear in total knee arthroplasty. Knee 19:560–563
Suh DS, Kang KT, Son J, Kwon OR, Baek C, Koh YG (2017) Computational study on the effect of malalignment of the tibial component on the biomechanics of total knee arthroplasty: a finite element analysis. Bone Joint Res 6:623–630
Teeter MG, Naudie DD, McCalden RW, Yuan X, Holdsworth DW, MacDonald SJ, Lanting BA (2018) Varus tibial alignment is associated with greater tibial baseplate migration at 10 years following total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26:1610–1617
van Hamersveld KT, Marang-van de Mheen P, Nelissen R (2019) The effect of coronal alignment on tibial component migration following total knee arthroplasty. A cohort study with long-term radiostereometric analysis results. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 101A:1203–1212
Vanlommel L, Vanlommel J, Claes S, Bellemans J (2013) Slight undercorrection following total knee arthroplasty results in superior clinical outcomes in varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2325–2330
Whitehouse SL, Lingard EA, Katz JN, Learmonth ID (2003) Development and testing of a reduced WOMAC function scale. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85B:706–711
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work. No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript. No funding was received for conducting this study. No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by FAM-M, MR-M and LB-T. Substantial contributions to the design of the work was performed by SG-P and interpretation of data for the work was performed by CA-M. The first draft of the manuscript was written by FAM-M and AL-U and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the Bioethics Committee of the Elda University Hospital, Elda, Spain (number PI.2020-024).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and radiographs.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miralles-Muñoz, F.A., Rubio-Morales, M., Bello-Tejada, L. et al. Varus alignment of the tibial component up to seven degrees is not associated with poor long-term outcomes in a neutrally aligned total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 30, 2768–2775 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-021-06627-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-021-06627-3